Introduction
Perhaps biology faces no greater feat than the generation of a complex, multicellular organism from a single cell origin. The eye quintessentially represents this process through the formation of highly specific cell types, regulated by an intricate network of cellular interactions and genetic interplay of the early embryo.
Development
Early Morphogenesis
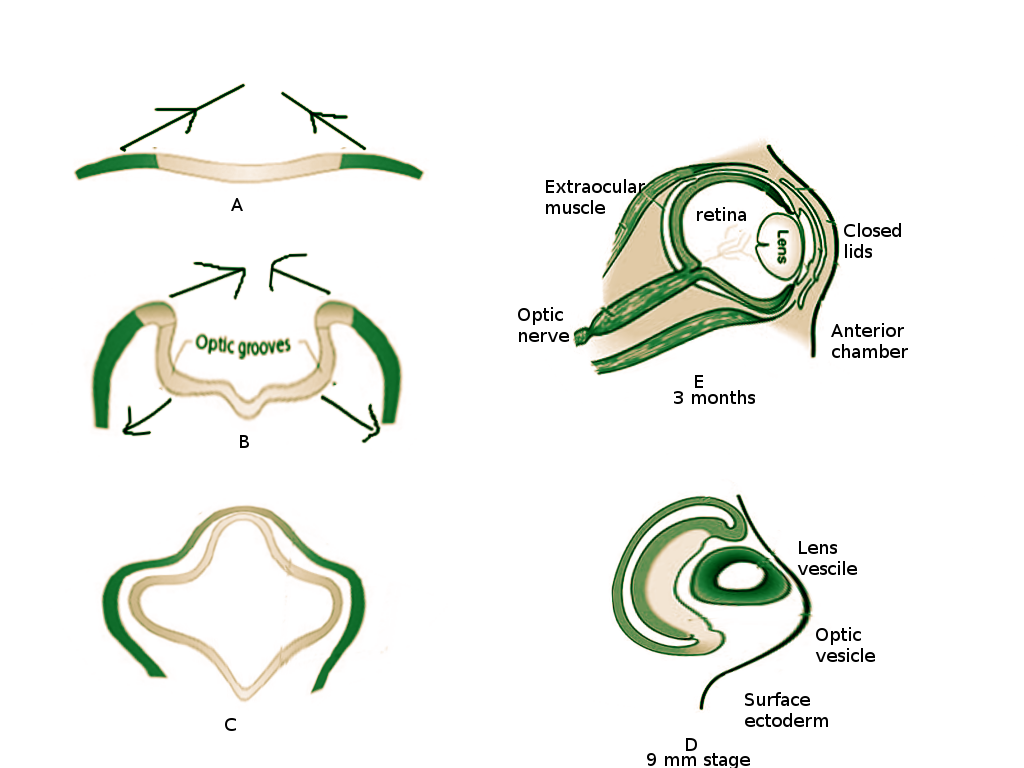
The appearance of optic grooves (neuroectoderm origin) from the developing forebrain marks the first sign of eye development at week three of gestation (see Figure. Embryology of the Eye).[1] As the neural folds fuse, the optic grooves, induced by surrounding mesenchyme, evaginate forming the optic vesicle. The optic vesicles are hollow diverticula that protrude through the surrounding mesenchyme towards the surface ectoderm. This protrusion not only leads to the eventual formation of the optic stalk (future optic nerve) but also induces changes necessary in the surface ectoderm for lens placode formation. The lens placode invaginates towards the optic vesicle and forms the lens pit. As the pit deepens, it becomes the lens vesicle (Figure 1C). The edges of the lens vesicle approach each other, and the lens is pinched off from the outer surface ectoderm layer. The lens vesicle sinks deeper and drifts from the surface ectoderm where it will come to lie in the optic cup.[2]
At four weeks gestation, the optic vesicle invaginates and creates the optic cup [1] (Figure 1C) - this will become the retina. Grooves form along the ventral surface of the optic cup and stalk, called retinal (or choroid) fissures, to allow the passage of the hyaloid artery and vein [3][4]. The hyaloid vessels become entrapped in the optic nerve as the optic cup fuses around them. The hyaloid vessels become the central retinal artery and vein. The distal hyaloid vessels, which supplied the developing lens, degenerate in the vitreous body and leave a remnant known as the hyaloid canal [4].
The structures of the eye and its adnexa heavily derive from mesenchyme, particularly neural crest cells. The neural crest contributes to the corneal stroma and endothelium, the ciliary body, the uveal stroma and melanocytes, the sclera, meningeal sheaths, connective tissue of the optic nerve and extraocular muscles, and bones of the orbit [5][6]. Neuroectoderm also contributes as the source of the retina, posterior iris, and optic nerve. Surface ectoderm gives rise to the lens and corneal epithelium [6]. Mesoderm differentiates into vascular endothelium of the eye and the extraocular muscles [7].
Retina and Optic Nerve
The retina emerges as the optic vesicle invaginates and forms the optic cup [8]. The invagination process results in both inner and outer layers, and these layers create an intraretinal space, which later gets obliterated as the two layers come to adjoin each other. The outer layer contains pigment granules and becomes the pigmented layer of the retina. The inner layer differentiates into the neural retina which will contain rod and cone cells - the light-sensing cells of the retina. The axons from the neural retina then project into the optic stalk. The proliferation of axons in the optic stalk lumen causes obliteration of the lumen. As a result, it forms the optic nerve [9].
Iris and Ciliary Body
The iris and ciliary body derive from the anterior-most tip of the optic cup [10]. The iris is composed of an external layer containing pigment, an unpigmented layer, and a vascularized layer of pupillary muscles. The margins of the optic cup extend towards the location of the pupil forming the iris. The optic cup inner wall gives rise to the posterior iris pigment epithelium. The optic cup outer wall gives rise to the anterior pigment epithelium [11]. Smooth muscle markers are identifiable on the extending cells, which will form the dilator pupillae and sphincter pupillae muscles. The ciliary epithelium also emerges from the anterior tip of the optic cup. Importantly, the ciliary epithelium will secrete fibrillins that contribute to the suspensory ligaments of the lens. The ciliary muscle, which is responsible for lens accommodation, emerges from mesenchymal cells [12].
Lens
As the optic vesicle emerges, it induces the overlying surface ectoderm to differentiate into the lens placode. The lens placode then invaginates, eventually separating from the surface ectoderm and becoming the lens vesicle [4]. The lens vesicle moves towards the cavity created by the optic cup [1][8]. As the lens vesicle settles into the cavity, the hyaloid artery passes through the retinal fissure. It will supply the developing lens and the inner layer of the optic cup before later regressing [4]. The lens vesicle then matures into the lens proper as tall columnar cells on the posterior aspect of the lens vesicle lose their nuclei and lengthen, forming primary lens fibers [13]. Primary lens fibers are transparent due to the expression of ordered crystalline proteins [2]. The cavity of the lens vesicle obliterates because of primary lens fiber proliferation [4]. The hyaloid artery regresses as the anterior chamber forms, and the lens gets nourished by the aqueous humor. Interestingly, no vitreous hemorrhage occurs during regression, suggesting blood flow has ceased before regression begins [14]. Another important aspect of the lens is the lens capsule. The lens capsule forms as the lens vesicle becomes surrounded by the basement membrane as a result of the invagination from the surface ectoderm. Because of the lens capsule, the lens is an immune-privileged organ. The capsule offers pathogen protection while still allowing the passage of solutes and water [15].
Vitreous
In the mature eye, the vitreous serves to maintain the shape of the globe as well as secure the retina in place. During development, mesenchyme invades the optic cup through the retinal fissures. Among other things, this mesenchyme forms the primary vitreous body, which becomes entrapped as the retinal fissures close and seal off the optic cup. The primary vitreous body loses its vasculature, developing into an acellular gel known as the secondary vitreous body. Finally, the tertiary vitreous forms, giving rise to suspension fibers of the lens [1][16]. In the vitreous' process of becoming avascular, the hyaloid artery regresses and a vestigial structure notable in the mature eye forms - the hyaloid canal [4].
Choroid & Sclera
The developing eye begins to take on the mature form with the formation of the choroid and sclera. Development of the choroid, the vascular layer that supplies the outer retina, begins during the sixth to seventh weeks as the outer retinal pigment epithelium of the optic cup induces surrounding mesenchyme [16]. At week 12, capillaries are visible tracing the retinal pigment epithelium, followed by arterioles and venules at week 15. By week 22, arteries and veins resembling the adult eye are apparent [17]. The sclera, an outer fibrous layer of the eye continuous with the dura mater, is also induced from para-ocular mesenchyme and forms exteriorly to the choroid. The sclera contributes to the stromal layer of the cornea [16].
Cornea
The cornea, a clear portion of the outer eye, allows the passage of light into the eye and provides a large component of refraction. There are three major layers to the cornea: external corneal epithelium, derived from surface ectoderm, the central stroma layer derived from mesenchyme, and interior endothelium derived from neural crest cells [6]. After the lens vesicle departs from the surface ectoderm, the intervening space fills with mesenchyme (continuous with scleral mesenchyme). The lens vesicle induces the development of the cornea, resulting in a transparent, avascular structure [18]. Importantly, keratocytes, derived from stromal mesenchyme, produce a highly organized collagen matrix necessary for transparency and refraction [6].
Eyelids
At approximately week six of gestation the eyelids begin to form, deriving from surface ectoderm and mesenchyme. The surface ectoderm contributes to the epidermis anteriorly and palpebral conjunctiva posteriorly. Between the epidermis and palpebral conjunctiva is a core of mesenchymal tissue which forms the orbicularis oculi muscle. It is the accumulation of neural crest mesenchyme at the lateral margin of the optic cup that induces the appendage-like growth of the eyelids, covering the globe [6]. Interestingly, as the superior and inferior lid grow to cover the front of the eye, they fuse with an epithelial plug (Figure 1E). The lids remained fused, separating between the fifth and seventh months of development [19]. Eyelashes and glands will develop from surface ectoderm [1].
Lacrimal Gland
The lacrimal gland is believed to arise during the seventh week of gestation and will come to position itself in the superolateral position of the orbit [7]. In humans, there is debate about its precise cellular origins. Suggestions are that glandular parenchyma derives from the epithelium and surrounding mesenchyme. Development of the lacrimal gland has been described in a triphasic process:
- The presumptive glandular stage: Thickening of the superior fornix epithelium and surrounding mesenchymal condensation
- The bud stage: Appearance of nodules through the formation of lumina within epithelial buds
- Glandular maturity stage: Appearance of adulthood features (beginning week 9) and continued maturation[20]
Recent work also shows a developmental role for myoepithelial cells (MECs). MECs may provide a communicative medium for epithelial and mesenchymal cells, which their physical location between acinar epithelial cells and the basement membrane reinforces [21].
Molecular Level
Recent work in eye embryology has begun to elucidate the complex orchestration of numerous gene products necessary for proper eye development. Among the most notable of these are PAX6, PAX2, sonic hedgehog (SHH), and Rx. Throughout this interplay the importance not only of accurate products but also of accurate gene dosage cannot be overlooked: both deleterious and over-expressive mutations have been shown to result in eye malformations [22].
PAX6 is expressed at the anterior neural plate, indicating the eye field. At this stage, the eye field has not yet been divided to create two globes. The division of the eye field is accomplished by sonic hedgehog (SHH), which is responsible for central nervous system polarity [23]. SHH divides the eye field via the division of the forebrain from which the optic vesicles arise. SHH also upregulates the expression of PAX2 [24]. PAX2 will become restricted in its expression to the proximal optic vesicle and be essential for optic stalk formation as well as the closure of the retinal fissures [25]. Rx is also expressed in the anterior neural plate and will continue to express in the optic vesicles. Rx plays a critical role in spatial patterning and morphogenesis of the optic vesicle. Additionally, Rx is essential for optic vesicle evagination and PAX6 expression [8]. Later, Rx becomes localized to the neural retina and may be necessary for retinal differentiation and proliferation [22].
Clinical Significance
The delicate development of the eye is sensitive to embryologic errors. Some examples of congenital eye malformations include anophthalmia, coloboma, cyclopia, cataract, aniridia, detached retina, hyaloid artery persistence, aphakia, and cryptophthalmos. For brevity, the reader is encouraged to review other sources to learn more about these malformations as they have been well-described elsewhere.
Understanding the components of normal embryology will guide disease management and treatment options. This point is evident by the advent of therapeutic stem cell technologies, such as those under development for retinal and lacrimal gland regeneration [26][27]. Thus, there is a bright horizon in eye embryology that may provide therapeutic options to individuals that have exhausted current practice.