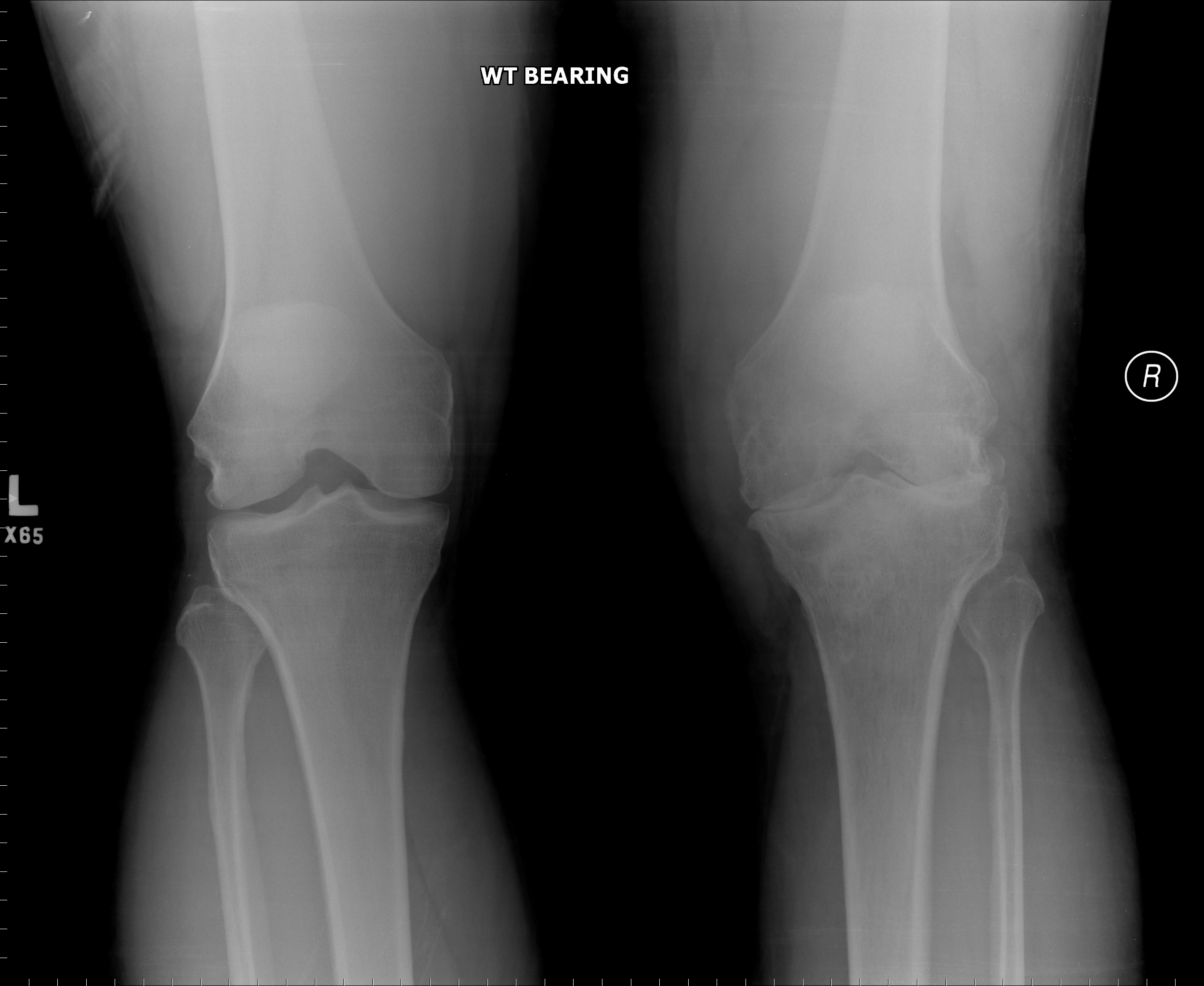
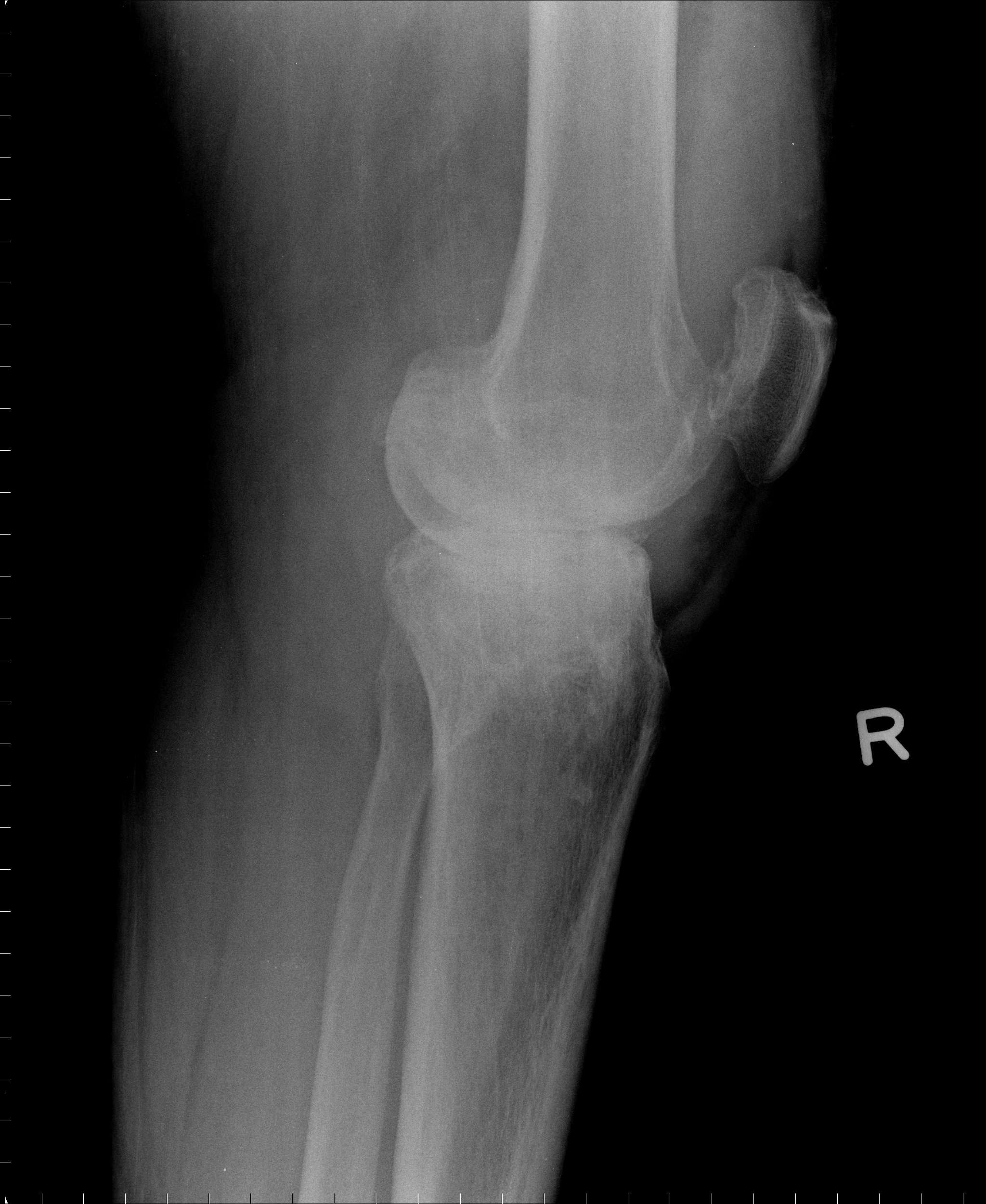
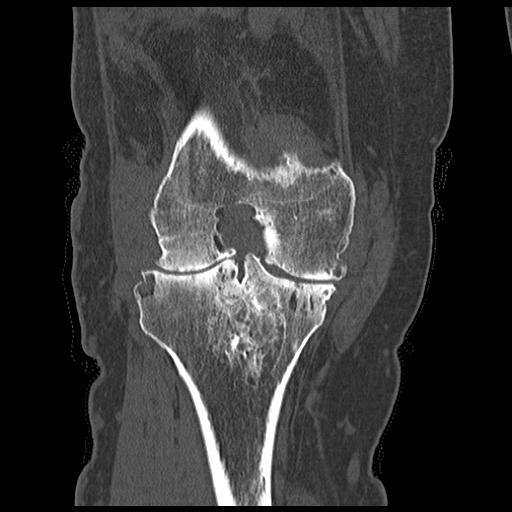
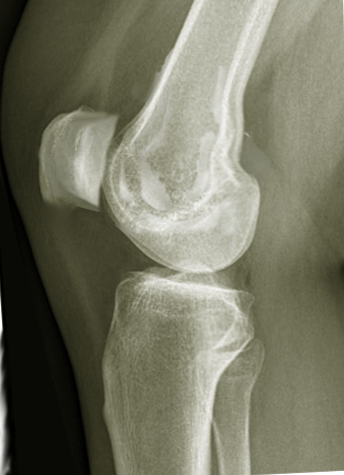
[1]
Burton TM, Ye X, Parker ED, Bancroft T, Healey J. Burden of Illness Associated with Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumors. Clinical therapeutics. 2018 Apr:40(4):593-602.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Mar 24
[PubMed PMID: 29580718]
[2]
Staals EL, Ferrari S, Donati DM, Palmerini E. Diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumour: Current treatment concepts and future perspectives. European journal of cancer (Oxford, England : 1990). 2016 Aug:63():34-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.04.022. Epub 2016 Jun 5
[PubMed PMID: 27267143]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[3]
West RB, Rubin BP, Miller MA, Subramanian S, Kaygusuz G, Montgomery K, Zhu S, Marinelli RJ, De Luca A, Downs-Kelly E, Goldblum JR, Corless CL, Brown PO, Gilks CB, Nielsen TO, Huntsman D, van de Rijn M. A landscape effect in tenosynovial giant-cell tumor from activation of CSF1 expression by a translocation in a minority of tumor cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2006 Jan 17:103(3):690-5
[PubMed PMID: 16407111]
[4]
Xie GP, Jiang N, Liang CX, Zeng JC, Chen ZY, Xu Q, Qi RZ, Chen YR, Yu B. Pigmented villonodular synovitis: a retrospective multicenter study of 237 cases. PloS one. 2015:10(3):e0121451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121451. Epub 2015 Mar 23
[PubMed PMID: 25799575]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[5]
Mastboom MJL, Verspoor FGM, Verschoor AJ, Uittenbogaard D, Nemeth B, Mastboom WJB, Bovée JVMG, Dijkstra PDS, Schreuder HWB, Gelderblom H, Van de Sande MAJ, TGCT study group. Higher incidence rates than previously known in tenosynovial giant cell tumors. Acta orthopaedica. 2017 Dec:88(6):688-694. doi: 10.1080/17453674.2017.1361126. Epub 2017 Aug 8
[PubMed PMID: 28787222]
[6]
Brahmi M, Vinceneux A, Cassier PA. Current Systemic Treatment Options for Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor/Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis: Targeting the CSF1/CSF1R Axis. Current treatment options in oncology. 2016 Feb:17(2):10. doi: 10.1007/s11864-015-0385-x. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 26820289]
[7]
Zhao L, Zhou K, Hua Y, Li Y, Mu D. Multifocal pigmented villonodular synovitis in a child: A case report. Medicine. 2016 Aug:95(33):e4572. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004572. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 27537585]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[8]
Frassica FJ, Bhimani MA, McCarthy EF, Wenz J. Pigmented villonodular synovitis of the hip and knee. American family physician. 1999 Oct 1:60(5):1404-10; discussion 1415
[PubMed PMID: 10524485]
[9]
Al Farii H, Zhou S, Turcotte R. The surgical outcome and recurrence rate of tenosynovial giant cell tumor in the elbow: a literature review. Journal of shoulder and elbow surgery. 2019 Sep:28(9):1835-1840. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2019.05.007. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 31447124]
[10]
Ramesh B, Shetty S, Bastawrous SS. Pigmented villonodular synovitis of the knee in a patient on oral anticoagulation therapy: a case report. Journal of medical case reports. 2009 Nov 13:3():121. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-3-121. Epub 2009 Nov 13
[PubMed PMID: 20062764]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[11]
Houdek MT, Scorianz M, Wyles CC, Trousdale RT, Sim FH, Taunton MJ. Long-term outcome of knee arthroplasty in the setting of pigmented villonodular synovitis. The Knee. 2017 Aug:24(4):851-855. doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2017.04.019. Epub 2017 May 25
[PubMed PMID: 28552192]
[12]
Willimon SC, Schrader T, Perkins CA. Arthroscopic Management of Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis of the Hip in Children and Adolescents. Orthopaedic journal of sports medicine. 2018 Mar:6(3):2325967118763118. doi: 10.1177/2325967118763118. Epub 2018 Mar 21
[PubMed PMID: 29594178]
[13]
Myers BW, Masi AT. Pigmented villonodular synovitis and tenosynovitis: a clinical epidemiologic study of 166 cases and literature review. Medicine. 1980 May:59(3):223-38
[PubMed PMID: 7412554]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[14]
Chang JS, Higgins JP, Kosy JD, Theodoropoulos J. Systematic Arthroscopic Treatment of Diffuse Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis in the Knee. Arthroscopy techniques. 2017 Oct:6(5):e1547-e1551. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2017.06.029. Epub 2017 Oct 12
[PubMed PMID: 29354472]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[15]
Yang B, Liu D, Lin J, Jin J, Weng XS, Qian WW, Qian J. Surgical treatment of diffuse pigmented villonodular synovitis of the knee. Zhongguo yi xue ke xue yuan xue bao. Acta Academiae Medicinae Sinicae. 2015 Apr:37(2):234-9. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2015.02.017. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 25936715]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[16]
Mollon B, Lee A, Busse JW, Griffin AM, Ferguson PC, Wunder JS, Theodoropoulos J. The effect of surgical synovectomy and radiotherapy on the rate of recurrence of pigmented villonodular synovitis of the knee: an individual patient meta-analysis. The bone & joint journal. 2015 Apr:97-B(4):550-7. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.97B4.34907. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 25820897]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[17]
Tap WD, Gelderblom H, Palmerini E, Desai J, Bauer S, Blay JY, Alcindor T, Ganjoo K, Martín-Broto J, Ryan CW, Thomas DM, Peterfy C, Healey JH, van de Sande M, Gelhorn HL, Shuster DE, Wang Q, Yver A, Hsu HH, Lin PS, Tong-Starksen S, Stacchiotti S, Wagner AJ, ENLIVEN investigators. Pexidartinib versus placebo for advanced tenosynovial giant cell tumour (ENLIVEN): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet (London, England). 2019 Aug 10:394(10197):478-487. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30764-0. Epub 2019 Jun 19
[PubMed PMID: 31229240]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[18]
Çevik HB, Kayahan S, Eceviz E, Gümüştaş SA. Tenosynovial giant cell tumor in the foot and ankle. Foot and ankle surgery : official journal of the European Society of Foot and Ankle Surgeons. 2020 Aug:26(6):712-716. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2019.08.014. Epub 2019 Sep 6
[PubMed PMID: 31526689]
[19]
Chen EL, de Castro CM 4th, Hendzel KD, Iwaz S, Kim MA, Valeshabad AK, Shokouh-Amiri M, Xie KL. Histologically benign metastasizing tenosynovial giant cell tumor mimicking metastatic malignancy: A case report and review of literature. Radiology case reports. 2019 Aug:14(8):934-940. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2019.05.013. Epub 2019 May 24
[PubMed PMID: 31193787]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[20]
Zwarenstein M, Goldman J, Reeves S. Interprofessional collaboration: effects of practice-based interventions on professional practice and healthcare outcomes. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2009 Jul 8:(3):CD000072. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000072.pub2. Epub 2009 Jul 8
[PubMed PMID: 19588316]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[21]
Cao V, Tan LD, Horn F, Bland D, Giri P, Maken K, Cho N, Scott L, Dinh VA, Hidalgo D, Nguyen HB. Patient-Centered Structured Interdisciplinary Bedside Rounds in the Medical ICU. Critical care medicine. 2018 Jan:46(1):85-92. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002807. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 29088002]
[22]
Arbuthnott A, Sharpe D. The effect of physician-patient collaboration on patient adherence in non-psychiatric medicine. Patient education and counseling. 2009 Oct:77(1):60-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2009.03.022. Epub 2009 Apr 22
[PubMed PMID: 19395222]