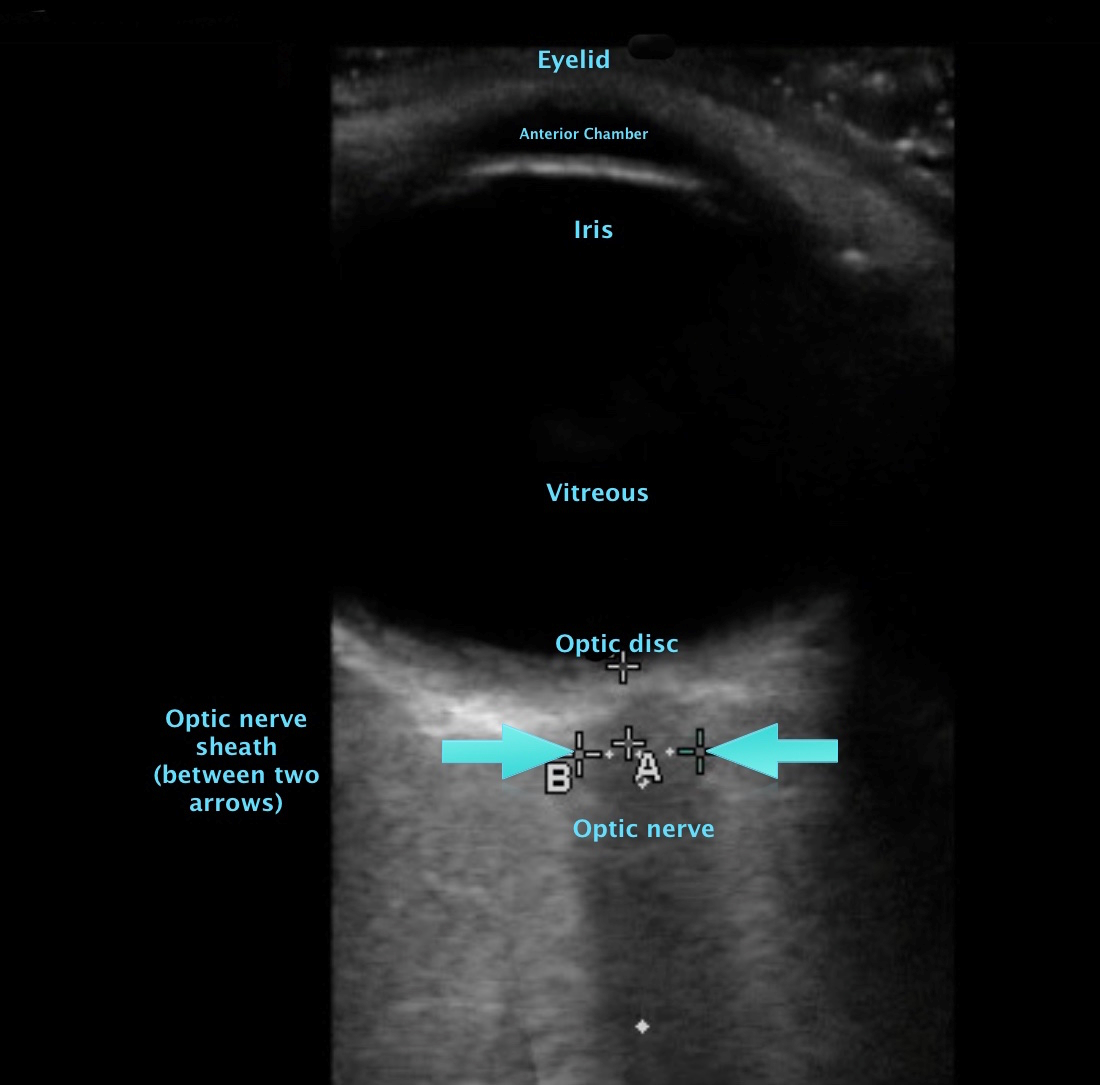
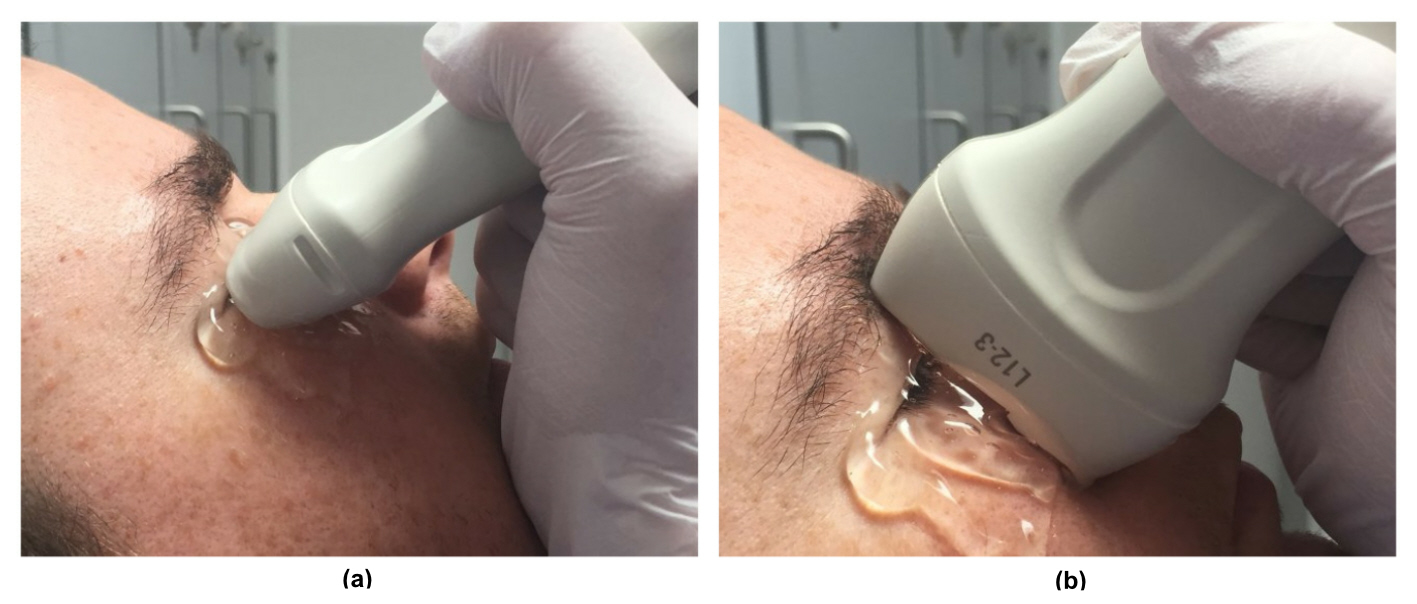
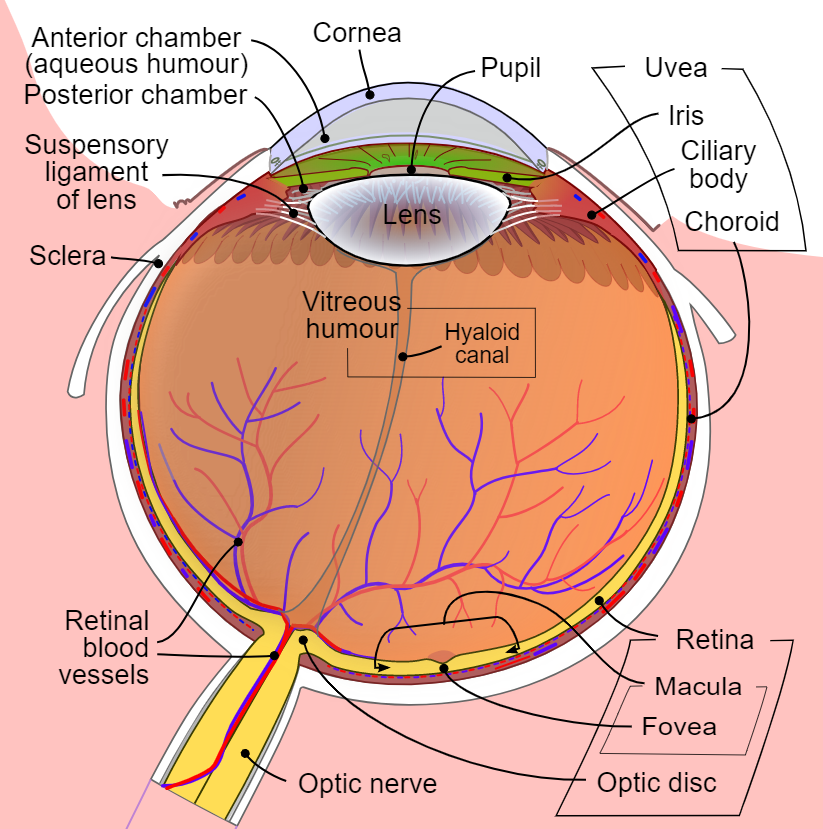
[1]
Varsou O, The Use of Ultrasound in Educational Settings: What Should We Consider When Implementing this Technique for Visualisation of Anatomical Structures? Advances in experimental medicine and biology. 2019
[PubMed PMID: 31338774]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[2]
American College of Emergency Physicians. ACEP emergency ultrasound guidelines-2001. Annals of emergency medicine. 2001 Oct
[PubMed PMID: 11574810]
[3]
Beal EW,Sigmond BR,Sage-Silski L,Lahey S,Nguyen V,Bahner DP, Point-of-Care Ultrasound in General Surgery Residency Training: A Proposal for Milestones in Graduate Medical Education Ultrasound. Journal of ultrasound in medicine : official journal of the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine. 2017 Dec
[PubMed PMID: 28649711]
[4]
Mahmood F,Matyal R,Skubas N,Montealegre-Gallegos M,Swaminathan M,Denault A,Sniecinski R,Mitchell JD,Taylor M,Haskins S,Shahul S,Oren-Grinberg A,Wouters P,Shook D,Reeves ST, Perioperative Ultrasound Training in Anesthesiology: A Call to Action. Anesthesia and analgesia. 2016 Jun
[PubMed PMID: 27195630]
[5]
Whitson MR,Mayo PH, Ultrasonography in the emergency department. Critical care (London, England). 2016 Aug 15
[PubMed PMID: 27523885]
[6]
Nations JA,Browning RF, Battlefield applications for handheld ultrasound. Ultrasound quarterly. 2011 Sep
[PubMed PMID: 21873854]
[7]
Gharahbaghian L,Anderson KL,Lobo V,Huang RW,Poffenberger CM,Nguyen PD, Point-of-Care Ultrasound in Austere Environments: A Complete Review of Its Utilization, Pitfalls, and Technique for Common Applications in Austere Settings. Emergency medicine clinics of North America. 2017 May
[PubMed PMID: 28411935]
[9]
Helmke K,Hansen HC, Fundamentals of transorbital sonographic evaluation of optic nerve sheath expansion under intracranial hypertension II. Patient study. Pediatric radiology. 1996 Oct
[PubMed PMID: 8805600]
[10]
Moretti R,Pizzi B, Ultrasonography of the optic nerve in neurocritically ill patients. Acta anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 2011 Jul
[PubMed PMID: 21463263]
[11]
Zhu S,Cheng C,Zhao D,Zhao Y,Liu X,Zhang J, The clinical and prognostic values of optic nerve sheath diameter and optic nerve sheath diameter/eyeball transverse diameter ratio in comatose patients with supratentorial lesions. BMC neurology. 2021 Jul 2
[PubMed PMID: 34215217]
[12]
Liu D,Kahn M, Measurement and relationship of subarachnoid pressure of the optic nerve to intracranial pressures in fresh cadavers. American journal of ophthalmology. 1993 Nov 15
[PubMed PMID: 8238213]
[13]
Hylkema C, Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Ultrasound and the Diagnosis of Increased Intracranial Pressure. Critical care nursing clinics of North America. 2016 Mar
[PubMed PMID: 26873762]
[14]
Tayal VS,Neulander M,Norton HJ,Foster T,Saunders T,Blaivas M, Emergency department sonographic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter to detect findings of increased intracranial pressure in adult head injury patients. Annals of emergency medicine. 2007 Apr
[PubMed PMID: 16997419]
[15]
Betcher J,Becker TK,Stoyanoff P,Cranford J,Theyyunni N, Military trainees can accurately measure optic nerve sheath diameter after a brief training session. Military Medical Research. 2018 Dec 20
[PubMed PMID: 30572931]
[16]
Caffery TS,Perret JN,Musso MW,Jones GN, Optic nerve sheath diameter and lumbar puncture opening pressure in nontrauma patients suspected of elevated intracranial pressure. The American journal of emergency medicine. 2014 Dec
[PubMed PMID: 25284485]
[17]
Hassen GW,Al-Juboori M,Koppel B,Akfirat G,Kalantari H, Real time optic nerve sheath diameter measurement during lumbar puncture. The American journal of emergency medicine. 2018 Apr
[PubMed PMID: 29338967]
[18]
Singleton J,Dagan A,Edlow JA,Hoffmann B, Real-time optic nerve sheath diameter reduction measured with bedside ultrasound after therapeutic lumbar puncture in a patient with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. The American journal of emergency medicine. 2015 Jun
[PubMed PMID: 25595270]
[19]
Karmaniolou I,Petropoulos G,Theodoraki K, Management of idiopathic intracranial hypertension in parturients: anesthetic considerations. Canadian journal of anaesthesia = Journal canadien d'anesthesie. 2011 Jul
[PubMed PMID: 21519980]
[20]
Atanassoff PG,Alon E,Weiss BM,Lauper U, Spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section in a patient with brain neoplasma. Canadian journal of anaesthesia = Journal canadien d'anesthesie. 1994 Feb
[PubMed PMID: 8131237]
[21]
Sitanaya SN,Kamayanti F,Nugroho HA,Prabowo B, Comparing ultrasonographic optic nerve sheath diameter to head computed tomography scan to predict intracranial pressure elevation. SAGE open medicine. 2022
[PubMed PMID: 35198210]
[22]
Cannata G,Pezzato S,Esposito S,Moscatelli A, Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Ultrasound: A Non-Invasive Approach to Evaluate Increased Intracranial Pressure in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients. Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland). 2022 Mar 21
[PubMed PMID: 35328319]
[23]
Hanafi MG,Verki MM,Parei SN, Ultrasonic Assessment of Optic Nerve Sheath to Detect Increased Intracranial Pressure. Journal of medical ultrasound. 2019 Apr-Jun
[PubMed PMID: 31316215]
[24]
Dağdelen K,Ekici M, Measuring optic nerve sheath diameter using ultrasonography in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Arquivos de neuro-psiquiatria. 2022 May 20
[PubMed PMID: 35613208]
[25]
Korsbæk JJ,Hagen SM,Schytz HW,Vukovic-Cvetkovic V,Wibroe EA,Hamann S,Jensen RH, Transorbital sonography: A non-invasive bedside screening tool for detection of pseudotumor cerebri syndrome. Cephalalgia : an international journal of headache. 2022 Apr 25
[PubMed PMID: 35469442]
[26]
Wang LJ,Zhang Y,Li C,Liu Y,Dong YN,Cui L,Xing YQ, Ultrasonographic optic nerve sheath diameter as a noninvasive marker for intracranial hypotension. Therapeutic advances in neurological disorders. 2022
[PubMed PMID: 35186123]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[27]
Kalim Z,Siddiqui OA,Nadeem A,Hasan M,Rashid H, Assessment of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter and Its Postoperative Regression among Patients Undergoing Brain Tumor Resection in a Tertiary Care Center. Journal of neurosciences in rural practice. 2022 Apr
[PubMed PMID: 35694055]
[28]
Gauthey M,Tessaro MO,Breitbart S,Kulkarni AV,Davis AL, Reliability and feasibility of optic nerve point-of-care ultrasound in pediatric patients with ventricular shunts. Child's nervous system : ChNS : official journal of the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery. 2022 Apr 20
[PubMed PMID: 35441844]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[29]
Şık N,Ulusoy E,Çitlenbik H,Öztürk A,Er A,Yılmaz D,Duman M, The role of sonographic optic nerve sheath diameter measurements in pediatric head trauma. Journal of ultrasound. 2022 Apr 8
[PubMed PMID: 35396696]
[30]
Patel R,Chowdhury MAB,Gul S,Fahy BG,Gonzalez A,Fitzpatrick D,DePortu G,Weeks E,Elie-Turenne MC,Ocampo S,Ponnaluri S,Pizzi MA, Ultrasound of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter and Stroke Outcomes. Critical care explorations. 2021 Nov
[PubMed PMID: 34841250]
[31]
Oliveira BDD,Lima FO,Homem HDC,Figueirêdo AA,Freire VMB,Maia Carvalho FM, Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Detects Intracranial Hypertension in Acute Malignant Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction. Journal of stroke and cerebrovascular diseases : the official journal of National Stroke Association. 2022 Mar
[PubMed PMID: 35032755]
[32]
Xu H,Li Y,Liu J,Chen Z,Chen Q,Xiang Y,Zhang M,He W,Zhuang Y,Yang Y,Chen W,Chen Y, Dilated Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Predicts Poor Outcome in Acute Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Cerebrovascular diseases (Basel, Switzerland). 2022
[PubMed PMID: 34569518]
[34]
Kilker BA,Holst JM,Hoffmann B, Bedside ocular ultrasound in the emergency department. European journal of emergency medicine : official journal of the European Society for Emergency Medicine. 2014 Aug
[PubMed PMID: 24002686]
[35]
Canakci Y,Koksal O,Durak VA, The value of bedside ocular ultrasound assessment of optic nerve sheath diameter in the detection of increased intracranial pressure in patients presenting to the emergency room with headache. Nigerian journal of clinical practice. 2018 Jun
[PubMed PMID: 29888727]
[36]
Matalia J,Shirke S,Kekatpure M, An alternate technique for assessing optic nerve in papilledema by ultrasound B scan. The American journal of emergency medicine. 2015 Jul
[PubMed PMID: 25921967]
[38]
Chronopoulos A,Ong JM,Thumann G,Schutz JS, Occult globe rupture: diagnostic and treatment challenge. Survey of ophthalmology. 2018 Sep - Oct
[PubMed PMID: 29649485]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[39]
Engelbert PR,Palma JK, Petroleum Jelly: A Novel Medium for Ocular Ultrasound. The Journal of emergency medicine. 2015 Aug;
[PubMed PMID: 26014760]
[40]
Romagnuolo L,Tayal V,Tomaszewski C,Saunders T,Norton HJ, Optic nerve sheath diameter does not change with patient position. The American journal of emergency medicine. 2005 Sep
[PubMed PMID: 16140179]
[41]
Kim SH,Kim HJ,Jung KT, Position does not affect the optic nerve sheath diameter during laparoscopy. Korean journal of anesthesiology. 2015 Aug
[PubMed PMID: 26257848]
[42]
Verdonck P,Kalmar AF,Suy K,Geeraerts T,Vercauteren M,Mottrie A,De Wolf AM,Hendrickx JF, Optic nerve sheath diameter remains constant during robot assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. PloS one. 2014
[PubMed PMID: 25369152]
[43]
You AH,Song Y,Kim DH,Suh J,Baek JW,Han DW, Effects of positive end-expiratory pressure on intraocular pressure and optic nerve sheath diameter in robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: A randomized, clinical trial. Medicine. 2019 Apr
[PubMed PMID: 30946349]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[44]
Chin JH,Kim WJ,Lee J,Han YA,Lim J,Hwang JH,Cho SS,Kim YK, Effect of Positive End-Expiratory Pressure on the Sonographic Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter as a Surrogate for Intracranial Pressure during Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. PloS one. 2017
[PubMed PMID: 28107408]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[45]
Ohle R,McIsaac SM,Woo MY,Perry JJ, Sonography of the Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter for Detection of Raised Intracranial Pressure Compared to Computed Tomography: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Journal of ultrasound in medicine : official journal of the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine. 2015 Jul
[PubMed PMID: 26112632]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[46]
De Bernardo M,Vitiello L,De Pascale I,Capasso L,Cornetta P,Rosa N, Optic Nerve Ultrasound Evaluation in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. Frontiers in medicine. 2022
[PubMed PMID: 35299843]
[47]
Kim DH,Jun JS,Kim R, Ultrasonographic measurement of the optic nerve sheath diameter and its association with eyeball transverse diameter in 585 healthy volunteers. Scientific reports. 2017 Nov 21
[PubMed PMID: 29162911]
[48]
Robba C,Santori G,Czosnyka M,Corradi F,Bragazzi N,Padayachy L,Taccone FS,Citerio G, Optic nerve sheath diameter measured sonographically as non-invasive estimator of intracranial pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive care medicine. 2018 Aug
[PubMed PMID: 30019201]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[49]
Kim DH,Jun JS,Kim R, Measurement of the Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter with Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Its Association with Eyeball Diameter in Healthy Adults. Journal of clinical neurology (Seoul, Korea). 2018 Jul
[PubMed PMID: 29856162]
[50]
Wang LJ,Chen LM,Chen Y,Bao LY,Zheng NN,Wang YZ,Xing YQ, Ultrasonography Assessments of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter as a Noninvasive and Dynamic Method of Detecting Changes in Intracranial Pressure. JAMA ophthalmology. 2018 Mar 1
[PubMed PMID: 29392301]
[51]
Vaiman M,Gottlieb P,Bekerman I, Quantitative relations between the eyeball, the optic nerve, and the optic canal important for intracranial pressure monitoring. Head & face medicine. 2014 Aug 17
[PubMed PMID: 25130267]
[52]
Petrou S,Raio C,Klein L,Felicetta M, Posterior Globe Depth for Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurement in Ocular Ultrasound in Healthy Volunteers. Journal of ultrasound in medicine : official journal of the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine. 2021 Dec 19
[PubMed PMID: 34927283]
[53]
Montorfano L,Yu Q,Bordes SJ,Sivanushanthan S,Rosenthal RJ,Montorfano M, Mean value of B-mode optic nerve sheath diameter as an indicator of increased intracranial pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The ultrasound journal. 2021 Jul 2
[PubMed PMID: 34215966]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[54]
Copetti R,Cattarossi L, Optic nerve ultrasound: artifacts and real images. Intensive care medicine. 2009 Aug
[PubMed PMID: 19367390]
[55]
Beckmann U,Gillies DM,Berenholtz SM,Wu AW,Pronovost P, Incidents relating to the intra-hospital transfer of critically ill patients. An analysis of the reports submitted to the Australian Incident Monitoring Study in Intensive Care. Intensive care medicine. 2004 Aug
[PubMed PMID: 14991102]
[56]
Aliaga M,Forel JM,De Bourmont S,Jung B,Thomas G,Mahul M,Bisbal M,Nougaret S,Hraiech S,Roch A,Chaumoitre K,Jaber S,Gainnier M,Papazian L, Diagnostic yield and safety of CT scans in ICU. Intensive care medicine. 2015 Mar
[PubMed PMID: 25518950]
[57]
Caruana M,Culp K, Intrahospital transport of the critically ill adult: a research review and implications. Dimensions of critical care nursing : DCCN. 1998 May-Jun
[PubMed PMID: 9633345]
[58]
Indeck M,Peterson S,Smith J,Brotman S, Risk, cost, and benefit of transporting ICU patients for special studies. The Journal of trauma. 1988 Jul
[PubMed PMID: 3135417]
[59]
Lazarus R,Helmick K,Malik S,Gregory E,Agimi Y,Marion D, Continuum of the United States military's traumatic brain injury care: adjusting to the changing battlefield. Neurosurgical focus. 2018 Dec 1
[PubMed PMID: 30544329]
[60]
Bratton SL,Chestnut RM,Ghajar J,McConnell Hammond FF,Harris OA,Hartl R,Manley GT,Nemecek A,Newell DW,Rosenthal G,Schouten J,Shutter L,Timmons SD,Ullman JS,Videtta W,Wilberger JE,Wright DW, Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. IX. Cerebral perfusion thresholds. Journal of neurotrauma. 2007
[PubMed PMID: 17511547]
[61]
Carney N,Totten AM,O'Reilly C,Ullman JS,Hawryluk GW,Bell MJ,Bratton SL,Chesnut R,Harris OA,Kissoon N,Rubiano AM,Shutter L,Tasker RC,Vavilala MS,Wilberger J,Wright DW,Ghajar J, Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Fourth Edition. Neurosurgery. 2017 Jan 1
[PubMed PMID: 27654000]
[62]
Caffery TS,Musso MW, Questions regarding the utility of the 30-degree test in measuring optic nerve sheath diameters in ED patients. The American journal of emergency medicine. 2015 Apr
[PubMed PMID: 25744151]
[63]
Bhosale A,Shah VM,Shah PK, Accuracy of crescent sign on ocular ultrasound in diagnosing papilledema. World journal of methodology. 2017 Sep 26
[PubMed PMID: 29026691]
[64]
Bittencourt Rynkowski C,Caldas J, Ten Good Reasons to Practice Neuroultrasound in Critical Care Setting. Frontiers in neurology. 2021
[PubMed PMID: 35095741]
[65]
Dinsmore M,Venkatraghavan L, Clinical applications of point-of-care ultrasound in brain injury: a narrative review. Anaesthesia. 2022 Jan
[PubMed PMID: 35001377]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[66]
Johnson GGRJ,Jelic T,Derksen A,Unger B,Zeiler FA,Ziesmann MT,Gillman LM, Accuracy of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurements in Pocket-Sized Ultrasound Devices in a Simulation Model. Frontiers in medicine. 2022
[PubMed PMID: 35308521]
[67]
Killer HE, Laeng HR, Flammer J, Groscurth P. Architecture of arachnoid trabeculae, pillars, and septa in the subarachnoid space of the human optic nerve: anatomy and clinical considerations. The British journal of ophthalmology. 2003 Jun:87(6):777-81
[PubMed PMID: 12770980]
[68]
Wu GB,Tian J,Liu XB,Wang ZY,Guo JY, Can optic nerve sheath diameter assessment be used as a non-invasive tool to dynamically monitor intracranial pressure? Journal of integrative neuroscience. 2022 Mar 22
[PubMed PMID: 35364642]
[69]
Dubourg J,Javouhey E,Geeraerts T,Messerer M,Kassai B, Ultrasonography of optic nerve sheath diameter for detection of raised intracranial pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive care medicine. 2011 Jul
[PubMed PMID: 21505900]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[70]
Chen LM,Wang LJ,Hu Y,Jiang XH,Wang YZ,Xing YQ, Ultrasonic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter: a non-invasive surrogate approach for dynamic, real-time evaluation of intracranial pressure. The British journal of ophthalmology. 2019 Apr
[PubMed PMID: 30361274]
[71]
Hirzallah MI,Lochner P,Hafeez MU,Lee AG,Krogias C,Dongarwar D,Manchanda R,Ouellette L,Hartman ND,Ertl M,Schlachetzki F,Robba C, Quality assessment of optic nerve sheath diameter ultrasonography: Scoping literature review and Delphi protocol. Journal of neuroimaging : official journal of the American Society of Neuroimaging. 2022 Jun 16
[PubMed PMID: 35711135]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence