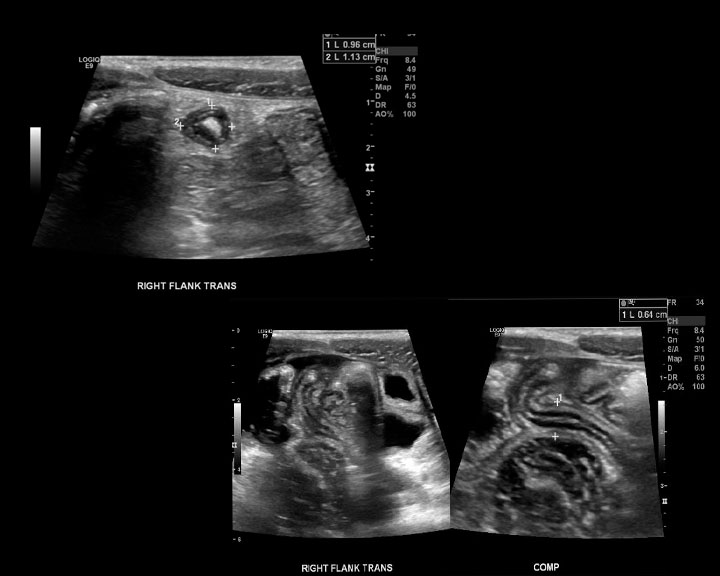
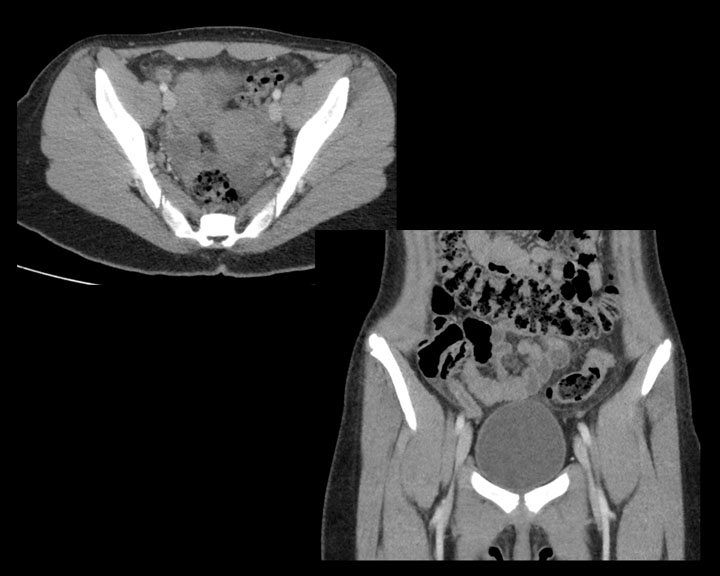
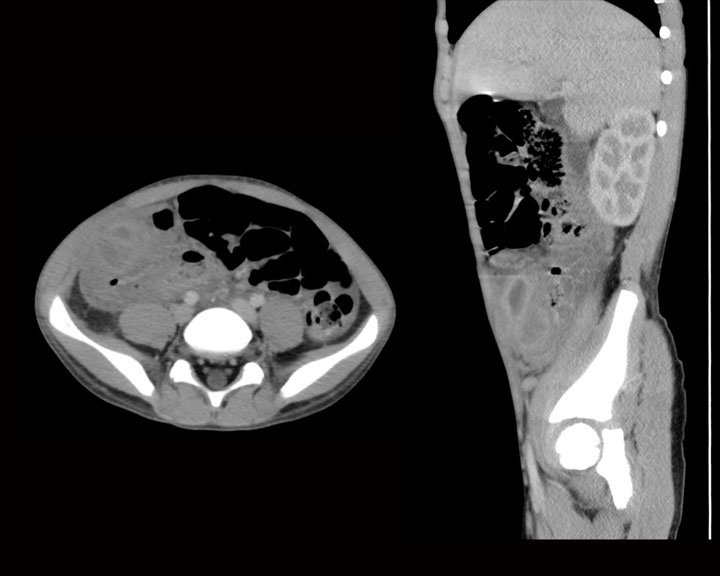
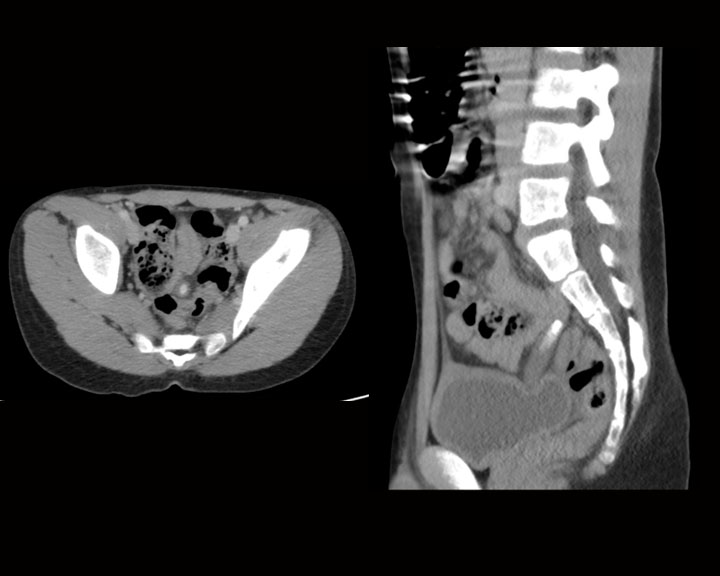
[1]
Tang LH. Epithelial neoplasms of the appendix. Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine. 2010 Nov:134(11):1612-20
[PubMed PMID: 21043814]
[2]
Wu H, Chintagumpala M, Hicks J, Nuchtern JG, Okcu MF, Venkatramani R. Neuroendocrine Tumor of the Appendix in Children. Journal of pediatric hematology/oncology. 2017 Mar:39(2):97-102. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000000598. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 27306228]
[3]
Komo T, Kohashi T, Hihara J, Oishi K, Yoshimitsu M, Kanou M, Nakashima A, Aoki Y, Miguchi M, Kaneko M, Mukaida H, Hirabayashi N. Intestinal obstruction caused by low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm: A case report and review of the literature. International journal of surgery case reports. 2018:51():37-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2018.08.001. Epub 2018 Aug 9
[PubMed PMID: 30138868]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[4]
Rizvi SA, Syed W, Shergill R. Approach to pseudomyxoma peritonei. World journal of gastrointestinal surgery. 2018 Aug 27:10(5):49-56. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v10.i5.49. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 30190782]
[5]
Humes D, Speake WJ, Simpson J. Appendicitis. BMJ clinical evidence. 2007 Jul 1:2007():. pii: 0408. Epub 2007 Jul 1
[PubMed PMID: 19454096]
[6]
Grover CA, Sternbach G. Charles McBurney: McBurney's point. The Journal of emergency medicine. 2012 May:42(5):578-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2011.06.039. Epub 2011 Oct 5
[PubMed PMID: 21982626]
[7]
Bickell NA, Aufses AH Jr, Rojas M, Bodian C. How time affects the risk of rupture in appendicitis. Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 2006 Mar:202(3):401-6
[PubMed PMID: 16500243]
[8]
Leonards LM, Pahwa A, Patel MK, Petersen J, Nguyen MJ, Jude CM. Neoplasms of the Appendix: Pictorial Review with Clinical and Pathologic Correlation. Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 2017 Jul-Aug:37(4):1059-1083. doi: 10.1148/rg.2017160150. Epub 2017 Jun 9
[PubMed PMID: 28598731]
[9]
Bhangu A, Søreide K, Di Saverio S, Assarsson JH, Drake FT. Acute appendicitis: modern understanding of pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Lancet (London, England). 2015 Sep 26:386(10000):1278-1287. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00275-5. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 26460662]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[12]
Mizumoto T. B and T cells in lymphoid tissues of human appendix. International archives of allergy and applied immunology. 1976:51(1):80-93
[PubMed PMID: 132409]
[13]
Willekens I, Peeters E, De Maeseneer M, de Mey J. The normal appendix on CT: does size matter? PloS one. 2014:9(5):e96476. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096476. Epub 2014 May 6
[PubMed PMID: 24802879]
[14]
Ulukaya Durakbaşa C, Taşbaşi I, Tosyali AN, Mutus M, Sehiralti V, Zemheri E. An evaluation of individual plain abdominal radiography findings in pediatric appendicitis: results from a series of 424 children. Ulusal travma ve acil cerrahi dergisi = Turkish journal of trauma & emergency surgery : TJTES. 2006 Jan:12(1):51-8
[PubMed PMID: 16456751]
[15]
Campos Canelas AL, Fernandez HM, Crociati Meguins L, Silva Barros S, Crociati Meguins EM, Ishak G, Rodrigues De Moraes LA. Pneumoperitoneum in association with perforated appendicitis in a Brazilian Amazon woman. Case report. Il Giornale di chirurgia. 2010 Mar:31(3):80-2
[PubMed PMID: 20426916]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[16]
van Randen A, Laméris W, Luitse JS, Gorzeman M, Hesselink EJ, Dolmans DE, Peringa J, van Geloven AA, Bossuyt PM, Stoker J, Boermeester MA, OPTIMA study group. The role of plain radiographs in patients with acute abdominal pain at the ED. The American journal of emergency medicine. 2011 Jul:29(6):582-589.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2009.12.020. Epub 2010 Apr 24
[PubMed PMID: 20825832]
[17]
Iamwat J, Teerasamit W, Apisarnthanarak P, Noppakunsomboon N, Kaewlai R. Predictive ability of CT findings in the differentiation of complicated and uncomplicated appendicitis: a retrospective investigation of 201 patients undergone appendectomy at initial admission. Insights into imaging. 2021 Oct 21:12(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s13244-021-01086-3. Epub 2021 Oct 21
[PubMed PMID: 34674054]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[18]
Park G, Lee SC, Choi BJ, Kim SJ. Stratified computed tomography findings improve diagnostic accuracy for appendicitis. World journal of gastroenterology. 2014 Oct 14:20(38):13942-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13942. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 25320531]
[19]
Moskowitz E, Khan AD, Cribari C, Schroeppel TJ. Size matters: Computed tomographic measurements of the appendix in emergency department scans. American journal of surgery. 2019 Aug:218(2):271-274. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2018.12.010. Epub 2018 Dec 11
[PubMed PMID: 30558802]
[20]
Pickhardt PJ, Levy AD, Rohrmann CA Jr, Kende AI. Primary neoplasms of the appendix manifesting as acute appendicitis: CT findings with pathologic comparison. Radiology. 2002 Sep:224(3):775-81
[PubMed PMID: 12202713]
[21]
Spyropoulos C, Rentis A, Alexaki E, Triantafillidis JK, Vagianos C. Appendiceal mucocele and pseudomyxoma peritonei; the clinical boundaries of a subtle disease. The American journal of case reports. 2014 Aug 27:15():355-60. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.890837. Epub 2014 Aug 27
[PubMed PMID: 25163976]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[22]
Bayhan Z, Yildiz YA, Akdeniz Y, Gonullu E, Altintoprak F, Mantoglu B, Capoglu R, Kahyaoglu Akkaya Z. Appendix Neuroendocrine Tumor: Retrospective Analysis of 4026 Appendectomy Patients in a Single Center. Emergency medicine international. 2020:2020():4030527. doi: 10.1155/2020/4030527. Epub 2020 Sep 3
[PubMed PMID: 32963833]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[23]
Kim DW, Suh CH, Yoon HM, Kim JR, Jung AY, Lee JS, Cho YA. Visibility of Normal Appendix on CT, MRI, and Sonography: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 2018 Sep:211(3):W140-W150. doi: 10.2214/AJR.17.19321. Epub 2018 Jul 24
[PubMed PMID: 30040469]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[24]
Duke E, Kalb B, Arif-Tiwari H, Daye ZJ, Gilbertson-Dahdal D, Keim SM, Martin DR. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Performance of MRI for Evaluation of Acute Appendicitis. AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 2016 Mar:206(3):508-17. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.14544. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 26901006]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[25]
Franke C, Böhner H, Yang Q, Ohmann C, Röher HD. Ultrasonography for diagnosis of acute appendicitis: results of a prospective multicenter trial. Acute Abdominal Pain Study Group. World journal of surgery. 1999 Feb:23(2):141-6
[PubMed PMID: 9880422]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[26]
Pacharn P, Ying J, Linam LE, Brody AS, Babcock DS. Sonography in the evaluation of acute appendicitis: are negative sonographic findings good enough? Journal of ultrasound in medicine : official journal of the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine. 2010 Dec:29(12):1749-55
[PubMed PMID: 21098847]
[27]
Xu Y, Jeffrey RB, DiMaio MA, Olcott EW. Lymphoid Hyperplasia of the Appendix: A Potential Pitfall in the Sonographic Diagnosis of Appendicitis. AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 2016 Jan:206(1):189-94. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.14846. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 26700351]
[28]
Kwon LM, Lee K, Min SK, Ahn SM, Ha HI, Kim MJ. Ultrasound features of secondary appendicitis in pediatric patients. Ultrasonography (Seoul, Korea). 2018 Jul:37(3):233-243. doi: 10.14366/usg.17029. Epub 2017 Aug 25
[PubMed PMID: 29141286]
[29]
Sanchez TR, Corwin MT, Davoodian A, Stein-Wexler R. Sonography of Abdominal Pain in Children: Appendicitis and Its Common Mimics. Journal of ultrasound in medicine : official journal of the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine. 2016 Mar:35(3):627-35. doi: 10.7863/ultra.15.04047. Epub 2016 Feb 18
[PubMed PMID: 26892821]
[30]
Joshi MK, Joshi R, Alam SE, Agarwal S, Kumar S. Negative Appendectomy: an Audit of Resident-Performed Surgery. How Can Its Incidence Be Minimized? The Indian journal of surgery. 2015 Dec:77(Suppl 3):913-7. doi: 10.1007/s12262-014-1063-0. Epub 2014 Apr 9
[PubMed PMID: 27011482]