Introduction
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN) is a benign epidermal growth that presents as hyperpigmented or skin-colored papules that develop on the face and neck beginning in adolescence. It typically occurs in individuals with Fitzpatrick skin types III to VI, most commonly affecting people of African and Asian descent. It is considered to be a common variant of seborrheic keratoses (SKs). It was first described in 1925 by Dr. Aldo Castellani based on his observations while visiting Jamaica and Central America.
Etiology
Register For Free And Read The Full Article
Search engine and full access to all medical articles
10 free questions in your specialty
Free CME/CE Activities
Free daily question in your email
Save favorite articles to your dashboard
Emails offering discounts
Learn more about a Subscription to StatPearls Point-of-Care
Etiology
The cause of DPN is unknown. Similar to SKs, a somatic activating mutation in FGFR3 has been found in lesions of DPN, supporting the concept that these two lesions share common genetic pathogenesis and may explain the genetic predisposition observed in DPN.[1] Because the lesions occur mainly in a photodistribution on the head, neck, and upper trunk, a potential association with cumulative ultraviolet (UV) exposure has been proposed. FGFR3 mutations have been found to occur more in sun-exposed regions and with increasing age. One study showed that darker-skinned patients who used topical treatments for artificial depigmentation had an exacerbation of DPNs, possibly due to decreased UV protection from loss of skin pigment.[2] These features suggest that UV exposure may have a role in the pathogenesis of DPN.
Epidemiology
DPN is common in those of African descent and relatively common in Asians, with reported incidences ranging from 10% to 75% in selected study populations of individuals with darker pigmentation.[3] The condition has been reported in populations of African heritage, Filipinos, Vietnamese, Europeans, and Mexicans.[4] Up to one-third of African American adults in the United States have DPN. Studies have reported that more lightly pigmented African-Americans had a lower frequency of involvement when compared to those with Fitzpatrick skin type VI.[2] DPN occurs with a strong familial predisposition. Various studies of patients with DPN reported positive family histories in 77% to 93% of cases.[5] Women are twice as likely to be affected as men. The onset of DPN is typical during adolescence, in contrast to SKs. Rarely, it occurs in children and has been reported in patients as young as age 3. The number and size of lesions increase with age, peaking in the sixth decade. DPN is not related to any systemic disease or syndrome; however, an eruptive form has been reported in association with adenocarcinoma of the colon.[6]
Histopathology
DPN is characterized by irregular acanthosis, papillomatosis, and hyperkeratosis of the epidermis. There are elongated and interconnected rete ridges, with deposits of unusually large amounts of pigment throughout the rete, particularly in the basal layer.[5] Keratin-filled invaginations of the epidermis are often present. A prominent fibrous stroma is typically seen within papillomatous acanthotic structures. The pattern is similar to the acanthotic and reticulate types of SKs, although horn pseudocysts are not commonly seen, and the epithelial proliferation is not usually composed of basaloid cells in DPN lesions.[3]
History and Physical
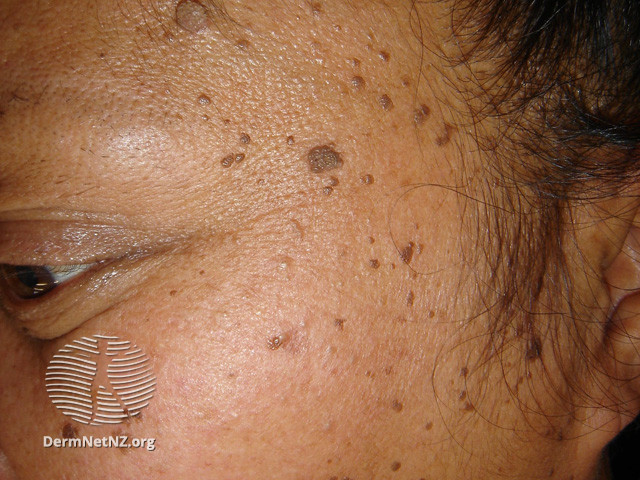
The lesions of DPN initially present in adolescent patients as minute, round, skin-colored to dark brown macules, resembling freckles, gradually becoming papular and increasing in size and number with age. There may be a family history of similar lesions. The lesions often become hyperpigmented, filiform to sessile, smooth-surfaced papules, ranging from 1- to 5-mm in diameter and 1- to 3-mm in elevation. They most commonly appear in a symmetric distribution on the malar cheeks, temples, and forehead. They may also occur on the neck, upper chest, and back with less frequency. Approximately one-fourth of patients with facial lesions will also have lesions on the body. The papules are asymptomatic, without scaling, crusting, or ulceration. Lesions do not spontaneously resolve.
Evaluation
DPN can usually be diagnosed clinically. Dermoscopy may be a useful, noninvasive, cost-effective diagnostic tool in distinguishing DPN from other pigmented lesions. One study in 2017 reported the most common dermoscopy finding was fissures and ridges in a cerebriform pattern, seen in 59% of cases. Another common finding is comedo-like openings, seen in 27% of cases in the study. Milia-like cysts and a combination of the above findings may also be seen.[5]
If there is any concern for malignancy, the lesion should be biopsied and sent for histopathology.
Treatment / Management
Treatment of DPN is not necessary and is generally performed for cosmetic purposes. Due to the tendency of darker skin types to heal with dyspigmentation, caution should be used when choosing treatment modalities, and all patients should be counseled that removal of DPN lesions may result in dyspigmentation. Initial treatment should be limited to a small number of lesions to allow for the evaluation of post-inflammatory dyspigmentation. Aggressive treatment should be avoided to minimize scarring and pigmentation problems.
The most common treatment modalities include snip excision with scissors, light curettage with or without anesthesia, and light electrodesiccation, which are generally effective for smaller lesions.[7] Electrodesiccation should be done at a low setting after applying a topical anesthetic, and the patient should be instructed to apply ointment to the desiccated crust daily until healed.[8] Cryotherapy is problematic due to the risk of hypopigmentation secondary to melanocyte damage and should be used with extreme caution. Studies and case reports have described successful treatment of DPN lesions with KTP, PDL, Nd:YAG, and CO2 lasers, with minimal adverse events and efficacy comparable to electrodesiccation.[9][10][11] Repeated laser treatments may be necessary. A 2016 study of 45 patients treated with CO2 laser reported high patient satisfaction with cosmetic outcomes after an average of 3 treatment sessions, although 28% reported a recurrence of a few lesions after CO2 ablation.[12] Patients should be counseled that lesions may recur after treatment with any modality.(A1)
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of DPN includes seborrheic keratoses, acrochordons, verrucae, melanocytic nevi, angiofibromas, and various adnexal tumors, including trichoepitheliomas, fibrofolliculomas, tricholemmomas, basaloid follicular hamartomas, syringomas.
Prognosis
DPN is a benign and asymptomatic cutaneous condition without the risk of malignancy. DPN lesions may increase in number and size with age and do not spontaneously resolve.
Complications
Similarly to seborrheic keratoses, DPN lesions can become inflamed and irritated. Removal of lesions can lead to cosmetic complications, including infection, scarring, and dyspigmentation.
Consultations
For primary care providers, consultation with a dermatologist may be indicated if there is uncertainty regarding the diagnosis or any concern for cutaneous malignancy.
Pearls and Other Issues
DPN is presumed to be a variant of seborrheic keratoses (SKs); however, some clinicians believe it to be a clinically and histopathologically distinct entity. There are key differences between DPN and SKs that lead to this debate. The two lesions affect different demographics, with DPN affecting darker skin types with a female predominance. SKs are found in all skin types with a predominance in lighter-pigmented individuals with Fitzpatrick skin type I to II.[13] Clinically, DPN lesions are largely limited to sun-exposed areas, whereas SKs have a more widespread distribution. Morphologically, DPN lesions are relatively small and uniform, while SKs vary widely in size and shape, with diameters that can reach several centimeters. Genetically, DPN and SKs share a common somatic activating mutation in FGFR3; however, DPN lacks the mutation in PIK3CA that is found in SKs, suggesting different genetic causes.[14] Subtle but consistent differences between the histology of DPN and SKs have been reported, including the prominence of fibrous stroma within papillomatous acanthotic structures, seen in DPN but not SKs. Further studies on the pathogenesis of DPN may yield insight into whether it is truly a variant of SKs or its own distinct entity.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN) is a benign epidermal growth that presents as hyperpigmented or skin-colored papules that develop on the face and neck beginning in adolescence. Most healthcare workers including nurse practitioners are probably unfamiliar with this skin disorder, hence referral to a dermatologist is recommended. The key reason patients seek care is for cosmesis.
Media
(Click Image to Enlarge)
References
Hafner C, Landthaler M, Mentzel T, Vogt T. FGFR3 and PIK3CA mutations in stucco keratosis and dermatosis papulosa nigra. The British journal of dermatology. 2010 Mar:162(3):508-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09488.x. Epub 2009 Sep 1 [PubMed PMID: 19845664]
Dunwell P, Rose A. Study of the skin disease spectrum occurring in an Afro-Caribbean population. International journal of dermatology. 2003 Apr:42(4):287-9 [PubMed PMID: 12694494]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidenceMetin SA, Lee BW, Lambert WC, Parish LC. Dermatosis papulosa nigra: a clinically and histopathologically distinct entity. Clinics in dermatology. 2017 Sep-Oct:35(5):491-496. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 8 [PubMed PMID: 28916031]
Alani A, Natarajan S. First case of dermatosis papulosa nigra in a white child. Clinical and experimental dermatology. 2017 Oct:42(7):803-805. doi: 10.1111/ced.13186. Epub 2017 Aug 28 [PubMed PMID: 28846142]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceBhat RM, Patrao N, Monteiro R, Sukumar D. A clinical, dermoscopic, and histopathological study of Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra (DPN) - An Indian perspective. International journal of dermatology. 2017 Sep:56(9):957-960. doi: 10.1111/ijd.13633. Epub 2017 May 8 [PubMed PMID: 28485013]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceSchwartzberg JB, Ricotti CA Jr, Ballard CJ, Nouri K. Eruptive dermatosis papulosa nigra as a possible sign of internal malignancy. International journal of dermatology. 2007 Feb:46(2):186-7 [PubMed PMID: 17269973]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceAli FR, Bakkour W, Ferguson JE, Madan V. Carbon dioxide laser ablation of dermatosis papulosa nigra: high satisfaction and few complications in patients with pigmented skin. Lasers in medical science. 2016 Apr:31(3):593-5. doi: 10.1007/s10103-016-1906-y. Epub 2016 Feb 11 [PubMed PMID: 26868030]
Carter EL, Coppola CA, Barsanti FA. A randomized, double-blind comparison of two topical anesthetic formulations prior to electrodesiccation of dermatosis papulosa nigra. Dermatologic surgery : official publication for American Society for Dermatologic Surgery [et al.]. 2006 Jan:32(1):1-6 [PubMed PMID: 16393591]
Level 1 (high-level) evidenceKundu RV, Joshi SS, Suh KY, Boone SL, Huggins RH, Alam M, White L, Rademaker AW, West DP, Yoo S. Comparison of electrodesiccation and potassium-titanyl-phosphate laser for treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra. Dermatologic surgery : official publication for American Society for Dermatologic Surgery [et al.]. 2009 Jul:35(7):1079-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.2009.01186.x. Epub 2009 May 15 [PubMed PMID: 19469798]
Level 1 (high-level) evidenceKaradag AS, Ozkanli Ş, Mansuroglu C, Ozlu E, Zemheri E. Effectiveness of the Pulse Dye Laser Treatment in a Caucasian Women With Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra. Indian journal of dermatology. 2015 May-Jun:60(3):321. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.156447. Epub [PubMed PMID: 26120179]
Garcia MS, Azari R, Eisen DB. Treatment of dermatosis papulosa nigra in 10 patients: a comparison trial of electrodesiccation, pulsed dye laser, and curettage. Dermatologic surgery : official publication for American Society for Dermatologic Surgery [et al.]. 2010 Dec:36(12):1968-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.2010.01769.x. Epub 2010 Oct 11 [PubMed PMID: 21040130]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceBruscino N, Conti R, Campolmi P, Bonan P, Cannarozzo G, Lazzeri L, Moretti S. Dermatosis Papulosa Nigra and 10,600-nm CO2 laser, a good choice. Journal of cosmetic and laser therapy : official publication of the European Society for Laser Dermatology. 2014 Jun:16(3):114-6. doi: 10.3109/14764172.2013.854640. Epub 2013 Nov 18 [PubMed PMID: 24131098]
Alapatt GF, Sukumar D, Bhat MR. A Clinicopathological and Dermoscopic Correlation of Seborrheic Keratosis. Indian journal of dermatology. 2016 Nov-Dec:61(6):622-627 [PubMed PMID: 27904179]
Heidenreich B, Denisova E, Rachakonda S, Sanmartin O, Dereani T, Hosen I, Nagore E, Kumar R. Genetic alterations in seborrheic keratoses. Oncotarget. 2017 May 30:8(22):36639-36649. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16698. Epub [PubMed PMID: 28410231]