Introduction
Salter-Harris fractures (physeal fractures) refer to fractures through a growth plate (physis) and are, therefore, specifically applied to bone fractures in children. The classification system used to grade fractures according to the involvement of the physis, metaphysis, and epiphysis is important as it has implications for both prognosis and treatment.[1][2][3][4] This classification also facilitates communication between providers.
Etiology
Register For Free And Read The Full Article
Search engine and full access to all medical articles
10 free questions in your specialty
Free CME/CE Activities
Free daily question in your email
Save favorite articles to your dashboard
Emails offering discounts
Learn more about a Subscription to StatPearls Point-of-Care
Etiology
Most of these injuries occur during a child's growth spurt when physes are the weakest. Active children are the most likely to encounter injuries involving the growth plate as the ligaments and joint capsules surrounding the growth plate tend to be much stronger and more stable. The ligaments and capsules can sustain greater external loads to the joint relative to the growth plate itself.[5][6] Once the physis fuses, ligamentous and tendon soft tissue injuries become more frequent, as well as metadiaphyseal fractures.
Epidemiology
The physis, or growth plate, is a weak part of cartilage present in the developing bone. The physis closes in children at varying ages.
Physeal injuries are common among children and comprise 15% to 30% of all bony injuries. Salter-Harris fractures are described exclusively in children and do not occur in the well-developed bones of adults.
In general, upper-extremity injuries are more common than lower-extremity injuries.
Of the five most common Salter-Harris fracture types, type II is the most common (75%), followed by types III (10%), IV (10%), type I (5%), and lastly, type V, which is very rare and typically diagnosed retrospectively.
Males are more likely to be affected because they have an increased tendency to engage in high-risk activities. Girls are affected at a younger age (11 to 12 years) than boys (12 to 14 years).
Pathophysiology
Most long bones in the body contain at least two growth plates. Near both ends of the bone, a hyaline cartilage plate is located between the epiphysis and metaphysis. Once a child or adolescent completes their growth spurt, the plate will eventually ossify and form an epiphyseal line.
In the physis, four zones are described from the epiphysis toward the metaphysis: (1) resting cells, (2) proliferating cells, (3) hypertrophic/maturing cells, and (4) provisional calcification.
Physeal fractures tend to occur through the zone of provisional calcification; however, they may cross several zones depending on the type of injury or the external force applied (e.g., shear vs. compression vs. tension forces).
The zone of hypertrophic/maturing cells is commonly affected when fractures occur. In the event of a fracture, the blood supply, which enters the bone through the epiphysis, may become compromised.
History and Physical
The most common presentation of a Salter-Harris fracture is localized joint pain following a traumatic event (e.g., collision, crush injury, or fall). The patient may present with swelling around the joint and focal tenderness over the physis. If the injury occurs in the upper extremity, the patient may complain of a limited range of motion. If the injury involves a lower extremity, the patient may be unable to bear weight on the affected side. It is important to note that symptoms may mimic ligamentous injury, and there may be positive findings on ligamentous laxity tests. Therefore, one must be cautious to avoid misdiagnosing symptoms as related to joint tissues alone.
Evaluation
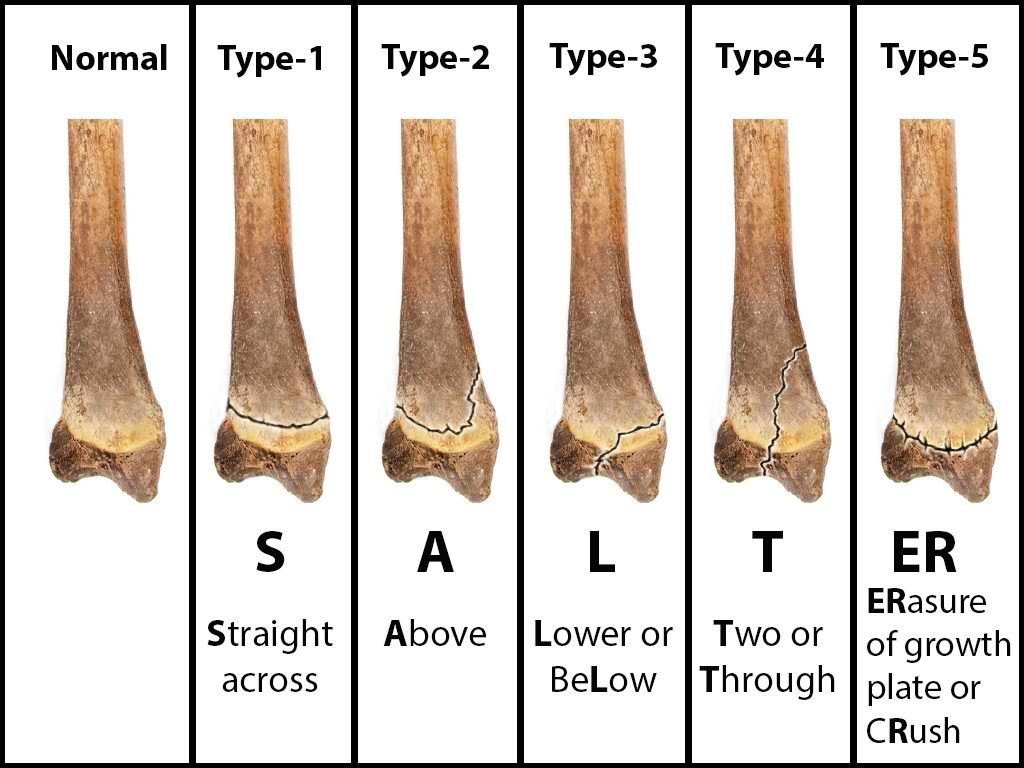
Salter-Harris fractures include a classification system that allows providers to risk-stratify injuries. Ranging from I to V, lower numbers are less severe and have less of a propensity for growth abnormalities.[7][8][9][10] Higher-grade Salter-Harris fractures have a higher incidence of premature physeal fusion.
Salter I (Slipped)
This is when the fracture line extends through the physis or within the growth plate. Type I fractures are due to the longitudinal force applied through the physis, which splits the epiphysis from the metaphysis. Beware that a normal radiograph cannot exclude a physis injury in a symptomatic pediatric patient. A radiograph may be normal due to lack of bony involvement, and mild to moderate soft tissue swelling may be noted. Look for the widening of the physis or displacement of the epiphysis, which may suggest a fracture. Diagnosis is based on clinical findings, such as the presence of focal tenderness or swelling surrounding the growth plate. An example is Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE).
Salter II (Above)
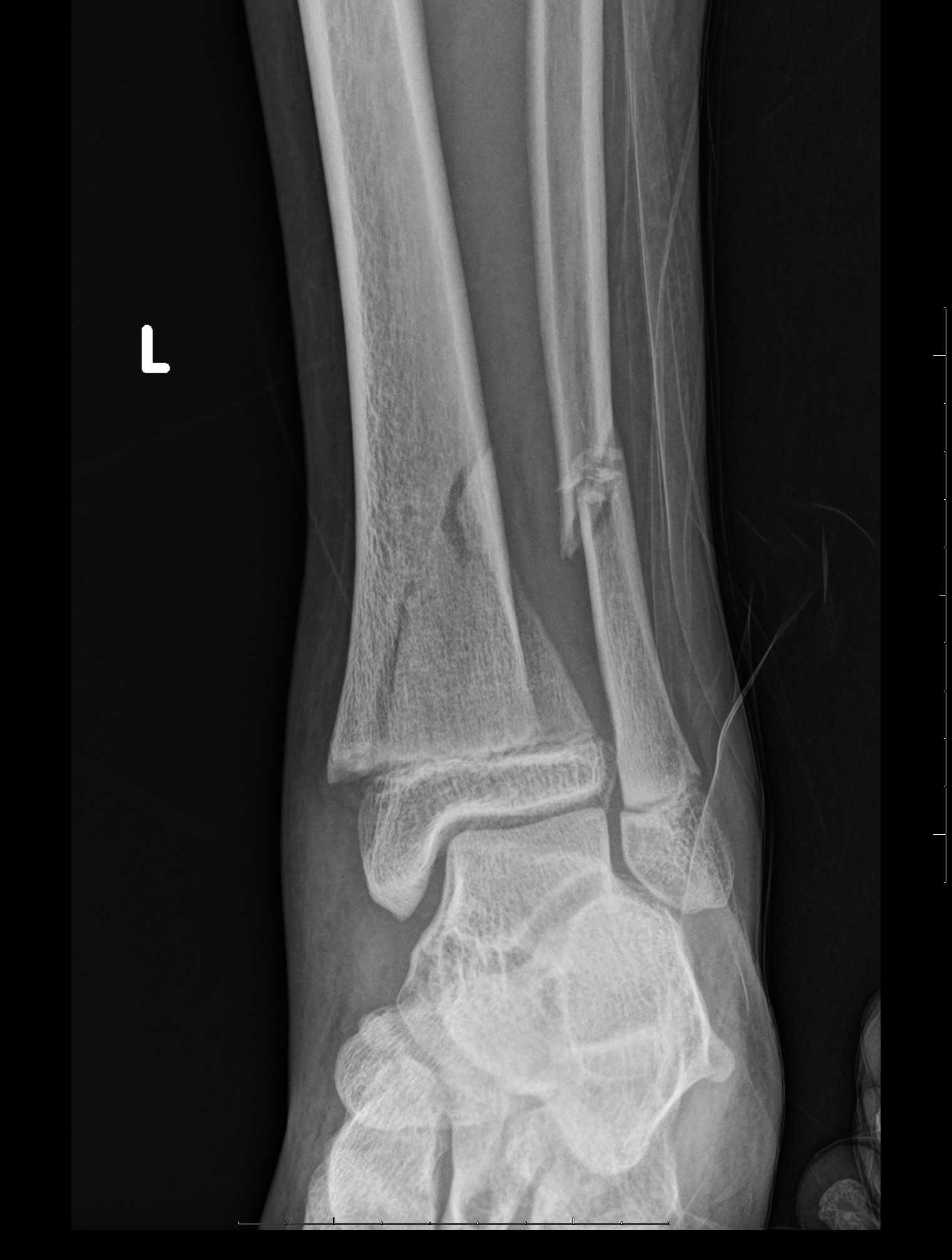
These are when the fracture extends through both the physis and metaphysis. These are most common and occur away from the joint space.
When the small corner of the metaphysis is visible, this is known as a corner sign or Thurston-Holland fragment.
Be careful in using the terms proximal and distal to describe the extension because the position of the physis is relative to the metaphysis and is not fixed. If the proximal end of the bone is involved, the physis is proximal to the metaphysis, so this extends distally from the physis into the metaphysis. If it involves the distal end of the bone, the physis is distal to the metaphysis, which extends proximally from the physis into the metaphysis.
Salter III (Lower)
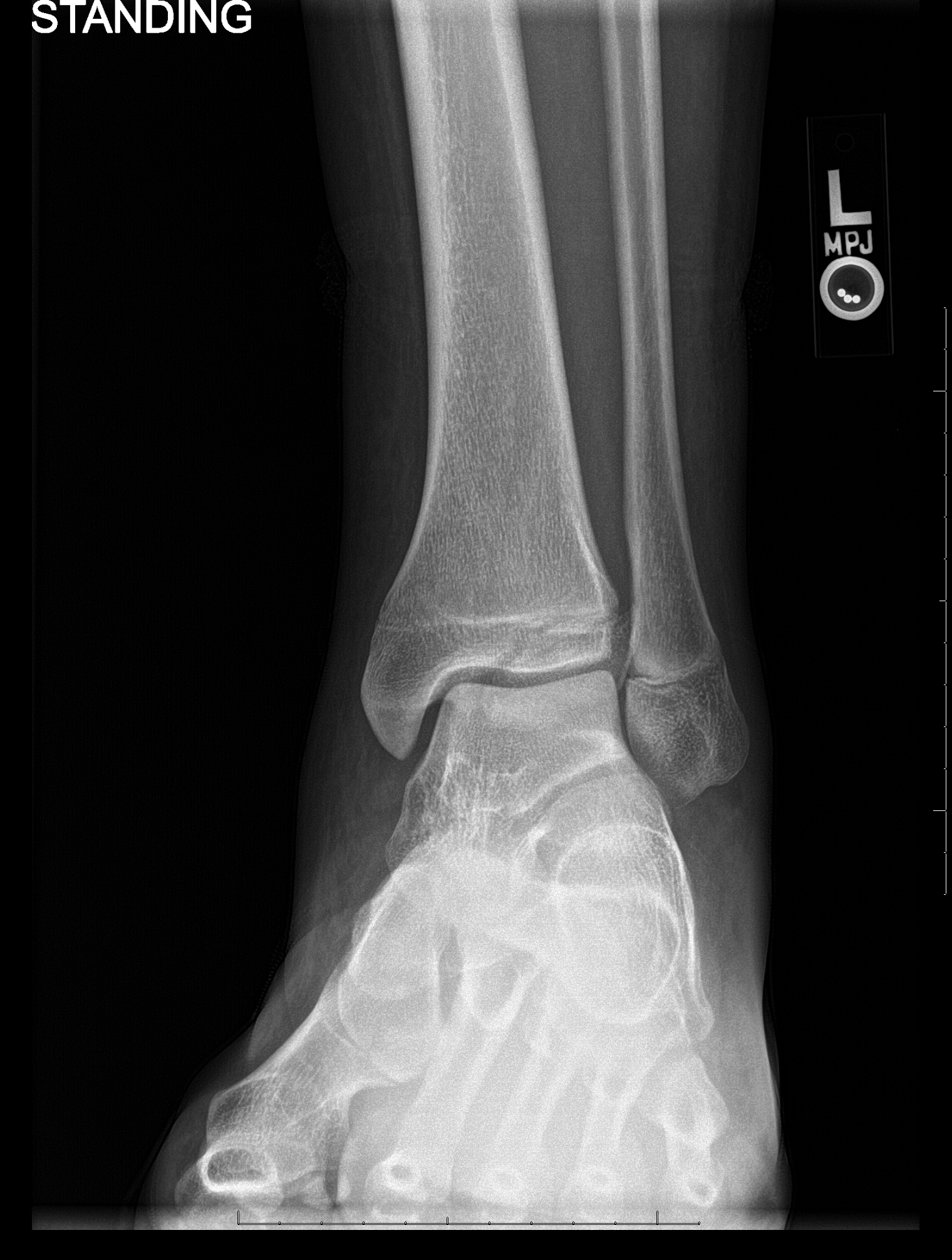
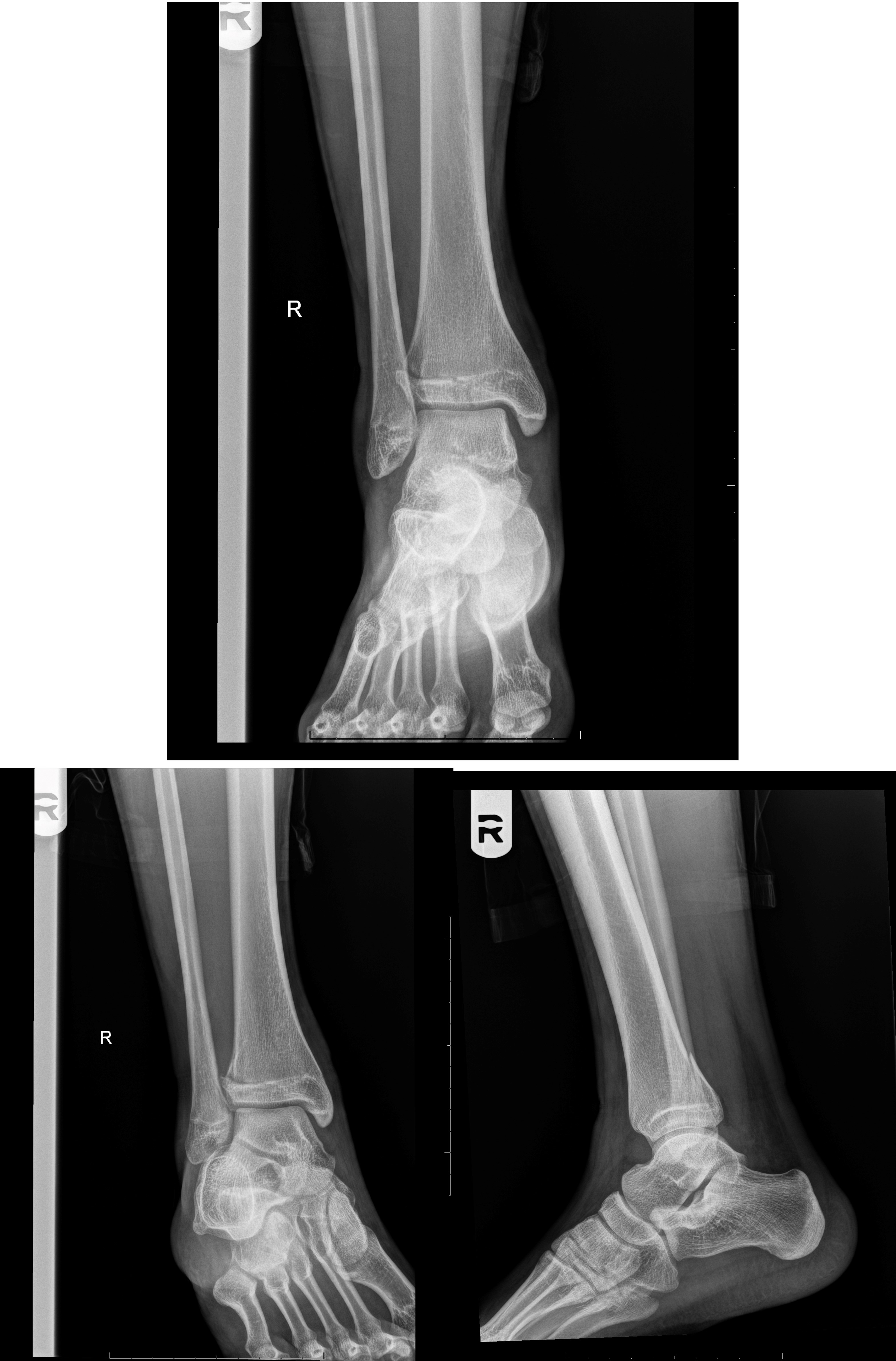
This is an intra-articular fracture extending from the physis into the epiphysis. If the fracture extends the complete length of the physis, this type of fracture may form two epiphyseal segments. Since the epiphysis is involved, damage to the articular cartilage may occur. One example is a Tillaux fracture of the ankle, which is a fracture of the anterolateral aspect of the growth plate and epiphysis.
Salter IV (Through/Transverse)
This is also an intra-articular fracture, in which the fracture passes through the epiphysis, physis, and metaphysis. As this fracture involves the epiphysis, the articular cartilage may be damaged. An example of this is a Triplane fracture at the ankle, which has the following three components:
- Vertical component through the epiphysis
- Horizontal component through the growth plate
- Oblique component through the metaphysis.
Types III and IV fractures each carry a risk for growth retardation, altered joint mechanics, and functional impairment. Therefore, both require urgent orthopedic evaluation.
Salter V (Rammed/Ruined)
This fracture type is due to a crush or compression injury of the growth plate. In type V, the force is transmitted through the epiphysis and physis, potentially disrupting the germinal matrix, hypertrophic region, and vascular supply. Though Harris-Salter V fractures are very rare, they may be seen in electric shock, frostbite, and irradiation cases. As this fracture pattern tends to result from severe injury, these typically have a poor prognosis leading to bone growth arrest.
Be aware that it can be radiographically occult, and thus the radiograph may appear normal. This may be diagnosed retrospectively once growth arrest has occurred. One should consider the possibility of type V in a symptomatic child with a normal radiograph in an appropriate setting. Nevertheless, there may be evidence of physeal widening, which may be a potential clue to displacement. Anteroposterior and lateral views may be necessary to delineate the fracture type properly and imaging of the opposite, unaffected extremity for comparison.
Additional Radiological Evaluations
When radiography is doubtful about the presence or extent of fractures, CT or MRI may be used to confirm or further delineate fractures. This is especially true in ensuring the involvement of an articular surface exists or measuring the degree of fracture diastasis.[11] The following features are observed on MRI in diagnosing physeal fractures:
- Widening and increased T2-weighted signal within the physis
- Adjacent bone marrow edema
- Associated metaphyseal(Salter-Harris II or IV) or epiphyseal (Salter-Harris III or IV) fracture lines
- Periosteal disruption
The most important complication of physeal injuries is growth arrest, which can lead to deformity and longitudinal growth arrest, potentially with limb length discrepancies.[12] A rare complication of physeal fracture diagnosed by MRI is entrapment of periosteum within the fracture which will prevent complete reduction of the fracture.
Treatment / Management
Salter-Harris I and II fractures can be treated with closed reduction, casting, or splinting. The reduction should be performed carefully to avoid damage to or grating of the physis on any metaphyseal bone fragments.[13][14][15](B3)
Salter-Harris III and IV fractures usually require open reduction and internal fixation (avoiding crossing the physis).
Salter V fracture diagnosis may be delayed unless there is a high degree of clinical suspicion, and often the diagnosis is not made at the initial presentation. An emergent orthopedic consultation should be obtained if the fracture is recognized. As these fractures involve the germinal matrix, they have a potential for growth arrest.
In all cases, a reexamination in seven to ten days is necessary to monitor proper reduction and healing. This is also important to determine whether any complications, such as growth arrest, have occurred. If clinically indicated, an additional follow-up radiograph may be obtained at six and 12 months to reassess for any growth arrest.
The complications include growth arrest with the potential for deformity and limb length discrepancy. Entrapment of the periosteum within the fracture is a rare complication that requires an MRI scan. Beware that entrapped periosteum can prevent a complete reduction of the fracture.
Differential Diagnosis
While fractures may often be missed on plain film radiographic imaging, maintaining a high suspicion paired with good clinical exam skills is essential to detect these injuries. Muscle sprains and tendon injuries are common diagnoses that are easy to blame if a fracture is not detected on imaging.
Prognosis
Overall, the prompt detection of these fractures leads to a favorable prognosis, provided the fractures are treated immediately. Whether it be close follow-up and pain control or orthopedic evaluation and surgery, the long-term outcome of treated fractures is generally successful.
Complications
As stated previously, many complications may arise if Salter-Harris fractures are not detected and treated promptly. Most notably, further injury and growth restriction are serious outcomes that severely impact a child's life. It must also be mentioned that prolonged pain and mobility restriction are side effects of delayed treatment.
Deterrence and Patient Education
As all post-visit care for injuries goes, Salter-Harris fractures are not significantly different. Resting the injured joint with elevation and pain control is essential. When patients return for evaluation weeks and even years after the initial injury and treatment, conducting a proper physical exam, including strength testing, limb length discrepancies, and range of motion, is crucial.
Pearls and Other Issues
Early closure or fusion of the physis leads to growth disturbances such as deformity and limb length discrepancies. Complications are usually found when fractures of the distal tibia and distal femur are involved.
When the closure of only a part of the plate occurs, angular deformities may be present.
Entrapment of the periosteum within the fracture may occur and can prevent a complete fracture reduction. MRI can identify this.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Fractures are usually encountered by the emergency department physician, urgent care nurse, and primary care provider. In all but the simplest non-displaced fractures, one should consult an orthopedic surgeon before discharge as part of an interprofessional team approach to diagnosing and managing these injuries. A missed or inappropriately treated Salter-Harris fracture has lifelong implications. Once the patient has been treated, follow-up is required to ensure that healing is taking place. Finally, healthcare providers must be aware that Salter V fracture diagnosis may be delayed unless there is a high degree of clinical suspicion. Often the diagnosis is not made at the initial presentation. An emergent orthopedic consultation should be obtained if the fracture is recognized in the emergency department.[4][16][17]
Orthopedic specialty nurses can also be valuable assets in the interprofessional approach by assisting with evaluation and, indeed, during surgery, providing counsel to patients/parents in all cases. They can also coordinate activities and information sharing between the various clinicians involved in the case. Physical therapists likewise play a crucial role on the interprofessional team and must keep other team members apprised of the patient's progress or lack thereof, so appropriate therapy changes can be implemented if necessary. These are a few examples of how interprofessional care benefits the patient, leading to improved outcomes. [Level 5]
Media
(Click Image to Enlarge)
(Click Image to Enlarge)
(Click Image to Enlarge)
(Click Image to Enlarge)
(Click Image to Enlarge)
References
Sheffer BW, Villarreal ED, Ochsner MG 3rd, Sawyer JR, Spence DD, Kelly DM. Concurrent Ipsilateral Tibial Shaft and Distal Tibial Fractures in Pediatric Patients: Risk Factors, Frequency, and Risk of Missed Diagnosis. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. 2020 Jan:40(1):e1-e5. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001384. Epub [PubMed PMID: 30969196]
Mills L, Zeppieri G Jr. Salter-Harris Type III Fracture in a Football Player. The Journal of orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. 2019 Mar:49(3):209. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2019.7984. Epub [PubMed PMID: 30819058]
Binkley A, Mehlman CT, Freeh E. Salter-Harris II Ankle Fractures in Children: Does Fracture Pattern Matter? Journal of orthopaedic trauma. 2019 May:33(5):e190-e195. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000001422. Epub [PubMed PMID: 30633083]
Gibreel W, Charafeddine A, Carlsen BT, Moran SL, Bakri K. Salter-Harris Fractures of the Distal Phalanx: Treatment Algorithm and Surgical Outcomes. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. 2018 Sep:142(3):720-729. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000004645. Epub [PubMed PMID: 30148775]
Rickert KD, Hosseinzadeh P, Edmonds EW. What's New in Pediatric Orthopaedic Trauma: The Lower Extremity. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. 2018 Sep:38(8):e434-e439. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001209. Epub [PubMed PMID: 29975292]
Beatty E, Archambault P. BET 1: Can Salter-Harris type I fractures be diagnosed by ultrasound? Emergency medicine journal : EMJ. 2018 May:35(5):335-336. doi: 10.1136/emermed-2018-207686.1. Epub [PubMed PMID: 29674383]
Brian JM, Choi DH, Moore MM. The Primary Physis. Seminars in musculoskeletal radiology. 2018 Feb:22(1):95-103. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1608002. Epub 2018 Feb 6 [PubMed PMID: 29409076]
Jackson TJ, Blumberg TJ, Shah AS, Sankar WN. Inappropriately Timed Pediatric Orthopaedic Referrals From the Emergency Department Result in Unnecessary Appointments and Financial Burden for Patients. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. 2018 Mar:38(3):e128-e132. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001132. Epub [PubMed PMID: 29324529]
Asad WA, Younis MHS, Ahmed AF, Ibrahim T. Open versus closed treatment of distal tibia physeal fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European journal of orthopaedic surgery & traumatology : orthopedie traumatologie. 2018 Apr:28(3):503-509. doi: 10.1007/s00590-017-2062-1. Epub 2017 Oct 19 [PubMed PMID: 29052010]
Level 1 (high-level) evidencePennock AT, Ellis HB, Willimon SC, Wyatt C, Broida SE, Dennis MM, Bastrom T. Intra-articular Physeal Fractures of the Distal Femur: A Frequently Missed Diagnosis in Adolescent Athletes. Orthopaedic journal of sports medicine. 2017 Oct:5(10):2325967117731567. doi: 10.1177/2325967117731567. Epub 2017 Oct 10 [PubMed PMID: 29051906]
Close BJ,Strouse PJ, MR of physeal fractures of the adolescent knee. Pediatric radiology. 2000 Nov [PubMed PMID: 11100491]
Jaramillo D, Shapiro F, Hoffer FA, Winalski CS, Koskinen MF, Frasso R, Johnson A. Posttraumatic growth-plate abnormalities: MR imaging of bony-bridge formation in rabbits. Radiology. 1990 Jun:175(3):767-73 [PubMed PMID: 2343128]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceD'Angelo F, Solarino G, Tanas D, Zani A, Cherubino P, Moretti B. Outcome of distal tibia physeal fractures: a review of cases as related to risk factors. Injury. 2017 Oct:48 Suppl 3():S7-S11. doi: 10.1016/S0020-1383(17)30650-2. Epub [PubMed PMID: 29025614]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceArnold A, Thigpen CA, Beattie PF, Kissenberth MJ, Shanley E. Overuse Physeal Injuries in Youth Athletes. Sports health. 2017 Mar/Apr:9(2):139-147. doi: 10.1177/1941738117690847. Epub 2017 Feb 6 [PubMed PMID: 28165873]
Ho-Fung VM, Zapala MA, Lee EY. Musculoskeletal Traumatic Injuries in Children: Characteristic Imaging Findings and Mimickers. Radiologic clinics of North America. 2017 Jul:55(4):785-802. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2017.02.011. Epub 2017 Mar 27 [PubMed PMID: 28601180]
Park H, Lee DH, Han SH, Kim S, Eom NK, Kim HW. What is the best treatment for displaced Salter-Harris II physeal fractures of the distal tibia? Acta orthopaedica. 2018 Feb:89(1):108-112. doi: 10.1080/17453674.2017.1373496. Epub 2017 Sep 19 [PubMed PMID: 28925312]
Sferopoulos NK. Classification of distal radius physeal fractures not included in the salter-harris system. The open orthopaedics journal. 2014:8():219-24. doi: 10.2174/1874325001408010219. Epub 2014 Jul 11 [PubMed PMID: 25132871]