Introduction
The neuromuscular junction (NMJ) is a synaptic connection between the terminal end of a motor nerve and a muscle (skeletal/ smooth/ cardiac). It is the site for the transmission of action potential from nerve to the muscle. It is also a site for many diseases and a site of action for many pharmacological drugs.[1][2][3][4] In this article, the NMJ of skeletal muscle will be discussed.
Issues of Concern
Diseases of the NMJ produce muscle weakness through different mechanisms that may affect presynaptic, synaptic, or postsynaptic portions of the NMJ. Three main diseases that involve NMJ are Myasthenia Gravis (MG), Lambert-Eaton syndrome (LES), and Botulism.
Cellular Level
Physiological Anatomy of Neuromuscular Junction
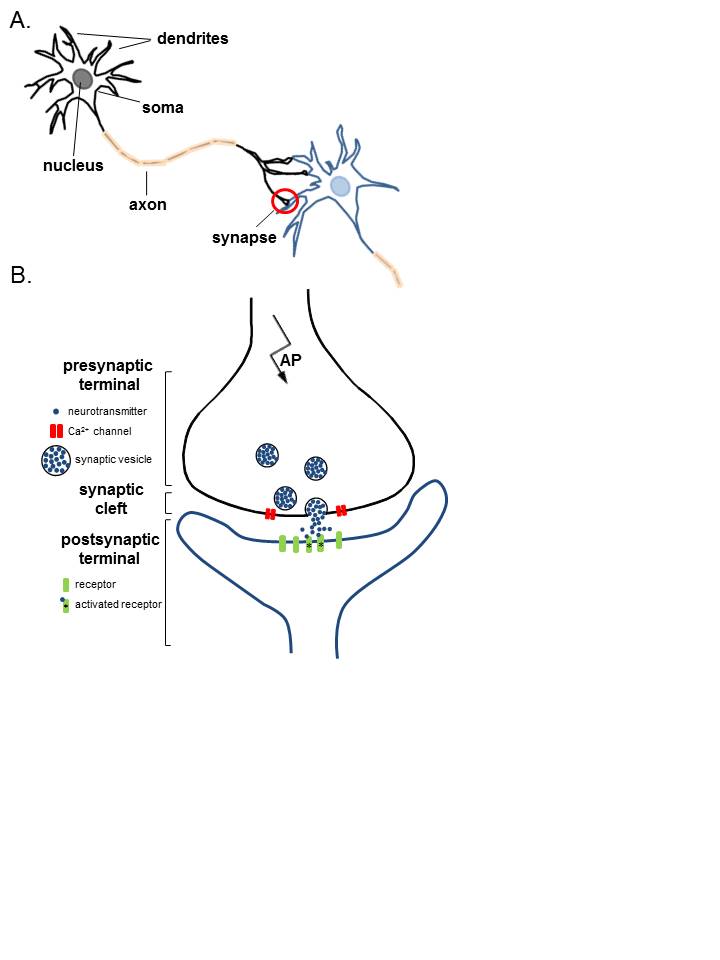
For convenience and understanding, the structure of NMJ can be divided into three main parts: a presynaptic part (nerve terminal), the postsynaptic part (motor endplate), and an area between the nerve terminal and motor endplate (synaptic cleft).
Nerve Terminal: A myelinated motor neuron, on reaching the target muscle, loses its myelin sheath to form a complex of 100-200 branching nerve endings. These nerve endings are called nerve terminals or terminal boutons. The nerve terminal membrane has areas of membrane thickening called active zones. Active zones have a family of SNAP proteins (syntaxins and synaptosomal-associated protein 25) and rows of voltage-gated calcium (Ca) channels. A nerve terminal also has potassium channels on its membrane and contains mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and synaptic vesicles (SVs). Each SV stores around 5000-10000 molecules of acetylcholine (ACh), the neurotransmitter at NMJ. The SVs are concentrated around the active zone. The membrane of SVs has synaptotagmin and synaptobrevin proteins. These proteins are essential for fusion and docking of SVs at active zones. On arrival of an action potential at the nerve terminal, Ca channels open to cause influx. Increased Ca inside the nerve terminal causes a series of events leading to docking of SVs at active zones and exocytosis of the ACh from the synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft.[2][3][2][4]
Synaptic Cleft / Junctional Cleft: The space between the nerve terminal and the plasma membrane of muscle is called synaptic/junctional cleft and measures ∼50 nm. It is the site where presynaptic neurotransmitters, ACh is released before it interacts with nicotinic ACh receptors on the motor endplate. Synaptic cleft of NMJ contains acetylcholinesterase enzyme, responsible for the catabolism of released ACh so that its effect on the post-synaptic receptors is not prolonged.[2][3][2][4]
Motor End Plate forms the postsynaptic part of NMJ. It is the thickened portion of the muscle plasma membrane (sarcolemma) that is folded to form depressions called junctional folds. The terminal nerve endings do not penetrate the motor endplate but fit into the junctional folds. Junctional folds have nicotinic ACh receptors concentrated at the top. These receptors are ACh gated ion channels. Binding of ACh to these receptors opens the channels allowing the influx of sodium ions from the extracellular fluid into the muscle membrane. This creates endplate potential and generates and transmits AP to the muscle membrane.[2][3][4]
Mechanism
ACh is synthesized in the pre-synaptic terminal using choline and acetyl-CoA and the enzyme choline acetyltransferase. It subsequently goes through a series of modifications before being packaged in vesicles. Upon depolarization, an action potential travels down the axon, causing voltage-gated calcium channels to open, resulting in an influx of calcium ions into the nerve terminal. This causes the vesicles to migrate towards the nerve terminal membrane and fuse with the active zones.
Different vesicular (SNAP-25, syntaxin) and nerve terminal membrane proteins (synaptobrevin and synaptotagmin) play a role in the fusion of SVs to active zones and exocytosis of ACh into the synaptic cleft. The released ACh subsequently binds to nicotinic ACh receptors on the junctional folds of the motor endplate. The binding of ACh to receptors triggers the opening of ACh gated ion channels that allow the influx of sodium ions into the muscle. The sodium influx changes the postsynaptic membrane potential from -90 mV to -45 mV. This decrease in membrane potential is called endplate potential. In the NMJ, endplate potential is strong enough to propagate action potential over the surface of the skeletal muscle membrane that ultimately results in muscle contraction. To prevent sustained depolarization and muscle contraction, as well as to allow for repolarization, ACh is metabolized by acetylcholinesterase into its subunits, choline, and acetate. Choline can then be re-used for the synthesis of ACh.[1][2]
Pathophysiology
Myasthenia Gravis is an auto-immune condition (type II hypersensitivity reaction), resulting in the production of auto-antibodies against ACh receptors, at the neuromuscular junction. The antibodies against ACh receptors decrease the availability of ACh receptors to endogenous ACh. This prevents endplate potential and muscle contraction. As a result, symptoms such as muscle weakness come as no surprise, especially in the extra-ocular muscle, as these muscles are in constant use and have a lower density of ACh receptors. Patients may also experience difficulty chewing and limb weakness. These symptoms worsen with use and progress throughout the day as the ACh in the pre-synaptic cleft gets depleted and insufficient to compete with the ACh receptor antibodies. MG is diagnosed by looking for the ACh receptor antibodies (80% to 90% sensitivity), or in cases where clinical suspicion is high but the ACh receptor antibodies are negative (seronegative MG), the anti-muscle specific kinase (MuSK) can help make the diagnosis.
Neurophysiological studies like supramaximal repetitive nerve stimulation (RNS) of the peripheral nerve at 3Hz and single nerve electromyography may also be used for diagnosis, but they are not specific for MG. However, a 10% decrement on RNS is considered consistent with MG. Approximately 10% of patients with autoimmune MG have a thymoma. Treatment in MG is directed at increasing the levels of ACh in the synaptic cleft using ACh esterase inhibitors which prevent the breakdown of ACh in the synaptic cleft and out-compete the antibodies. Examples of ACh esterase inhibitors include neostigmine or pyridostigmine, edrophonium, and physostigmine. Edrophonium is not used clinically for treating MG, because it is a very short-acting ACh esterase inhibitor, but it may be used to aid in the diagnosis of MG if the symptom of muscle and extra-ocular weakness abate upon administration. Physostigmine is also not used because it is a lipid-soluble tertiary amine that crosses the blood-brain barrier. Other medical management of MG includes the use of steroids (prednisone) and steroid-sparing agents (azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, tacrolimus, or mycophenolate). Rituximab, an anti-CD20 B cell monoclonal antibody may be used in refractory patients, especially with MuSK. Complications of MG include acute flare-ups of myasthenic crises wherein the patient develops acute muscle weakness and respiratory involvement. These patients are managed with IV immunoglobulins, which bind up the auto-antibodies, or plasmapheresis, which remove the autoantibodies from the blood. Patients with a respiratory crisis may also require ventilatory support.[3][4][5]
LES is an auto-immune condition caused by antibodies against voltage-gated calcium channels on the pre-synaptic membrane. This prevents Ca from entering the nerve terminal and triggering the fusion of ACh vesicles with the synaptic membrane. Therefore, it essentially prevents the release of ACh into the synaptic cleft and ultimately prevents muscle contraction. About 50% of LES patients have small cell lung carcinoma. Smoking markedly increases this risk. LES is subclassified into two main subgroups: LES with small cell lung carcinoma and LES with no small cell lung carcinoma. LES without small cell lung carcinoma is significantly associated with HLA-B8 (HLA- class I), and HLA -DR3 and -DQ2 (HLA-class II). These patients may have an increased incidence of other autoimmune disorders. LES with lung carcinoma has no relation to HLA. The symptoms of LES are similar to MG. However, in LES, proximal limb muscles are involved and tendon reflexes are depressed. The weakness improves with use. This is because, with repeated attempts at muscle contraction, a calcium gradient builds up outside the presynaptic Ca channel, which eventually allows the endogenous calcium to outcompete the auto-antibodies, and this triggers the release of ACh in the synaptic cleft. Eighty percent of LES patients complain of proximal muscle weakness in both arms and legs. Oropharyngeal and ocular muscles are mildly affected, so eyelid ptosis and mild diplopia may also be present. Autonomic symptoms such as dry mouth, constipation, impotence in males, and postural hypotension may be seen. The triad of proximal muscle weakness, depressed reflexes, and autonomic dysfunction help in making the diagnosis.
Similar to MG, LES can be diagnosed by looking for the antibodies. However, when LES is diagnosed, the more pressing issue is that it is a paraneoplastic syndrome and may be a sign of an underlying malignancy, most commonly small-cell lung cancer (50% to 70%). Treatment of LES includes addressing the underlying cause. Unfortunately, because it is associated with small-cell lung cancer, the cure is highly unlikely. For the symptomatic treatment guanidine, aminopyridines, or acetylcholinesterase inhibitors may be used. Amifampridine (3,4-diaminopyridine) is used to significantly improve muscle strength. Aminopyridines blocks the presynaptic voltage-gated potassium channels and thus extends the duration of the presynaptic action potential. Other therapies like plasma exchange may be used to deplete the serum autoantibodies. Immune suppression with steroids or steroid-sparing agents (azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil) or methotrexate may also be used.[3][4]
Botulism is a potentially fatal syndrome of diffuse, flaccid paralysis caused by Clostridium botulinum, an anaerobic gram-positive, spore-forming bacterium. Clostridium botulinum produces seven types of antigenically distinct neurotoxins, A through G. Botulinum toxins B, D, F, and G act on synaptobrevin, and botulinum toxin C acts on syntaxin. Botulinum toxins A and B act on SNAP-25. These toxins attack synaptobrevin, SNAP-25, and syntaxin proteins essential for docking and fusion of SVs to the active zones and thus the release of ACh into the synaptic cleft, resulting in reversible flaccid paralysis. Botulism can occur due to the ingestion of food contaminated with spores or toxins (home-canned food) of C.botulinum. It results in nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, diplopia, and descending flaccid paralysis. In severe cases, bulbar paralysis and respiratory failure may occur rapidly. In infants, botulism can occur due to the ingestion of honey contaminated with spores of C. botulinum. Toxins are produced within the GI tract of infants and infants present with constipation, weak feeding, weak crying, and flaccid paralysis. Botulism can also occur due to contamination of a wound with dust containing C. botulinum spores. History, clinical presentation, and the detection of botulinum toxin and the presence of C. botulinum spores in serum, stool, gastrointestinal content, or wound exudates form the basis of diagnosis. Treatment is done by administering antitoxin. Early administration of antitoxin decreases mortality and shortens the disease course. Patients may require prolonged periods of ventilation.[3][4][6][7]
Clinical Significance
Some of the pharmacology regarding the NMJ had been previously mentioned in the pathophysiology section. The rest will be covered here. There are some chemicals that cause irreversible inhibition of the ACh esterase, the enzyme responsible for degrading ACh into choline and acetic acid in the synaptic cleft. This results in the accumulation of ACh throughout the nervous system, resulting in overstimulation of muscarinic and nicotinic receptors. Irreversible inhibitors of ACh esterase include the They are commonly used as an insecticide, such as malathion and parathion. The effects of organophosphates are reversed using a competitive inhibitor such as atropine and/or pralidoxime, which regenerates ACh esterase if given early enough before enzyme aging occurs via hydrolysis of the R group.[8]
Others include the centrally acting type such as rivastigmine, galantamine, tacrine, and donepezil. These are used to treat Alzheimer dementia. Another pharmacologic significance involves the use of NMJ blockers to induce muscle paralysis in anesthesiology. Neuromuscular blockers can be categorized into depolarizing (succinylcholine) and non-depolarizing (tubocurarine, atracurium, mivacurium, pancuronium, vecuronium, rocuronium). Depolarizing agents work as an ACh receptor agonist at the NMJ and produce sustained depolarization that prevents repolarization of the motor endplate, resulting in ACh receptors becoming desensitized and inactivated. Non-depolarizing agents behave as competitive antagonists and compete with ACh for receptors. Also, non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents are the alternative when the patient is a slow metabolizer of pseudocholinesterase (the enzyme that degrades succinylcholine) or has a mutation in the ryanodine receptor, both of which prolong the action of succinylcholine and can lead to the deadly complication of malignant hyperthermia due to sustained muscle contraction.[9]
The direct agonist of ACh that directly binds to the ACh receptors includes bethanechol (which is used to treat post-operative ileus, urinary retention), carbachol, and pilocarpine (both used to treat glaucoma by constriction of the pupillary muscle), and methacholine (used for a challenge test to diagnose asthma in a patient who presents asymptomatically).[10] Lastly, botulinum toxin can be given medically to relieve sustained muscle contraction in cases of blepharospasm, dystonia, and achalasia.