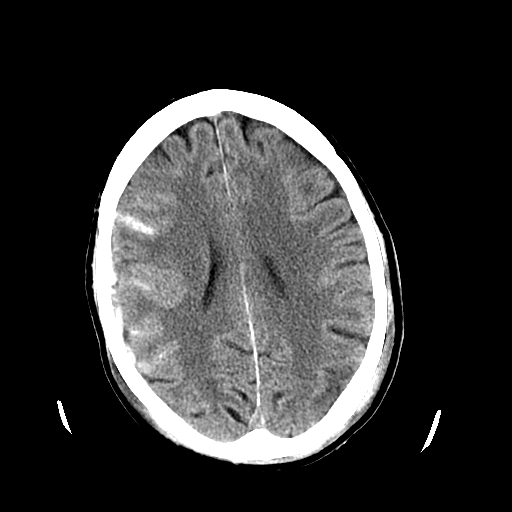
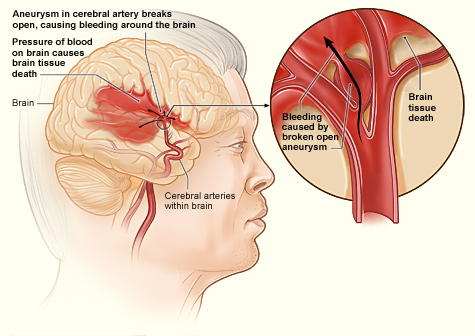
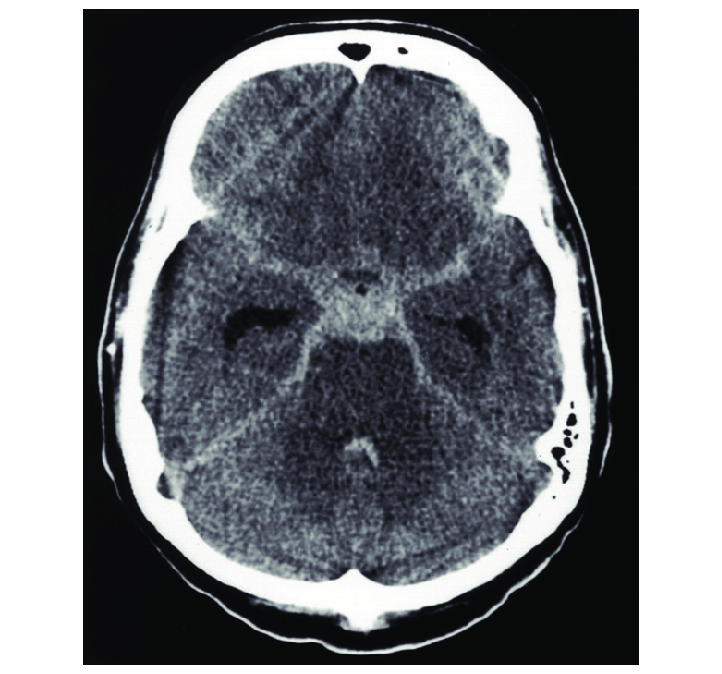
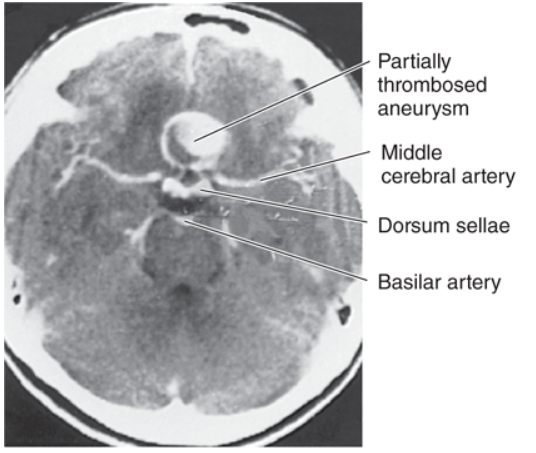
[1]
de Rooij NK, Linn FH, van der Plas JA, Algra A, Rinkel GJ. Incidence of subarachnoid haemorrhage: a systematic review with emphasis on region, age, gender and time trends. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry. 2007 Dec:78(12):1365-72
[PubMed PMID: 17470467]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[2]
Ikawa F,Michihata N,Matsushige T,Abiko M,Ishii D,Oshita J,Okazaki T,Sakamoto S,Kurogi R,Iihara K,Nishimura K,Morita A,Fushimi K,Yasunaga H,Kurisu K, In-hospital mortality and poor outcome after surgical clipping and endovascular coiling for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage using nationwide databases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurgical review. 2019 Apr 2;
[PubMed PMID: 30941595]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[3]
Schwartz TH,Solomon RA, Perimesencephalic nonaneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 1996 Sep
[PubMed PMID: 8875472]
[4]
Initial misdiagnosis and outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage., Kowalski RG,Claassen J,Kreiter KT,Bates JE,Ostapkovich ND,Connolly ES,Mayer SA,, JAMA, 2004 Feb 18
[PubMed PMID: 14970066]
[5]
Gallas S,Tuilier T,Ebrahiminia V,Bartoluci P,Hodel J,Gaston A, Intracranial aneurysms in Sickle Cell Disease: Aneurysms characteristics and modalities of endovascular approach to treat these patients. Journal of neuroradiology. Journal de neuroradiologie. 2019 Mar 20;
[PubMed PMID: 30904450]
[6]
Vlak MH,Rinkel GJ,Greebe P,van der Bom JG,Algra A, Trigger factors for rupture of intracranial aneurysms in relation to patient and aneurysm characteristics. Journal of neurology. 2012 Jul
[PubMed PMID: 22186848]
[7]
Rinkel GJ,Wijdicks EF,Vermeulen M,Ramos LM,Tanghe HL,Hasan D,Meiners LC,van Gijn J, Nonaneurysmal perimesencephalic subarachnoid hemorrhage: CT and MR patterns that differ from aneurysmal rupture. AJNR. American journal of neuroradiology. 1991 Sep-Oct;
[PubMed PMID: 1950905]
[8]
Canhão P,Ferro JM,Pinto AN,Melo TP,Campos JG, Perimesencephalic and nonperimesencephalic subarachnoid haemorrhages with negative angiograms. Acta neurochirurgica. 1995;
[PubMed PMID: 7754850]
[9]
Tatter SB,Crowell RM,Ogilvy CS, Aneurysmal and microaneurysmal "angiogram-negative" subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 1995 Jul
[PubMed PMID: 8587690]
[10]
Jung JY,Kim YB,Lee JW,Huh SK,Lee KC, Spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage with negative initial angiography: a review of 143 cases. Journal of clinical neuroscience : official journal of the Neurosurgical Society of Australasia. 2006 Dec
[PubMed PMID: 16931020]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[11]
Rinkel GJ,van Gijn J,Wijdicks EF, Subarachnoid hemorrhage without detectable aneurysm. A review of the causes. Stroke. 1993 Sep
[PubMed PMID: 8362440]
[12]
Cordonnier C,Al-Shahi Salman R,Bhattacharya JJ,Counsell CE,Papanastassiou V,Ritchie V,Roberts RC,Sellar RJ,Warlow C,SIVMS Collaborators., Differences between intracranial vascular malformation types in the characteristics of their presenting haemorrhages: prospective, population-based study. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry. 2008 Jan;
[PubMed PMID: 17488785]
[13]
Koch C, Spinal dural arteriovenous fistula. Current opinion in neurology. 2006 Feb
[PubMed PMID: 16415680]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[14]
Caplan LR. Dissections of brain-supplying arteries. Nature clinical practice. Neurology. 2008 Jan:4(1):34-42. doi: 10.1038/ncpneuro0683. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 18199995]
[15]
Santos-Franco JA,Zenteno M,Lee A, Dissecting aneurysms of the vertebrobasilar system. A comprehensive review on natural history and treatment options. Neurosurgical review. 2008 Apr
[PubMed PMID: 18309525]
[16]
Nolte KB,Brass LM,Fletterick CF, Intracranial hemorrhage associated with cocaine abuse: a prospective autopsy study. Neurology. 1996 May;
[PubMed PMID: 8628469]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[17]
Karabatsou K,Lecky BR,Rainov NG,Broome JC,White RP, Cerebral amyloid angiopathy with symptomatic or occult subarachnoid haemorrhage. European neurology. 2007
[PubMed PMID: 17179713]
[18]
Beitzke M,Gattringer T,Enzinger C,Wagner G,Niederkorn K,Fazekas F, Clinical presentation, etiology, and long-term prognosis in patients with nontraumatic convexal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2011 Nov
[PubMed PMID: 21921284]
[19]
Marcolini E,Hine J, Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. The western journal of emergency medicine. 2019 Mar;
[PubMed PMID: 30881537]
[20]
Kuroda H,Mochizuki T,Shimizu S,Kumabe T, Rupture of Thrombosed Cerebral Aneurysm During Antithrombotic Therapy for Ischemic Stroke: Case Report and Literature Review. World neurosurgery. 2019 Mar 18;
[PubMed PMID: 30898732]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[21]
Etminan N, Chang HS, Hackenberg K, de Rooij NK, Vergouwen MDI, Rinkel GJE, Algra A. Worldwide Incidence of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage According to Region, Time Period, Blood Pressure, and Smoking Prevalence in the Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA neurology. 2019 May 1:76(5):588-597. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.0006. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 30659573]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[22]
Shea AM, Reed SD, Curtis LH, Alexander MJ, Villani JJ, Schulman KA. Characteristics of nontraumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage in the United States in 2003. Neurosurgery. 2007 Dec:61(6):1131-7; discussion 1137-8
[PubMed PMID: 18162891]
[23]
Rinkel GJ,Djibuti M,Algra A,van Gijn J, Prevalence and risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review. Stroke. 1998 Jan;
[PubMed PMID: 9445359]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[24]
Chalouhi N, Ali MS, Jabbour PM, Tjoumakaris SI, Gonzalez LF, Rosenwasser RH, Koch WJ, Dumont AS. Biology of intracranial aneurysms: role of inflammation. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 2012 Sep:32(9):1659-76. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.84. Epub 2012 Jul 11
[PubMed PMID: 22781330]
[26]
Penn DL,Komotar RJ,Sander Connolly E, Hemodynamic mechanisms underlying cerebral aneurysm pathogenesis. Journal of clinical neuroscience : official journal of the Neurosurgical Society of Australasia. 2011 Nov
[PubMed PMID: 21917457]
[28]
Green DM,Burns JD,DeFusco CM, ICU management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of intensive care medicine. 2013 Nov-Dec
[PubMed PMID: 22328599]
[30]
Vermeulen M,van Gijn J, The diagnosis of subarachnoid haemorrhage. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry. 1990 May;
[PubMed PMID: 2191083]
[31]
Edlow JA, Managing Patients With Nontraumatic, Severe, Rapid-Onset Headache. Annals of emergency medicine. 2018 Mar
[PubMed PMID: 28601276]
[32]
Kumar A,Niknam K,Lumba-Brown A,Woodruff M,Bledsoe JR,Kohn MA,Perry JJ,Govindarajan P, Practice Variation in the Diagnosis of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Survey of US and Canadian Emergency Medicine Physicians. Neurocritical care. 2019 Feb 21;
[PubMed PMID: 30790225]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[33]
Li K,Barras CD,Chandra RV,Kok HK,Maingard JT,Carter NS,Russell JH,Lai L,Brooks M,Asadi H, A review on the management of cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. World neurosurgery. 2019 Mar 18;
[PubMed PMID: 30898740]
[34]
Dodson V,Majmundar N,El-Ghanem M,Amuluru K,Gupta G,Nuoman R,Wainwright J,Kaur G,Cole C,Santarelli J,Chandy D,Bowers C,Gandhi C,Al-Mufti F, Intracranial Administration of Nicardipine After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Review of the Literature. World neurosurgery. 2019 Jan 29;
[PubMed PMID: 30708083]
[35]
Chen S, Luo J, Reis C, Manaenko A, Zhang J. Hydrocephalus after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. BioMed research international. 2017:2017():8584753. doi: 10.1155/2017/8584753. Epub 2017 Mar 8
[PubMed PMID: 28373987]
[36]
Bederson JB, Connolly ES Jr, Batjer HH, Dacey RG, Dion JE, Diringer MN, Duldner JE Jr, Harbaugh RE, Patel AB, Rosenwasser RH, American Heart Association. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Stroke. 2009 Mar:40(3):994-1025. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.191395. Epub 2009 Jan 22
[PubMed PMID: 19164800]
[37]
Dodd WS,Laurent D,Dumont AS,Hasan DM,Jabbour PM,Starke RM,Hosaka K,Polifka AJ,Hoh BL,Chalouhi N, Pathophysiology of Delayed Cerebral Ischemia After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Review. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2021 Aug 3
[PubMed PMID: 34325514]
[38]
Djelilovic-Vranic J,Basic-Kes V,Tiric-Campara M,Djozic E,Kulenovic J, Follow-up of Vasospasm by Transcranial Doppler Sonography (TCD) in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH). Acta informatica medica : AIM : journal of the Society for Medical Informatics of Bosnia
[PubMed PMID: 28484291]
[39]
Connolly ES Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, Derdeyn CP, Dion J, Higashida RT, Hoh BL, Kirkness CJ, Naidech AM, Ogilvy CS, Patel AB, Thompson BG, Vespa P, American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention, Council on Cardiovascular Nursing, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, Council on Clinical Cardiology. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american Stroke Association. Stroke. 2012 Jun:43(6):1711-37. doi: 10.1161/STR.0b013e3182587839. Epub 2012 May 3
[PubMed PMID: 22556195]
[40]
Diringer MN, Bleck TP, Claude Hemphill J 3rd, Menon D, Shutter L, Vespa P, Bruder N, Connolly ES Jr, Citerio G, Gress D, Hänggi D, Hoh BL, Lanzino G, Le Roux P, Rabinstein A, Schmutzhard E, Stocchetti N, Suarez JI, Treggiari M, Tseng MY, Vergouwen MD, Wolf S, Zipfel G, Neurocritical Care Society. Critical care management of patients following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: recommendations from the Neurocritical Care Society's Multidisciplinary Consensus Conference. Neurocritical care. 2011 Sep:15(2):211-40. doi: 10.1007/s12028-011-9605-9. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 21773873]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[41]
Krejza J,Kochanowicz J,Mariak Z,Lewko J,Melhem ER, Middle cerebral artery spasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: detection with transcranial color-coded duplex US. Radiology. 2005 Aug
[PubMed PMID: 16040918]
[42]
van der Schaaf I,Wermer MJ,van der Graaf Y,Velthuis BK,van de Kraats CI,Rinkel GJ, Prognostic value of cerebral perfusion-computed tomography in the acute stage after subarachnoid hemorrhage for the development of delayed cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2006 Feb
[PubMed PMID: 16373646]
[43]
van der Schaaf I,Wermer MJ,van der Graaf Y,Hoff RG,Rinkel GJ,Velthuis BK, CT after subarachnoid hemorrhage: relation of cerebral perfusion to delayed cerebral ischemia. Neurology. 2006 May 23;
[PubMed PMID: 16717213]
[44]
Vatter H,Güresir E,Berkefeld J,Beck J,Raabe A,du Mesnil de Rochemont R,Seifert V,Weidauer S, Perfusion-diffusion mismatch in MRI to indicate endovascular treatment of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry. 2011 Aug;
[PubMed PMID: 21436228]
[45]
Suarez JI. Diagnosis and Management of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Continuum (Minneapolis, Minn.). 2015 Oct:21(5 Neurocritical Care):1263-87. doi: 10.1212/CON.0000000000000217. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 26426230]
[46]
Francoeur CL,Mayer SA, Management of delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Critical care (London, England). 2016 Oct 14
[PubMed PMID: 27737684]
[47]
Hellingman CA,van den Bergh WM,Beijer IS,van Dijk GW,Algra A,van Gijn J,Rinkel GJ, Risk of rebleeding after treatment of acute hydrocephalus in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2007 Jan
[PubMed PMID: 17122426]
[48]
Tang C,Zhang TS,Zhou LF, Risk factors for rebleeding of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a meta-analysis. PloS one. 2014
[PubMed PMID: 24911172]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[51]
Bath PM,Song L,Silva GS,Mistry E,Petersen N,Tsivgoulis G,Mazighi M,Bang OY,Sandset EC, Blood Pressure Management for Ischemic Stroke in the First 24 Hours. Stroke. 2022 Apr
[PubMed PMID: 35291822]
[52]
Osgood ML, Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Review of the Pathophysiology and Management Strategies. Current neurology and neuroscience reports. 2021 Jul 26;
[PubMed PMID: 34308493]
[53]
MacCarthy EP,Bloomfield SS, Labetalol: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, clinical uses and adverse effects. Pharmacotherapy. 1983 Jul-Aug
[PubMed PMID: 6310529]
[54]
Huang RQ,Jiang FG,Feng ZM,Wang TY, Nicardipine in the treatment of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: a meta-analysis of published data. Acta neurologica Belgica. 2013 Mar
[PubMed PMID: 23111775]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[55]
Varelas PN,Abdelhak T,Corry JJ,James E,Rehman MF,Schultz L,Mays-Wilson K,Mitsias P, Clevidipine for acute hypertension in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: a pilot study. The International journal of neuroscience. 2014 Mar;
[PubMed PMID: 24007334]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[56]
Dorhout Mees SM,Rinkel GJ,Feigin VL,Algra A,van den Bergh WM,Vermeulen M,van Gijn J, Calcium antagonists for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2007 Jul 18
[PubMed PMID: 17636626]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[57]
Pickard JD, Murray GD, Illingworth R, Shaw MD, Teasdale GM, Foy PM, Humphrey PR, Lang DA, Nelson R, Richards P. Effect of oral nimodipine on cerebral infarction and outcome after subarachnoid haemorrhage: British aneurysm nimodipine trial. BMJ (Clinical research ed.). 1989 Mar 11:298(6674):636-42
[PubMed PMID: 2496789]
[58]
Petruk KC,West M,Mohr G,Weir BK,Benoit BG,Gentili F,Disney LB,Khan MI,Grace M,Holness RO, Nimodipine treatment in poor-grade aneurysm patients. Results of a multicenter double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Journal of neurosurgery. 1988 Apr
[PubMed PMID: 3280746]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[59]
Carlson AP, Hänggi D, Wong GK, Etminan N, Mayer SA, Aldrich F, Diringer MN, Schmutzhard E, Faleck HJ, Ng D, Saville BR, Bleck T, Grubb R Jr, Miller M, Suarez JI, Proskin HM, Macdonald RL, NEWTON Investigators. Single-Dose Intraventricular Nimodipine Microparticles Versus Oral Nimodipine for Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Stroke. 2020 Apr:51(4):1142-1149. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.027396. Epub 2020 Mar 6
[PubMed PMID: 32138631]
[60]
Dorhout Mees SM,Algra A,Vandertop WP,van Kooten F,Kuijsten HA,Boiten J,van Oostenbrugge RJ,Al-Shahi Salman R,Lavados PM,Rinkel GJ,van den Bergh WM,MASH-2 Study Group., Magnesium for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (MASH-2): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (London, England). 2012 Jul 7;
[PubMed PMID: 22633825]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[61]
Dorhout Mees SM,Algra A,Wong GK,Poon WS,Bradford CM,Saver JL,Starkman S,Rinkel GJ,van den Bergh WM,writing groups of MASH-I, IMASH, MASH-II, MASH and FAST-MAG.,van Kooten F,Dirven CM,van Gijn J,Vermeulen M,Rinkel GJ,Boet R,Chan MT,Gin T,Ng SC,Zee BC,Al-Shahi Salman R,Boiten J,Kuijsten H,Lavados PM,van Oostenbrugge RJ,Vandertop WP,Finfer S,O'Connor A,Yarad E,Firth R,McCallister R,Harrington T,Steinfort B,Faulder K,Assaad N,Morgan M,Starkman S,Eckstein M,Stratton SJ,Pratt FD,Hamilton S,Conwit R,Liebeskind DS,Sung G,Kramer I,Moreau G,Goldweber R,Sanossian N, Early Magnesium Treatment After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis. Stroke. 2015 Nov
[PubMed PMID: 26463689]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[62]
Rhoney DH,McAllen K,Liu-DeRyke X, Current and future treatment considerations in the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Journal of pharmacy practice. 2010 Oct;
[PubMed PMID: 21507846]
[63]
Kirkpatrick PJ,Turner CL,Smith C,Hutchinson PJ,Murray GD,STASH Collaborators., Simvastatin in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (STASH): a multicentre randomised phase 3 trial. The Lancet. Neurology. 2014 Jul
[PubMed PMID: 24837690]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[64]
Wong GK,Chan DY,Siu DY,Zee BC,Poon WS,Chan MT,Gin T,Leung M,HDS-SAH Investigators., High-dose simvastatin for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: multicenter randomized controlled double-blinded clinical trial. Stroke. 2015 Feb
[PubMed PMID: 25516195]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[65]
Liu J,Chen Q, Effect of statins treatment for patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies and randomized controlled trials. International journal of clinical and experimental medicine. 2015;
[PubMed PMID: 26221259]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[66]
Frontera JA, Lewin JJ 3rd, Rabinstein AA, Aisiku IP, Alexandrov AW, Cook AM, del Zoppo GJ, Kumar MA, Peerschke EI, Stiefel MF, Teitelbaum JS, Wartenberg KE, Zerfoss CL. Guideline for Reversal of Antithrombotics in Intracranial Hemorrhage: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the Neurocritical Care Society and Society of Critical Care Medicine. Neurocritical care. 2016 Feb:24(1):6-46. doi: 10.1007/s12028-015-0222-x. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 26714677]
[67]
Rinkel GJ,Prins NE,Algra A, Outcome of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in patients on anticoagulant treatment. Stroke. 1997 Jan;
[PubMed PMID: 8996479]
[68]
Xu T,Yu X,Ou S,Liu X,Yuan J,Chen Y, Efficacy and Safety of Very Early Mobilization in Patients with Acute Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Scientific reports. 2017 Jul 26
[PubMed PMID: 28747763]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[69]
Muehlschlegel S. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Continuum (Minneapolis, Minn.). 2018 Dec:24(6):1623-1657. doi: 10.1212/CON.0000000000000679. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 30516599]
[70]
Teasdale G, Murray G, Parker L, Jennett B. Adding up the Glasgow Coma Score. Acta neurochirurgica. Supplementum. 1979:28(1):13-6
[PubMed PMID: 290137]
[71]
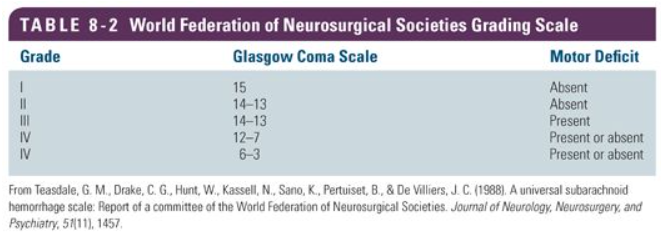
Teasdale GM, Drake CG, Hunt W, Kassell N, Sano K, Pertuiset B, De Villiers JC. A universal subarachnoid hemorrhage scale: report of a committee of the World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry. 1988 Nov:51(11):1457
[PubMed PMID: 3236024]
[72]
Surgical risk as related to time of intervention in the repair of intracranial aneurysms., Hunt WE,Hess RM,, Journal of neurosurgery, 1968 Jan
[PubMed PMID: 5635959]
[73]
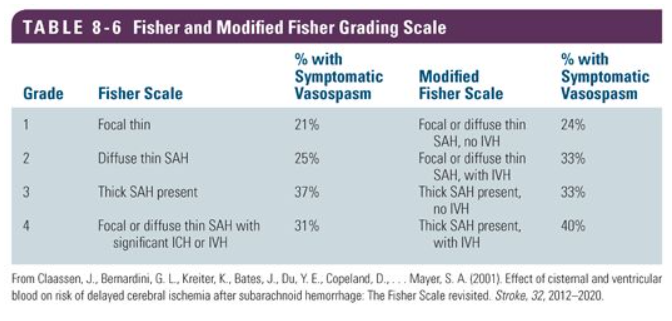
Claassen J, Bernardini GL, Kreiter K, Bates J, Du YE, Copeland D, Connolly ES, Mayer SA. Effect of cisternal and ventricular blood on risk of delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage: the Fisher scale revisited. Stroke. 2001 Sep:32(9):2012-20
[PubMed PMID: 11546890]
[75]
Lindbohm JV, Kaprio J, Jousilahti P, Salomaa V, Korja M. Risk Factors of Sudden Death From Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Stroke. 2017 Sep:48(9):2399-2404. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.018118. Epub 2017 Jul 24
[PubMed PMID: 28739833]
[76]
Schatlo B,Fung C,Stienen MN,Fathi AR,Fandino J,Smoll NR,Zumofen D,Daniel RT,Burkhardt JK,Bervini D,Marbacher S,Reinert M,D Alonzo D,Ahlborn P,Mendes Pereira V,Roethlisberger M,Seule M,Kerkeni H,Remonda L,Weyerbrock A,Woernle K,Venier A,Perren F,Sailer M,Robert T,Rohde V,Schöni D,Goldberg J,Nevzati E,Diepers M,Gralla J,Z'Graggen W,Starnoni D,Woernle C,Maldaner N,Kulcsar Z,Mostaguir K,Maduri R,Eisenring C,Bernays R,Ferrari A,Dan-Ura H,Finkenstädt S,Gasche Y,Sarrafzadeh A,Jakob SM,Corniola M,Baumann F,Regli L,Levivier M,Hildebrandt G,Landolt H,Mariani L,Guzman R,Beck J,Raabe A,Keller E,Bijlenga P,Schaller K, Incidence and Outcome of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: The Swiss Study on Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (Swiss SOS). Stroke. 2021 Jan;
[PubMed PMID: 33272133]
[78]
Pratt AK,Chang JJ,Sederstrom NO, A Fate Worse Than Death: Prognostication of Devastating Brain Injury. Critical care medicine. 2019 Apr;
[PubMed PMID: 30855326]
[79]
Zheng K,Zhong M,Zhao B,Chen SY,Tan XX,Li ZQ,Xiong Y,Duan CZ, Poor-Grade Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Risk Factors Affecting Clinical Outcomes in Intracranial Aneurysm Patients in a Multi-Center Study. Frontiers in neurology. 2019;
[PubMed PMID: 30873104]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence