Introduction
The abdominal arteries arise from the abdominal aorta and are comprised of three groups of arteries: unpaired visceral arteries, paired visceral arteries, and parietal arteries. The unpaired visceral arteries supply the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, spleen, pancreas, gallbladder, and liver and are made up of the celiac trunk, superior mesenteric artery (SMA), and inferior mesenteric artery (IMA). The paired visceral arteries supply the kidneys, adrenal glands, and gonads and are made up of the middle suprarenals, renals, and gonadal branches of the abdominal aorta. The parietal arteries supply the musculoskeletal structures of the abdominal wall and are made up of the inferior phrenic, lumbar, and median sacral branches of the abdominal aorta.
Structure and Function
Register For Free And Read The Full Article
Search engine and full access to all medical articles
10 free questions in your specialty
Free CME/CE Activities
Free daily question in your email
Save favorite articles to your dashboard
Emails offering discounts
Learn more about a Subscription to StatPearls Point-of-Care
Structure and Function
The celiac trunk is one of the major abdominal arteries and arises from the anterior aspect of the aorta at the T12 level of the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm. The celiac artery supplies oxygen-rich blood to the abdominal esophagus, stomach, liver, spleen, and superior portions of the duodenum and pancreas, which are collectively known as the embryonic foregut derivatives except the spleen. As a major branch of the abdominal aorta without extensive anastomosis with the other gut arteries, the celiac trunk is a vital artery that if ligated would result in severe foregut necrosis.[1]
The celiac artery gives rise to three major branches, including the left gastric, splenic, and common hepatic arteries. Collectively, these major branches of the celiac artery supply the stomach, spleen, liver, gallbladder, abdominal esophagus, pancreas, and duodenum. The left gastric artery gives rise to the esophageal branches and continues as the lesser curvature of the stomach to anastomose with the right gastric artery and supply the stomach. The splenic artery is contained within the splenorenal ligament and runs posterior to the stomach and along the superior pancreas.[2] Not only does the splenic artery supply the spleen, but it also gives rise to the left gastroepiploic, short gastric, and pancreatic arterial branches. The left gastroepiploic supplies the greater curvature of the stomach, the short gastrices supply the fundus of the stomach, and the pancreatic branches supply the body and tail of the pancreas. The common hepatic arteries are the only arterial supply to the liver and divide into the proper hepatic and gastroduodenal arteries. The proper hepatic arteries ascend through the lesser omentum and give rise to the right gastric, right and left hepatic, and cystic arteries. The right gastric supplies the pylorus and lesser curvature of the stomach, the right and left hepatic supply the corresponding liver lobes, and the cystic branch supplies the gallbladder. The gastroduodenal arteries descend posterior to the duodenum and give rise to the right gastroepiploic and superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries. The right gastroepiploic artery supplies the greater curvature of the stomach, and the superior pancreaticoduodenal artery supplies the head of the pancreas.
The SMA arises inferior to the celiac trunk origin and supplies arterial blood to the midgut organs, which involves the major duodenal papilla to the proximal two-thirds of the transverse colon. The SMA branches anteriorly from the abdominal aorta at L1 and gives rise to the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery, jejunal and ileal arteries, middle and right colic arteries, and ileocolic artery. The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery supplies the inferior portion of the pancreas head, the uncinate process, and the duodenum. The jejunal and ileal arteries supply the jejunum and ileum through anastomotic arcades known as the vasa recta. The middle and right colic arteries supply the transverse and ascending colon, respectively. The ileocolic artery gives rise to branches supplying the ascending colon, appendix, cecum, and ileum.
The IMA arises at L3 near the inferior border of the duodenum and supplies the hindgut organs, including the large intestine from the splenic flexure, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and the upper part of the rectum. The three major branches of the IMA are the left colic, sigmoid, and superior rectal arteries. The left colic artery supplies the distal third of the transverse colon and the descending colon. The sigmoid arteries supply the descending colon and the sigmoid colon. The superior rectal artery supplies the rectum and gives rise to branches that communicate with the middle and inferior rectal arteries.
Embryology
The gut embryology starts as a midline endoderm-lined tube that is divided into foregut, midgut, and hindgut regions. The celiac trunk and its branches derive from foregut development, the SMA and its branches derive from midgut development, and the IMA and its branches derive from the hindgut development. The vitelline arteries initially supply the yolk sac and gradually fuse to form the dorsal mesentery arteries of the gut, which become the celiac and SMA. The umbilical arteries course to the placenta with the allantois and eventually give rise to the IMA.
Blood Supply and Lymphatics
Lymphatic drainage from the retroperitoneal abdominal viscera drains medially and courses back to the lumbar and visceral preaortic (celiac, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric nodes) and lateral aortic lymph nodes. The lymph is collected into the cisterna chyli and brought back to the venous system by the thoracic duct.[3]
Nerves
Retroperitoneal visceral structures are supplied by parasympathetic fibers from the vagus nerve and by pelvic splanchnic nerves S2-S4. The celiac trunk and midgut parasympathetic nerve supply include the vagus nerve, while the sympathetic nerve supply involves the thoracic splanchnic T5-T11 for celiac artery and T11-T12 for the SMA. The IMA parasympathetic nerve supply involves the pelvic splanchnic S2-S4, while the sympathetic nerve supply includes the lumbar splanchnic L1-L2. Pain sensation afferents from the abdominal viscera course through the spinal cord in a retrograde fashion through the thoracic and lumbar splanchnic sympathetic nerves T5-L2. Somatic nerves of the posterior abdominal wall are formed from the lumbar plexus L1-L4.
Muscles
The posterior abdominal wall lies deep to the posterior abdominal cavity and includes the psoas major, iliacus, quadratus lumborum, and respiratory diaphragm.
Physiologic Variants
The orientation and order of branches arising from the celiac artery vary from person to person. For example, case reports in the literature have documented a false tripod, in which the left gastric artery arises proximal to the bifurcation of the splenic and common hepatic arteries.[4] The right gastric and right hepatic arteries may sometimes arise from the SMA instead of the celiac artery. The left hepatic artery may sometimes be seen as a branch of the left gastric artery. Similarly, the right gastric artery may be seen as a branch of the common hepatic rather than the proper hepatic artery.
Surgical Considerations
Celiac artery compression syndrome is an unusual disease that presents with postprandial abdominal pain and weight loss due to narrowing of the proximal celiac artery due to compression from a low inserting median arcuate ligament. Patients with celiac artery compression syndrome may be treated with laparoscopic release of the extrinsic compression by the division of the median arcuate ligament overlying the celiac axis and outline of the aorta and celiac trunk. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty and stenting of the celiac artery may also be used in celiac artery compression syndrome to relieve celiac axis external compression.
In cases of superior mesenteric artery syndrome, in which the third and final portion of the duodenum are compressed between the abdominal aorta and SMA, the Kocher Maneuver is a described surgical approach documented in the literature to expose retroperitoneal structures.[5]. In this approach, the peritoneum is incised at the border of the duodenum and is reflected to expose the extrinsic compression. SMA syndrome is also more commonly treated by duodenojejunostomy by either open or laparoscopic surgery.
Patients with colon cancer, diverticulitis, trauma to the colon, and inflammatory bowel disease may require surgical resection of the descending colon, also known as hemicolectomy. During the procedure, the surgeon must be careful to isolate the IMA branches from the inferior mesenteric vein. During the procedure, the surgeon traces back the IMA to the abdominal aorta to differentiate from the inferior mesenteric vein, which has a different course from the IMA and drains into the splenic vein. The IMA and its associated branches are ligated once traced back proximally to the aorta.
Clinical Significance
Due to its major branches and a vast supply of embryonic foregut structures, the celiac trunk is an important abdominal arterial branch with clinical significance in disorders, such as peptic ulcers, celiac trunk compression syndrome, and splenic artery aneurysms. Peptic ulcers in the duodenum and stomach may cause life-threatening GI bleeding if the ulcers erode into the nearby arteries, such as the gastroduodenal artery. In celiac trunk compression syndrome, the median arcuate ligament lies anterior to the celiac trunk, which causes compression of the celiac trunk, usually manifesting as pain secondary to abdominal organ ischemia or compression of the celiac ganglion. Splenic artery aneurysms must be removed by not only removing the spleen but, often, also partially removing the pancreas due to relative anatomical proximity.[6]
SMA occlusion is an acute cause of intestinal ischemia due to a number of causes of SMA blood flow restriction, including thrombosis, embolism, abdominal aortic aneurysm, and aortic dissection. SMA blood flow to the midgut structures is restricted, and symptoms of acute abdominal pain may develop due to intestinal ischemia, which leads to death in the elderly in up to 80% of cases.[7]
Superior mesenteric artery syndrome is an unusual cause of proximal intestinal obstruction caused by the decreased acuity of the angle between the aorta and SMA. Patients complain of small bowel obstruction symptoms, which are attributed to compression of the third portion of the duodenum due to narrowing between the SMA and aorta usually due to the loss of mesenteric fat pad cushioning. Nutcracker syndrome is another example of compression involving the SMA, but in this case, the left renal vein is compressed by both the abdominal aorta and SMA. Symptoms of nutcracker syndrome include hematuria, anemia, and abdominal or pelvic pain.[8]
The IMA has significant anastomoses with the SMA called the marginal artery of Drummond and arc of Riolan. The marginal artery of Drummond is formed from a combination of the ileocolic, right and middle colic of the SMA, and sigmoid branches of the IMA. The arc of Riolan is formed between the middle colic branch of the SMA and left colic branch of the IMA. Of significance, the splenic flexure is a watershed area between the two arteries that is sensitive to systemic abdominal hypotension.
The IMA also has clinical significance in cases of congenital disorder of the kidneys, known as horseshoe kidney.[9]. The fused kidneys become stuck in the lower abdomen underneath the IMA and may lead to complications including hydronephrosis, renal stones, and urinary tract infections.
Media
(Click Image to Enlarge)
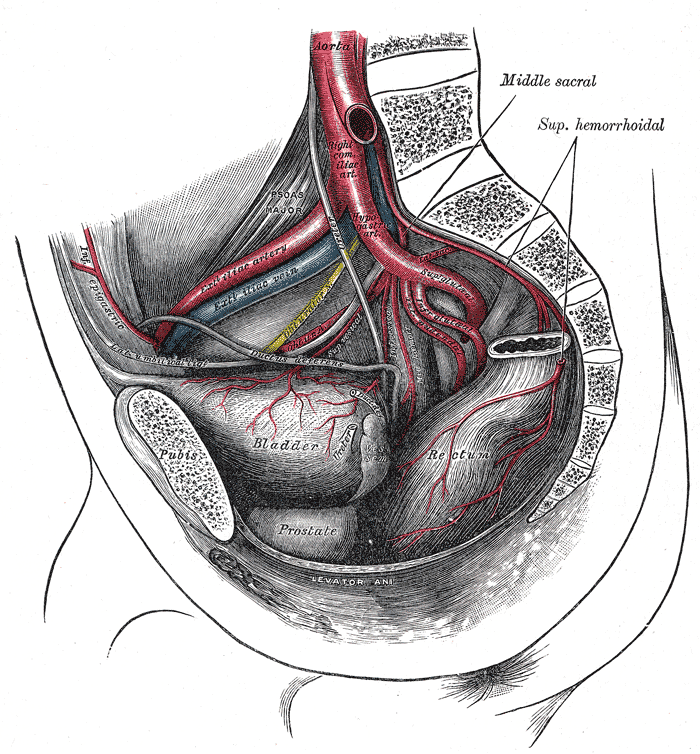
Arteries of the Pelvis, Male Abdomen. The right common iliac artery, hypogastric artery, superior gluteal artery, infra gluteal artery, inferior gluteal artery, external Iliac vein, external iliac artery, bladder, prostate, and rectum are seen in the illustration.
Henry Vandyke Carter, Public Domain, via Wikimedia Commons
References
Kronick MD, Doben AR, Morris ME, Gross RI, Kravetz A, Nahmias JT. Blunt traumatic celiac artery avulsion managed with celiac artery ligation and open aorto-celiac bypass. Trauma case reports. 2017 Oct:11():8-12. doi: 10.1016/j.tcr.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Oct 31 [PubMed PMID: 29644269]
Level 3 (low-level) evidencePang X, Li T, Wang C. Splenic artery embolization with detachable balloons for hypersplenism. The Journal of international medical research. 2018 Oct:46(10):4111-4119. doi: 10.1177/0300060518786419. Epub 2018 Jul 20 [PubMed PMID: 30027780]
Defize IL, Schurink B, Weijs TJ, Roeling TAP, Ruurda JP, van Hillegersberg R, Bleys RLAW. The anatomy of the thoracic duct at the level of the diaphragm: A cadaver study. Annals of anatomy = Anatomischer Anzeiger : official organ of the Anatomische Gesellschaft. 2018 May:217():47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Mar 3 [PubMed PMID: 29510243]
Pinal-Garcia DF, Nuno-Guzman CM, Gonzalez-Gonzalez ME, Ibarra-Hurtado TR. The Celiac Trunk and Its Anatomical Variations: A Cadaveric Study. Journal of clinical medicine research. 2018 Apr:10(4):321-329. doi: 10.14740/jocmr3356w. Epub 2018 Feb 18 [PubMed PMID: 29511421]
Bonnichon P, Rossat-Mignod JC, Corlieu P, Aaron C, Yandza T, Chapuis Y. Surgical approach to the superior mesenteric artery by the Kocher Maneuver: anatomy study and clinical applications. Annals of vascular surgery. 1987 May:1(4):505-8 [PubMed PMID: 3504363]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceGrippi FJ, Yu H. Acute upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage from a pseudoaneurysm of an unusual superior polar artery of the spleen. Radiology case reports. 2018 Aug:13(4):797-800. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2018.05.006. Epub 2018 Jun 8 [PubMed PMID: 30002784]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceMotta F, Vallabhaneni R, Kalbaugh CA, Farber MA. The role of selective stenting for superior mesenteric artery scallops during fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair. Journal of vascular surgery. 2019 Jan:69(1):47-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.05.016. Epub 2018 Jun 28 [PubMed PMID: 29960791]
Hangge PT, Gupta N, Khurana A, Quencer KB, Albadawi H, Alzubaidi SJ, Knuttinen MG, Naidu SG, Oklu R. Degree of Left Renal Vein Compression Predicts Nutcracker Syndrome. Journal of clinical medicine. 2018 May 8:7(5):. doi: 10.3390/jcm7050107. Epub 2018 May 8 [PubMed PMID: 29738433]
Majos M, Polguj M, Szemraj-Rogucka Z, Arazińska A, Stefańczyk L. The level of origin of renal arteries in horseshoe kidney vs. in separated kidneys: CT-based study. Surgical and radiologic anatomy : SRA. 2018 Oct:40(10):1185-1191. doi: 10.1007/s00276-018-2071-8. Epub 2018 Jul 24 [PubMed PMID: 30043151]