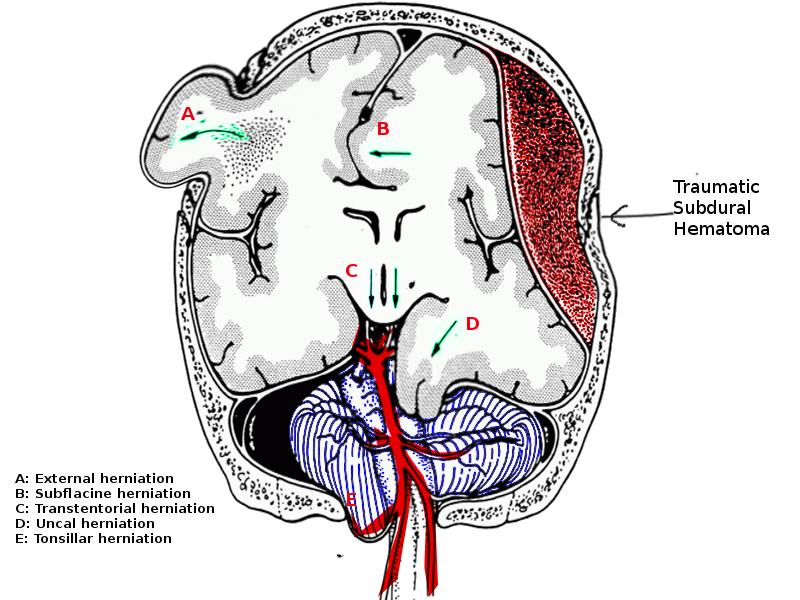
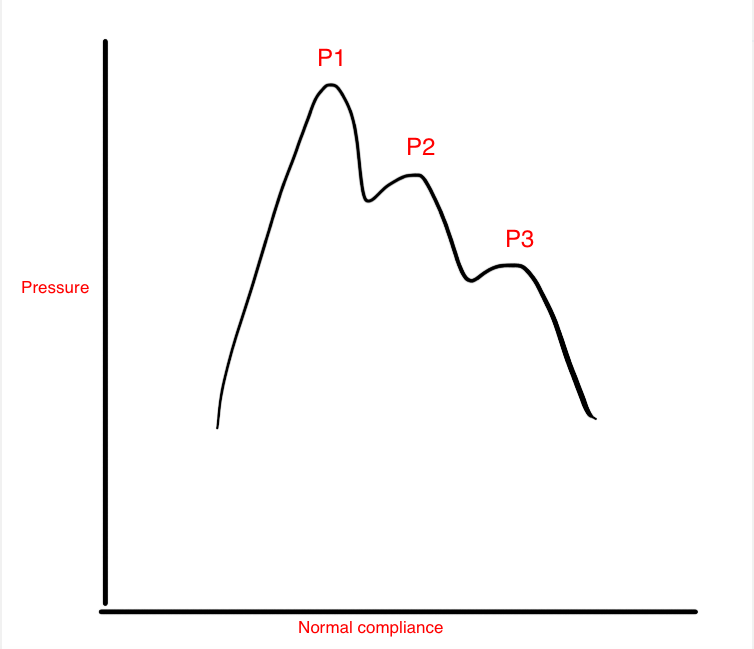
[1]
Adler DE, Milhorat TH. The tentorial notch: anatomical variation, morphometric analysis, and classification in 100 human autopsy cases. Journal of neurosurgery. 2002 Jun:96(6):1103-12
[PubMed PMID: 12066913]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[2]
Meyer GA, Winter DL. Spinal cord participation in the Cushing reflex in the dog. Journal of neurosurgery. 1970 Dec:33(6):662-75
[PubMed PMID: 5482797]
[3]
Plum F, Posner JB. The diagnosis of stupor and coma. Contemporary neurology series. 1972:10():1-286
[PubMed PMID: 4664014]
[4]
Stevens RD, Shoykhet M, Cadena R. Emergency Neurological Life Support: Intracranial Hypertension and Herniation. Neurocritical care. 2015 Dec:23 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S76-82. doi: 10.1007/s12028-015-0168-z. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 26438459]
[5]
Duffy GP. Lumbar puncture in the presence of raised intracranial pressure. British medical journal. 1969 Feb 15:1(5641):407-9
[PubMed PMID: 5763958]
[6]
KOREIN J, CRAVIOTO H, LEICACH M. Reevaluation of lumbar puncture; a study of 129 patients with papilledema or intracranial hypertension. Neurology. 1959 Apr:9(4):290-7
[PubMed PMID: 13644562]
[7]
Dewan MC, Rattani A, Gupta S, Baticulon RE, Hung YC, Punchak M, Agrawal A, Adeleye AO, Shrime MG, Rubiano AM, Rosenfeld JV, Park KB. Estimating the global incidence of traumatic brain injury. Journal of neurosurgery. 2018 Apr 27:130(4):1080-1097. doi: 10.3171/2017.10.JNS17352. Epub 2018 Apr 27
[PubMed PMID: 29701556]
[8]
Mokri B. The Monro-Kellie hypothesis: applications in CSF volume depletion. Neurology. 2001 Jun 26:56(12):1746-8
[PubMed PMID: 11425944]
[9]
Smith M. Cerebral perfusion pressure. British journal of anaesthesia. 2015 Oct:115(4):488-90. doi: 10.1093/bja/aev230. Epub 2015 Jul 18
[PubMed PMID: 26188341]
[10]
Wan WH, Ang BT, Wang E. The Cushing Response: a case for a review of its role as a physiological reflex. Journal of clinical neuroscience : official journal of the Neurosurgical Society of Australasia. 2008 Mar:15(3):223-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2007.05.025. Epub 2008 Jan 7
[PubMed PMID: 18182296]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[11]
Grady PA, Blaumanis OR. Physiologic parameters of the Cushing reflex. Surgical neurology. 1988 Jun:29(6):454-61
[PubMed PMID: 3375974]
[12]
Tsai YH, Lin JY, Huang YY, Wong JM. Cushing response-based warning system for intensive care of brain-injured patients. Clinical neurophysiology : official journal of the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. 2018 Dec:129(12):2602-2612. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2018.09.010. Epub 2018 Sep 21
[PubMed PMID: 30453271]
[14]
Lau EO, Lo CY, Yao Y, Mak AF, Jiang L, Huang Y, Yao X. Aortic Baroreceptors Display Higher Mechanosensitivity than Carotid Baroreceptors. Frontiers in physiology. 2016:7():384. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00384. Epub 2016 Aug 31
[PubMed PMID: 27630578]
[15]
Schmidt EA, Despas F, Pavy-Le Traon A, Czosnyka Z, Pickard JD, Rahmouni K, Pathak A, Senard JM. Intracranial Pressure Is a Determinant of Sympathetic Activity. Frontiers in physiology. 2018:9():11. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00011. Epub 2018 Feb 8
[PubMed PMID: 29472865]
[16]
Price DJ. Is diagnostic severity grading for head injuries possible? Acta neurochirurgica. Supplementum. 1986:36():67-9
[PubMed PMID: 3467566]
[17]
Laine FJ, Shedden AI, Dunn MM, Ghatak NR. Acquired intracranial herniations: MR imaging findings. AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 1995 Oct:165(4):967-73
[PubMed PMID: 7677003]
[18]
. The Brain Trauma Foundation. The American Association of Neurological Surgeons. The Joint Section on Neurotrauma and Critical Care. Initial management. Journal of neurotrauma. 2000 Jun-Jul:17(6-7):463-9
[PubMed PMID: 10937888]
[19]
Chesnut RM, Marshall LF, Klauber MR, Blunt BA, Baldwin N, Eisenberg HM, Jane JA, Marmarou A, Foulkes MA. The role of secondary brain injury in determining outcome from severe head injury. The Journal of trauma. 1993 Feb:34(2):216-22
[PubMed PMID: 8459458]
[20]
Bullock R, Chesnut RM, Clifton G, Ghajar J, Marion DW, Narayan RK, Newell DW, Pitts LH, Rosner MJ, Wilberger JW. Guidelines for the management of severe head injury. Brain Trauma Foundation. European journal of emergency medicine : official journal of the European Society for Emergency Medicine. 1996 Jun:3(2):109-27
[PubMed PMID: 9028756]
[21]
. The Brain Trauma Foundation. The American Association of Neurological Surgeons. The Joint Section on Neurotrauma and Critical Care. Hyperventilation. Journal of neurotrauma. 2000 Jun-Jul:17(6-7):513-20
[PubMed PMID: 10937894]
[22]
Carney N,Totten AM,O'Reilly C,Ullman JS,Hawryluk GW,Bell MJ,Bratton SL,Chesnut R,Harris OA,Kissoon N,Rubiano AM,Shutter L,Tasker RC,Vavilala MS,Wilberger J,Wright DW,Ghajar J, Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Fourth Edition. Neurosurgery. 2017 Jan 1
[PubMed PMID: 27654000]
[23]
Godoy DA, Seifi A, Garza D, Lubillo-Montenegro S, Murillo-Cabezas F. Hyperventilation Therapy for Control of Posttraumatic Intracranial Hypertension. Frontiers in neurology. 2017:8():250. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00250. Epub 2017 Jul 17
[PubMed PMID: 28769857]
[24]
Zhang Z, Guo Q, Wang E. Hyperventilation in neurological patients: from physiology to outcome evidence. Current opinion in anaesthesiology. 2019 Oct:32(5):568-573. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000764. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 31211719]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[25]
. The Brain Trauma Foundation. The American Association of Neurological Surgeons. The Joint Section on Neurotrauma and Critical Care. Resuscitation of blood pressure and oxygenation. Journal of neurotrauma. 2000 Jun-Jul:17(6-7):471-8
[PubMed PMID: 10937889]
[26]
Gu J, Huang H, Huang Y, Sun H, Xu H. Hypertonic saline or mannitol for treating elevated intracranial pressure in traumatic brain injury: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Neurosurgical review. 2019 Jun:42(2):499-509. doi: 10.1007/s10143-018-0991-8. Epub 2018 Jun 15
[PubMed PMID: 29905883]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[27]
Miller JD, Becker DP, Ward JD, Sullivan HG, Adams WE, Rosner MJ. Significance of intracranial hypertension in severe head injury. Journal of neurosurgery. 1977 Oct:47(4):503-16
[PubMed PMID: 903804]
[28]
Miller JD, Butterworth JF, Gudeman SK, Faulkner JE, Choi SC, Selhorst JB, Harbison JW, Lutz HA, Young HF, Becker DP. Further experience in the management of severe head injury. Journal of neurosurgery. 1981 Mar:54(3):289-99
[PubMed PMID: 7463128]
[29]
Weinberg JS, Rhines LD, Cohen ZR, Langford L, Levin VA. Posterior fossa decompression for life-threatening tonsillar herniation in patients with gliomatosis cerebri: report of three cases. Neurosurgery. 2003 Jan:52(1):216-23; discussion 223
[PubMed PMID: 12493121]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[30]
Bullock MR, Chesnut R, Ghajar J, Gordon D, Hartl R, Newell DW, Servadei F, Walters BC, Wilberger J, Surgical Management of Traumatic Brain Injury Author Group. Surgical management of traumatic parenchymal lesions. Neurosurgery. 2006 Mar:58(3 Suppl):S25-46; discussion Si-iv
[PubMed PMID: 16540746]
[31]
Cadena R, Shoykhet M, Ratcliff JJ. Emergency Neurological Life Support: Intracranial Hypertension and Herniation. Neurocritical care. 2017 Sep:27(Suppl 1):82-88. doi: 10.1007/s12028-017-0454-z. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 28913634]
[32]
. Trial of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic intracranial hypertension. Journal of the Intensive Care Society. 2017 Aug:18(3):236-238. doi: 10.1177/1751143716685246. Epub 2017 Jun 29
[PubMed PMID: 29118837]
[33]
Cooper DJ, Rosenfeld JV, Murray L, Arabi YM, Davies AR, D'Urso P, Kossmann T, Ponsford J, Seppelt I, Reilly P, Wolfe R, DECRA Trial Investigators, Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society Clinical Trials Group. Decompressive craniectomy in diffuse traumatic brain injury. The New England journal of medicine. 2011 Apr 21:364(16):1493-502. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1102077. Epub 2011 Mar 25
[PubMed PMID: 21434843]
[34]
Hutchinson PJ, Kolias AG, Timofeev IS, Corteen EA, Czosnyka M, Timothy J, Anderson I, Bulters DO, Belli A, Eynon CA, Wadley J, Mendelow AD, Mitchell PM, Wilson MH, Critchley G, Sahuquillo J, Unterberg A, Servadei F, Teasdale GM, Pickard JD, Menon DK, Murray GD, Kirkpatrick PJ, RESCUEicp Trial Collaborators. Trial of Decompressive Craniectomy for Traumatic Intracranial Hypertension. The New England journal of medicine. 2016 Sep 22:375(12):1119-30. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1605215. Epub 2016 Sep 7
[PubMed PMID: 27602507]
[39]
Shoung HM, Sichez JP, Pertuiset B. The early prognosis of craniocerebral gunshot wounds in civilian practice as an aid to the choice of treatment. A series of 56 cases studied by the computerized tomography. Acta neurochirurgica. 1985:74(1-2):27-30
[PubMed PMID: 3976441]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[40]
Kline LB, Morawetz RB, Swaid SN. Indirect injury of the optic nerve. Neurosurgery. 1984 Jun:14(6):756-64
[PubMed PMID: 6462414]
[42]
Robinson DL. Head injuries and bicycle helmet laws. Accident; analysis and prevention. 1996 Jul:28(4):463-75
[PubMed PMID: 8870773]