Introduction
Apocrine hidrocystoma is a rare, benign cystic tumor originating from the secretory part of the apocrine sweat glands. The tumor typically presents as a solitary, asymptomatic papule or nodule and is commonly found on the head and neck. Apocrine hidrocystomas usually range from 3 to 15 mm in size and may appear translucent, often exhibiting noted mobility. Occasionally, the benign tumor may present in other areas.[1]
Although apocrine hidrocystoma typically presents as a solitary growth, rare multiple forms can also occur, potentially serving as important markers for certain inherited diseases or ectodermal dysplasia, such as a particular form of Goltz-Gorlin syndrome and Schopf-Schultz-Passarge syndrome. Apocrine hidrocystoma is typically diagnosed through histological examination, allowing clinicians to confirm the diagnosis.[2]
Etiology
Register For Free And Read The Full Article
Search engine and full access to all medical articles
10 free questions in your specialty
Free CME/CE Activities
Free daily question in your email
Save favorite articles to your dashboard
Emails offering discounts
Learn more about a Subscription to StatPearls Point-of-Care
Etiology
Apocrine hidrocystomas arise from an inappropriate tumorous growth of apocrine sweat glands.[2] Although the exact etiological factors of this condition remain unknown, sun exposure is considered a potential risk factor and is not associated with familial incidence.[1]
Epidemiology
Apocrine hidrocystoma primarily affects adults aged 30 to 70, with rare occurrences during childhood or adolescence.[3] Solitary apocrine hidrocystomas occur equally in both men and women without any apparent ethnic or geographic predilection. Multiple forms of apocrine hidrocystomas are rare in the general population.
Pathophysiology
Although the pathogenesis of apocrine hidrocystoma is unclear, it involves the tumor originating from the secretory part of apocrine sweat glands. Apocrine hidrocystoma is currently considered a cystic proliferation of apocrine glands rather than a simple retention cyst. Although apocrine hidrocystoma typically presents as a solitary growth, rare multiple forms have been described in 2 rare ectodermal dysplasias, including a particular form of Goltz-Gorlin and Schopf-Schultz-Passarge syndromes.[4]
Goltz-Gorlin syndrome, also known as focal dermal hypoplasia, is an X-linked dominant disease characterized by linear skin atrophy, microcephaly, microphthalmia, midfacial hypoplasia, malformation of the ears, intellectual disability, and skeletal abnormalities.[5][6] Some additional clinical findings have been described in a particular form, featuring a combination of multiple apocrine hidrocystomas, bilateral keratoconus, esophageal papillomatosis, and hiatus hernia.
Schopf-Schultz-Passarge syndrome is an autosomal recessive condition characterized by multiple eyelid apocrine hidrocystomas accompanied by hypotrichosis, hypodontia, palmar and plantar hyperkeratosis, and nail fragility.[7][8]
Histopathology
Apocrine hidrocystoma typically features an inner cyst wall lined by luminal columnar cells indicating apocrine secretion alongside a peripheral layer of flattened myoepithelial cells, similarly seen in the secretory portion of the normal apocrine gland. These cysts can present as either unilocular or multilocular. The epithelium consists of a single or double layer of cuboidal-columnar cells located superiorly to an outer myoepithelial cell layer. The cystic space is lined by a bilaminar epithelium, with columnar cells on the inner surface displaying eosinophilic characteristics and prominent luminal blebbing, often referred to as apocrine snouts. Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive granules are also observed along with lipofuscin granules. In addition, apocrine hidrocystomas exhibit papillary projections and vascular connective tissue covered by the secretory epithelium.[9]
History and Physical
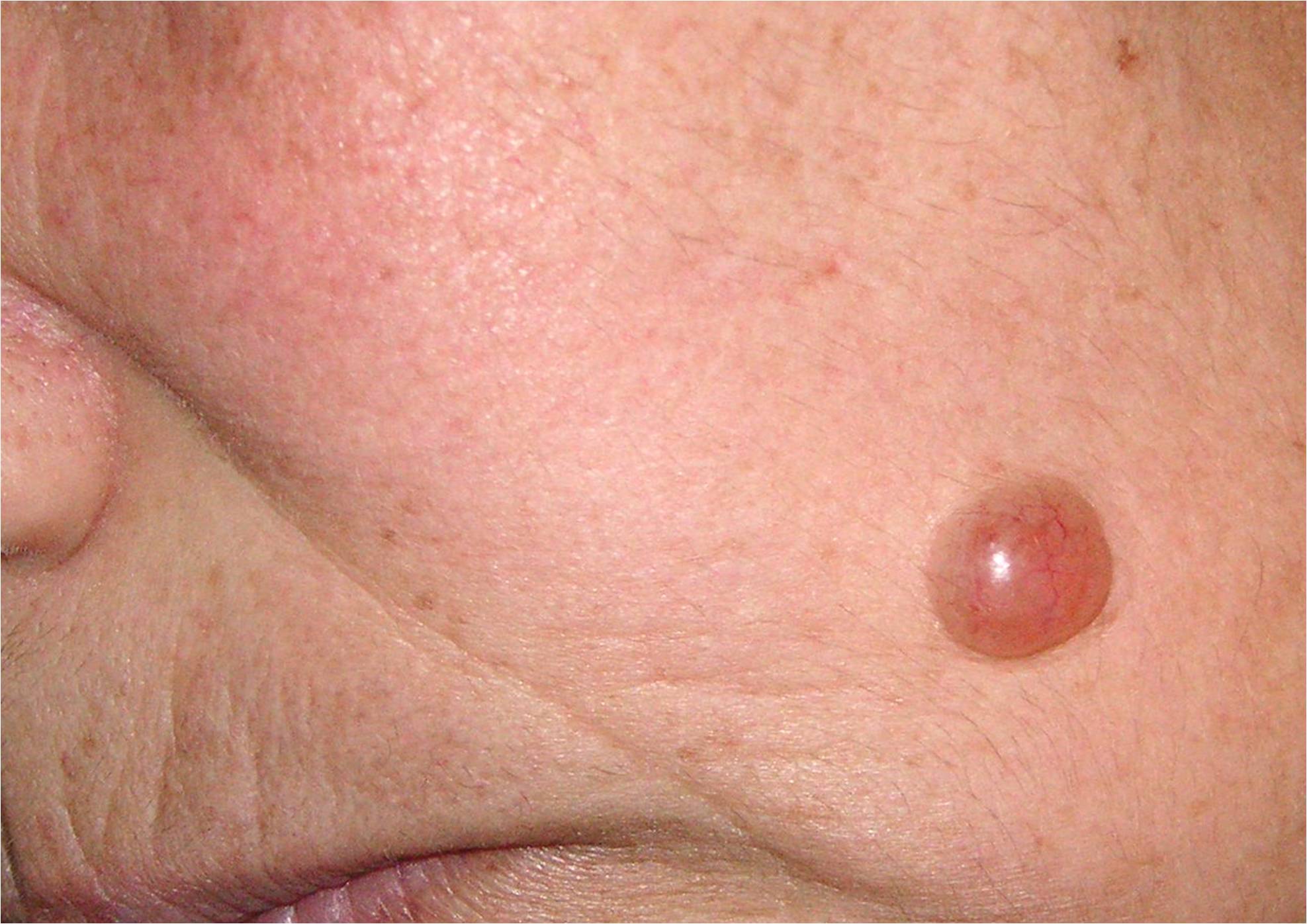
Apocrine hidrocystoma is predominantly solitary, although clinicians have documented multiple lesions. Typically intradermal, apocrine hidrocystoma manifests as a moderately firm, dome-shaped, translucent cystic nodule, often presenting with a blue, bluish-black, grayish, or purple hue (see Image. Apocrine Hidrocystoma). Sizes range from 3 to 15 mm in diameter, with rare giant variants measuring up to 7 cm. Apocrine hidrocystomas are more frequently pigmented than eccrine hidrocystomas. Furthermore, apocrine hidrocystomas do not change or become symptomatic even in hot weather conditions.[9]
Apocrine hidrocystoma is commonly found on the head, face, and neck, possibly because apocrine glands are frequent in sun-exposed areas.[10] The main differential diagnosis of the rare cases of multiple apocrine hidrocystomas is multiple eccrine hidrocystomas, which are typically smaller, with diameters ranging from 1 to 6 mm. Eccrine hidrocystomas tend to exhibit a brown or bluish color, which is clearer compared to apocrine hidrocystomas. Furthermore, another important differential fact of eccrine hidrocystomas is that they tend to increase in size and number in warmer summer environments and may disappear in cooler weather conditions.[11]
Evaluation
Dermoscopic findings reveal a homogeneous pale gray or bluish pattern, along with whitish cotton wool-like structures, linear vessels, and nonconstant focal brownish-orange areas.[12] The grayish color is likely attributed to sialomucin, inducing a diffraction effect similar to Kaposi sarcoma. The whitish structures result from the reflection of connective tissue, whereas the brownish-orange structures may be explicated by the presence of clear cells containing significant amounts of glycogen. The dermoscopic sign of peripheral linear vessels corresponds to dilated vessels in the papillary dermis.
The primary focus of dermoscopy is to ensure the absence of dermoscopic features indicative of a malignant tumor that may have a similar clinical presentation, mainly amelanotic melanoma and basal cell carcinoma.[13][14][15][16] Although apocrine hidrocystomas are clinically suspected, their definitive diagnosis relies on histological examination, where a tissue sample is examined under a microscope.
Treatment / Management
The primary treatment for apocrine hidrocystoma is surgical excision with narrow margins, as the lesion is benign. This approach is crucial for the definitive diagnosis by the treating clinician. While needle puncture is an alternative therapy, this form of treatment often leads to local recurrence.[11] Cyst puncture followed by hypertonic glucose sclerotherapy has shown successful outcomes in treating eyelid apocrine hidrocystoma.[17] Trichloroacetic acid injection followed by aspiration after cyst puncture offers a nonsurgical alternative. Additionally, botulinum toxin A has demonstrated effectiveness in some cases.[18](B3)
Differential Diagnosis
Apocrine hidrocystomas closely resemble several conditions and require differentiation from basal cell carcinoma, blue nevi, cutaneous melanoma, eccrine cystadenoma, follicular cyst, milia, and syringoma.
Prognosis
Apocrine hidrocystomas typically grow slowly and persist indefinitely once they reach their full size. Proper removal usually prevents their recurrence, as they are entirely benign. Although cysts may cause mild irritation in patients, the symptoms are generally mild or absent, and they rarely affect vision. The prognosis for apocrine hidrocystomas is generally favorable, with surgical excision serving as the curative treatment in most cases. However, individual factors such as location, size, and patient health should be considered, and regular follow-up is crucial to monitor for any potential recurrence.[19]
Complications
Apocrine hidrocystomas are typically benign lesions; however, like any medical condition, they are associated with certain complications, especially if they are left untreated or if they are presented unusually.
A few possible complications include:
-
Superadded or secondary infection: Although rare, apocrine hidrocystomas may become infected, especially if the lesion is traumatized or concurrent inflammation is present. Infected lesions present with increased pain, redness, swelling, warmth, and pus discharge. In such cases, antibiotic treatment or surgical drainage may be necessary.
-
Cosmetic concerns: Apocrine hidrocystomas usually occur on the face, particularly the eyelids, and depending on their size and location, can lead to cosmetic disfigurement or distress. Larger or multiple cysts may further impact facial aesthetics and negatively impact the patient's self-esteem.
-
Functional impairment: In some cases, apocrine hidrocystomas can grow large enough to interfere with normal eyelid function, leading to symptoms such as mechanical ptosis, ectropion, or entropion. Correcting functional impairment may require surgical intervention.
-
Recurrence: Although uncommon, apocrine hidrocystomas may rarely recur following treatment, especially if the cyst is incompletely excised. Addressing recurrence may require additional interventions and long-term close follow-up.
-
Malignant transformation: Although infrequent, isolated cases have reported apocrine hidrocystomas undergoing malignant transformation into a type of skin cancer known as hidradenocarcinoma. This complication underscores the importance of accurate diagnosis, appropriate management, and long-term monitoring of these lesions.
-
Psychological impact: Chronic skin conditions, especially those affecting the face, may have a significant psychological impact on patients, leading to feelings of self-consciousness, anxiety, or depression. Addressing the psychosocial aspects of coping with apocrine hidrocystomas is an important aspect of comprehensive care.
Although typically benign, apocrine hidrocystomas can lead to complications, including infection, cosmetic concerns, functional impairment, chronic discomfort, recurrence, and, in rare instances, malignant transformation. Effective management strategies should be personalized to address both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition.
Deterrence and Patient Education
Patients are advised to consult their clinician upon noticing a single raised skin lesion or multiple entities. This proactive step aids in evaluating the possibility of malignancies and determining appropriate measures to prevent further growth.
Pearls and Other Issues
Apocrine hidrocystoma is a benign cystic lesion that commonly manifests on the face. While clinical features may raise suspicion, the formal diagnosis relies on histological examination. Management of apocrine hidrocystoma mainly involves surgical excision; however, alternatives such as electrodesiccation, carbon dioxide laser vaporization, botulinum toxin A, and trichloroacetic acid are also viable, akin to the treatment of eccrine hidrocystomas.
Lesions typically grow gradually and do not spontaneously resolve after reaching full size. Recurrence following surgical excision is rare. Although cysts may cause aesthetic concerns and psychological distress in patients, they are generally asymptomatic. Notably, no cases of malignant transformation of apocrine hidrocystoma have been reported to date.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Apocrine hidrocystoma is a benign cystic lesion that typically occurs on the face and is a rare lesion that primary care clinicians may encounter. Referral to a dermatologist is strongly advised for further evaluation. Although the diagnosis may be suspected based on clinical characteristics, confirmation is based on histological examination. Management of apocrine hidrocystoma mainly involves surgical excision. However, alternative treatments such as electrodesiccation, carbon dioxide laser vaporization, botulinum toxin A, and trichloroacetic acid are recommended for multiple lesions, similar to the treatment of eccrine hidrocystomas.
Media
(Click Image to Enlarge)
References
Belaldavar BP, Suranagi V, Kalakuntla M, Raj B, Tiwari A. Apocrine Hidrocystoma: A Rare Case Report. Indian journal of otolaryngology and head and neck surgery : official publication of the Association of Otolaryngologists of India. 2019 Oct:71(Suppl 1):59-61. doi: 10.1007/s12070-016-1012-2. Epub 2016 Jul 19 [PubMed PMID: 31741931]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceBirkenbeuel J, Goshtasbi K, Mahboubi H, Djalilian HR. Recurrent apocrine hidrocystoma of the external auditory canal. American journal of otolaryngology. 2019 Mar-Apr:40(2):312-313. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2019.01.011. Epub 2019 Jan 28 [PubMed PMID: 30717993]
Sarabi K, Khachemoune A. Hidrocystomas--a brief review. MedGenMed : Medscape general medicine. 2006 Sep 6:8(3):57 [PubMed PMID: 17406184]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceCape HT, Mukit FA, Mukit M, Anelo OM, Krassilnik N, Dadireddy K. Apocrine Hidrocystoma of the Upper Eyelid. Eplasty. 2022:22():ic13 [PubMed PMID: 36072057]
Igarashi T, Kase S, Suimon Y, Takakuwa E, Ishida S. Conjunctival cyst with apocrine hidrocystoma-like features: a case report. International journal of ophthalmology. 2023:16(3):465-467. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.03.18. Epub 2023 Mar 18 [PubMed PMID: 36935784]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceConnolly DM, McGeehin EL, Lee JB. Apocrine cystadenoma: A long-standing apocrine hidrocystoma with an adenomatous proliferation. Journal of cutaneous pathology. 2024 Mar:51(3):251-257. doi: 10.1111/cup.14573. Epub 2023 Dec 12 [PubMed PMID: 38084825]
May C, Chang O, Compton N. A giant apocrine hidrocystoma of the trunk. Dermatology online journal. 2017 Sep 15:23(9):. pii: 13030/qt8bm3r2h4. Epub 2017 Sep 15 [PubMed PMID: 29469730]
Ma L, Jakobiec FA, Wolkow N, Dryja TP, Borodic GE. Multiple Eyelid Cysts (Apocrine and Eccrine Hidrocystomas, Trichilemmal Cyst, and Hybrid Cyst) in a Patient With a Prolactinoma. Ophthalmic plastic and reconstructive surgery. 2018 May/Jun:34(3):e83-e85. doi: 10.1097/IOP.0000000000001069. Epub [PubMed PMID: 29351118]
Chen Y, James C, Leibovitch I, Selva D. Primary orbital apocrine hidrocystoma with sebaceous elements. Clinical & experimental ophthalmology. 2018 Jul:46(5):560-562. doi: 10.1111/ceo.13122. Epub 2017 Dec 28 [PubMed PMID: 29205711]
Magdaleno-Tapial J, Valenzuela-Oñate C, Martínez-Doménech Á, García-Legaz-Martínez M, Martínez-Aparicio A, Alegre-de Miquel V, Pérez-Ferriols A. Apocrine hidrocystoma on the nipple: the first report in this unusual location. Dermatology online journal. 2019 Oct 15:25(10):. pii: 13030/qt89n4f0sf. Epub 2019 Oct 15 [PubMed PMID: 31735014]
Nam JH, Lee GY, Kim WS, Kim KJ. Eccrine hidrocystoma in a child: an atypical presentation. Annals of dermatology. 2010 Feb:22(1):69-72. doi: 10.5021/ad.2010.22.1.69. Epub 2010 Feb 28 [PubMed PMID: 20548887]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceLudzik J, Lee C, Mengden S, Nguyen H, Pleshakov D, Witkowski A. Dermoscopy and Reflectance Confocal Microscopy of Apocrine Hidrocystoma. Dermatology practical & conceptual. 2023 Jan 1:13(1):. doi: 10.5826/dpc.1301a39. Epub 2023 Jan 1 [PubMed PMID: 36892387]
Mendoza-Cembranos MD, Haro R, Requena L, Alegría-Landa V. Digital Apocrine Hidrocystoma: The Exception Confirms the Rule. The American Journal of dermatopathology. 2019 Jan:41(1):79-80. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000001044. Epub [PubMed PMID: 29135506]
Nitzsche G, Ziemer M, Voth H. Surgical management of apocrine hidrocystoma on the penile shaft. International journal of dermatology. 2018 Jan:57(1):92-93. doi: 10.1111/ijd.13738. Epub 2017 Oct 9 [PubMed PMID: 28994105]
Johnson G, Gardner JM, Shalin SC. Polarizable crystals in apocrine sweat gland tumors: A series of 3 cases. Journal of cutaneous pathology. 2017 Aug:44(8):698-702. doi: 10.1111/cup.12962. Epub 2017 Jun 13 [PubMed PMID: 28497640]
Level 3 (low-level) evidencePoli PP, Creminelli L, Moramarco V, Del Gobbo A, Ferrante F, Maiorana C. Diagnostic Workup and Treatment of a Rare Apocrine Hidrocystoma Affecting the Oral Mucosa: A Clinical and Histological Case Report. Case reports in dentistry. 2017:2017():9382812. doi: 10.1155/2017/9382812. Epub 2017 Jul 11 [PubMed PMID: 28781903]
Level 3 (low-level) evidenceOsaki TH, Osaki MH, Osaki T, Viana GA. A Minimally Invasive Approach for Apocrine Hidrocystomas of the Eyelid. Dermatologic surgery : official publication for American Society for Dermatologic Surgery [et al.]. 2016 Jan:42(1):134-6. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000000567. Epub [PubMed PMID: 26716715]
Anandasabapathy N, Soldano AC. Multiple apocrine hidrocystomas. Dermatology online journal. 2008 May 15:14(5):12 [PubMed PMID: 18627748]
Level 3 (low-level) evidencePandher K, Cerci FB, Tolkachjov SN. Apocrine hidrocystoma: a slowly growing postauricular translucent nodule. Dermatology online journal. 2021 Jan 15:27(1):. pii: 13030/qt55j3p0mw. Epub 2021 Jan 15 [PubMed PMID: 33560798]