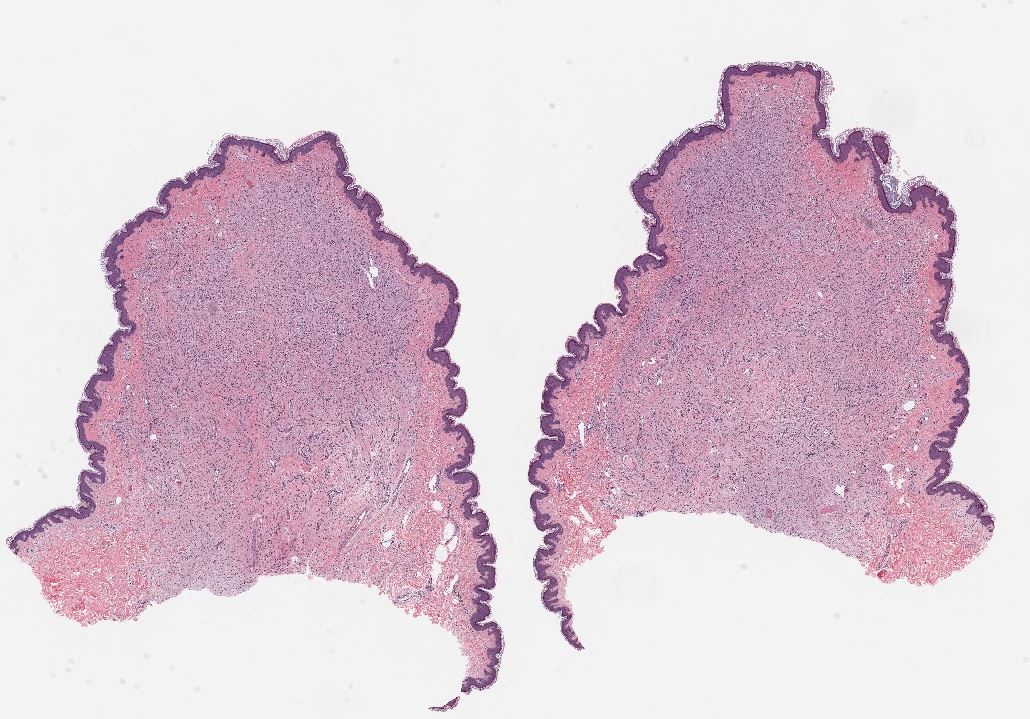
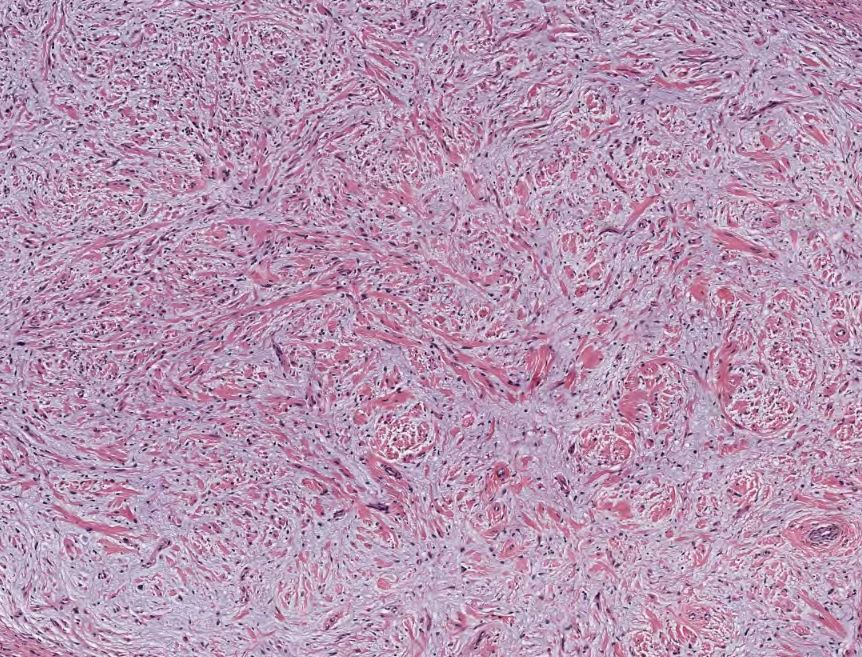
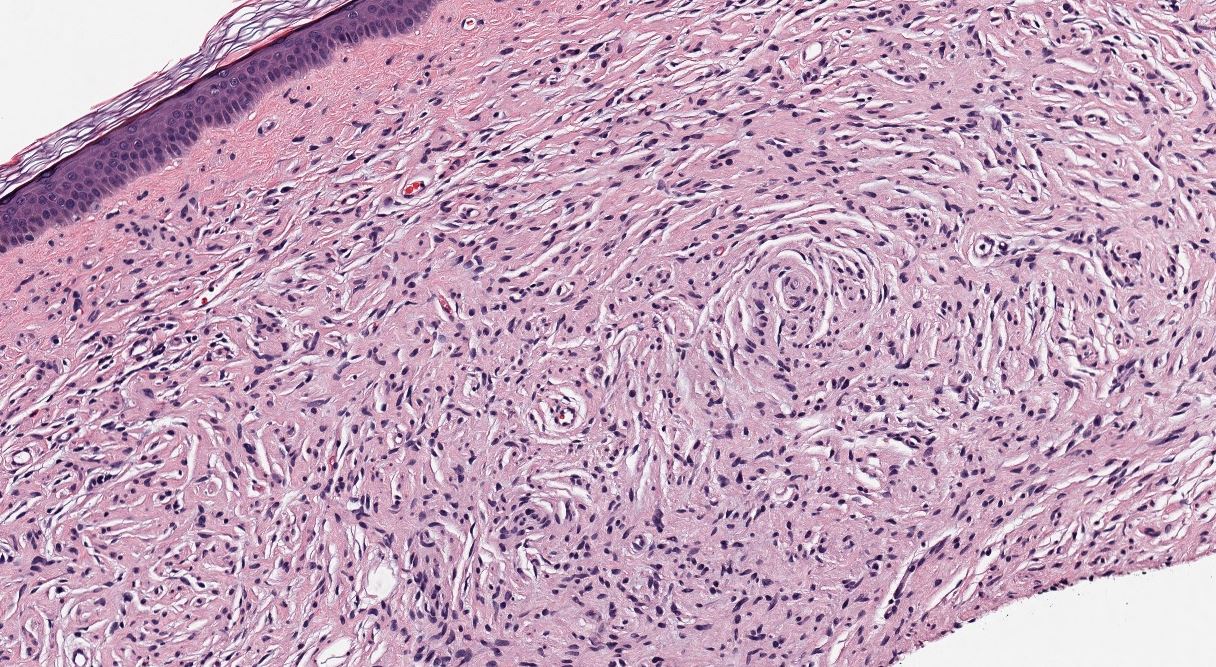
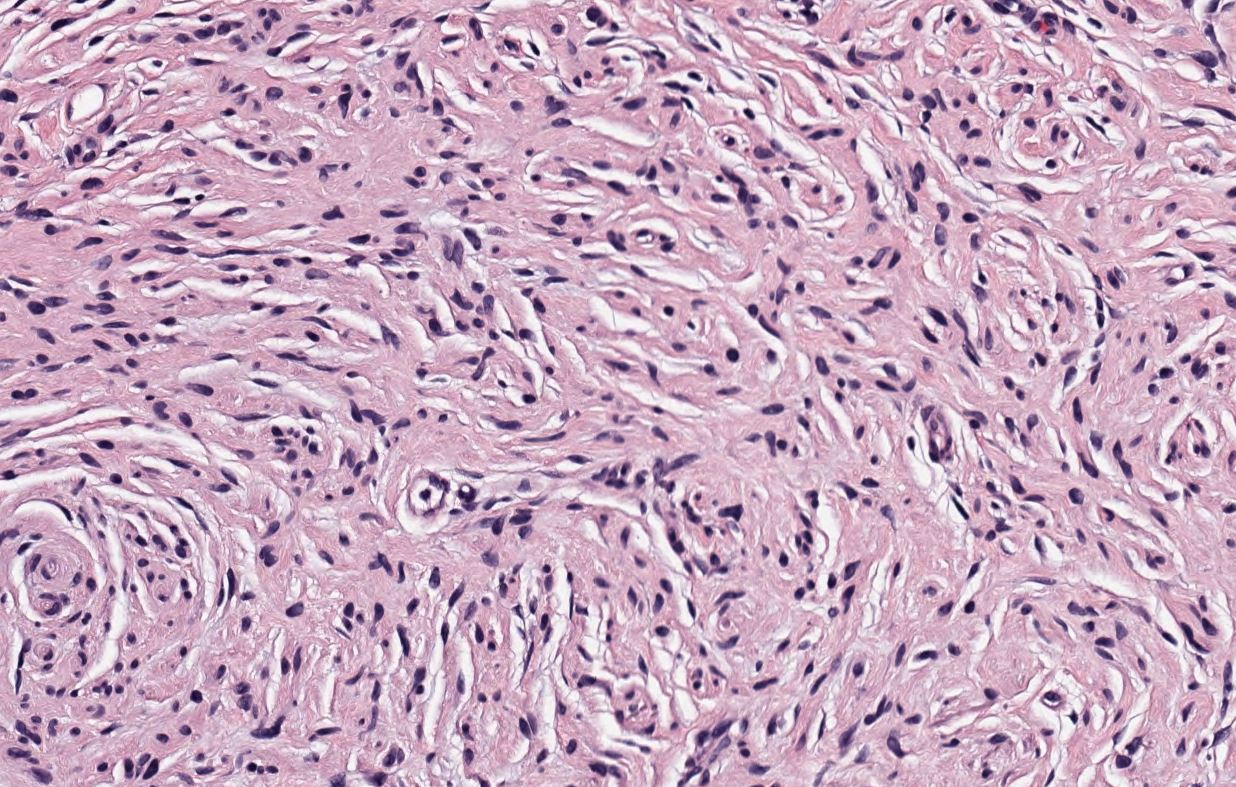
[1]
Ferner RE, O'Doherty MJ. Neurofibroma and schwannoma. Current opinion in neurology. 2002 Dec:15(6):679-84
[PubMed PMID: 12447105]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[2]
Lassmann H, Jurecka W, Lassmann G, Gebhart W, Matras H, Watzek G. Different types of benign nerve sheath tumors. Light microscopy, electron microscopy and autoradiography. Virchows Archiv. A, Pathological anatomy and histology. 1977 Sep 28:375(3):197-210
[PubMed PMID: 143775]
[3]
Skovronsky DM, Oberholtzer JC. Pathologic classification of peripheral nerve tumors. Neurosurgery clinics of North America. 2004 Apr:15(2):157-66
[PubMed PMID: 15177315]
[4]
Hernández-Martín A, Duat-Rodríguez A. An Update on Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Not Just Café-au-Lait Spots, Freckling, and Neurofibromas. An Update. Part I. Dermatological Clinical Criteria Diagnostic of the Disease. Actas dermo-sifiliograficas. 2016 Jul-Aug:107(6):454-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2016.01.004. Epub 2016 Mar 12
[PubMed PMID: 26979265]
[5]
Ferner RE, Gutmann DH. Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1): diagnosis and management. Handbook of clinical neurology. 2013:115():939-55. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-52902-2.00053-9. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 23931823]
[6]
Tucker T, Riccardi VM, Brown C, Fee J, Sutcliffe M, Vielkind J, Wechsler J, Wolkenstein P, Friedman JM. S100B and neurofibromin immunostaining and X-inactivation patterns of laser-microdissected cells indicate a multicellular origin of some NF1-associated neurofibromas. Journal of neuroscience research. 2011 Sep:89(9):1451-60. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22654. Epub 2011 Jun 14
[PubMed PMID: 21674567]
[7]
Woodruff JM. Pathology of tumors of the peripheral nerve sheath in type 1 neurofibromatosis. American journal of medical genetics. 1999 Mar 26:89(1):23-30
[PubMed PMID: 10469433]
[8]
Magro G, Amico P, Vecchio GM, Caltabiano R, Castaing M, Kacerovska D, Kazakov DV, Michal M. Multinucleated floret-like giant cells in sporadic and NF1-associated neurofibromas: a clinicopathologic study of 94 cases. Virchows Archiv : an international journal of pathology. 2010 Jan:456(1):71-6. doi: 10.1007/s00428-009-0859-y. Epub 2009 Nov 25
[PubMed PMID: 19937344]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[9]
Shiurba RA, Eng LF, Urich H. The structure of pseudomeissnerian corpuscles. An immunohistochemical study. Acta neuropathologica. 1984:63(2):174-6
[PubMed PMID: 6428156]
[10]
Tchernev G, Chokoeva AA, Patterson JW, Bakardzhiev I, Wollina U, Tana C. Plexiform Neurofibroma: A Case Report. Medicine. 2016 Feb:95(6):e2663. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002663. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 26871793]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[11]
Lin BT, Weiss LM, Medeiros LJ. Neurofibroma and cellular neurofibroma with atypia: a report of 14 tumors. The American journal of surgical pathology. 1997 Dec:21(12):1443-9
[PubMed PMID: 9414187]
[12]
Motoi T, Ishida T, Kawato A, Motoi N, Fukayama M. Pigmented neurofibroma: review of Japanese patients with an analysis of melanogenesis demonstrating coexpression of c-met protooncogene and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. Human pathology. 2005 Aug:36(8):871-7
[PubMed PMID: 16112003]
[13]
Jokinen CH, Argenyi ZB. Atypical neurofibroma of the skin and subcutaneous tissue: clinicopathologic analysis of 11 cases. Journal of cutaneous pathology. 2010 Jan:37(1):35-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01293.x. Epub 2009 Mar 25
[PubMed PMID: 19469864]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[14]
Laskin WB, Fetsch JF, Lasota J, Miettinen M. Benign epithelioid peripheral nerve sheath tumors of the soft tissues: clinicopathologic spectrum of 33 cases. The American journal of surgical pathology. 2005 Jan:29(1):39-51
[PubMed PMID: 15613855]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[15]
Finkel G, Lane B. Granular cell variant of neurofibromatosis: ultrastructure of benign and malignant tumors. Human pathology. 1982 Oct:13(10):959-63
[PubMed PMID: 6290371]
[16]
Val-Bernal JF, González-Vela MC. Cutaneous lipomatous neurofibroma: characterization and frequency. Journal of cutaneous pathology. 2005 Apr:32(4):274-9
[PubMed PMID: 15769276]
[17]
Michal M, Fanburg-Smith JC, Mentzel T, Kutzner H, Requena L, Zamecnik M, Miettinen M. Dendritic cell neurofibroma with pseudorosettes: a report of 18 cases of a distinct and hitherto unrecognized neurofibroma variant. The American journal of surgical pathology. 2001 May:25(5):587-94
[PubMed PMID: 11342769]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[18]
Harder A, Wesemann M, Hagel C, Schittenhelm J, Fischer S, Tatagiba M, Nagel C, Jeibmann A, Bohring A, Mautner VF, Paulus W. Hybrid neurofibroma/schwannoma is overrepresented among schwannomatosis and neurofibromatosis patients. The American journal of surgical pathology. 2012 May:36(5):702-9. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31824d3155. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 22446939]
[19]
Yeh I, McCalmont TH. Distinguishing neurofibroma from desmoplastic melanoma: the value of the CD34 fingerprint. Journal of cutaneous pathology. 2011 Aug:38(8):625-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2011.01700.x. Epub 2011 Apr 4
[PubMed PMID: 21457155]
[20]
Wolkenstein P, Zeller J, Revuz J, Ecosse E, Leplège A. Quality-of-life impairment in neurofibromatosis type 1: a cross-sectional study of 128 cases. Archives of dermatology. 2001 Nov:137(11):1421-5
[PubMed PMID: 11708944]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[21]
Staser K, Yang FC, Clapp DW. Pathogenesis of plexiform neurofibroma: tumor-stromal/hematopoietic interactions in tumor progression. Annual review of pathology. 2012:7():469-95. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011811-132441. Epub 2011 Nov 7
[PubMed PMID: 22077553]
[22]
Kumar BS, Gopal M, Talwar A, Ramesh M. Diffuse neurofibroma of the scalp presenting as circumscribed alopecic patch. International journal of trichology. 2010 Jan:2(1):60-2. doi: 10.4103/0974-7753.66919. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 21188030]
[23]
Raffensperger J, Cohen R. Plexiform neurofibromas in childhood. Journal of pediatric surgery. 1972 Apr:7(2):144-51
[PubMed PMID: 4623404]
[24]
Serletis D, Parkin P, Bouffet E, Shroff M, Drake JM, Rutka JT. Massive plexiform neurofibromas in childhood: natural history and management issues. Journal of neurosurgery. 2007 May:106(5 Suppl):363-7
[PubMed PMID: 17566202]
[25]
Allaway RJ, Gosline SJC, La Rosa S, Knight P, Bakker A, Guinney J, Le LQ. Cutaneous neurofibromas in the genomics era: current understanding and open questions. British journal of cancer. 2018 Jun:118(12):1539-1548. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0073-2. Epub 2018 Apr 26
[PubMed PMID: 29695767]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[26]
Kebudi R, Cakir FB, Gorgun O. Interferon-α for unresectable progressive and symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas. Journal of pediatric hematology/oncology. 2013 Apr:35(3):e115-7. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0b013e318270cd24. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 23042022]
[27]
Hornick JL. Limited biopsies of soft tissue tumors: the contemporary role of immunohistochemistry and molecular diagnostics. Modern pathology : an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc. 2019 Jan:32(Suppl 1):27-37. doi: 10.1038/s41379-018-0139-y. Epub 2019 Jan 2
[PubMed PMID: 30600320]
[28]
Jo VY, Fletcher CDM. SMARCB1/INI1 Loss in Epithelioid Schwannoma: A Clinicopathologic and Immunohistochemical Study of 65 Cases. The American journal of surgical pathology. 2017 Aug:41(8):1013-1022. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000849. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 28368924]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[29]
Zelger B, Weinlich G, Zelger B. Perineuroma. A frequently unrecognized entity with emphasis on a plexiform variant. Advances in clinical pathology : the official journal of Adriatic Society of Pathology. 2000 Jan:4(1):25-33
[PubMed PMID: 10936896]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[30]
Sadullahoğlu C, Dere Y, Atasever TR, Öztop MT, Karaaslan Ö. The Role of CD34 and D2-40 in the Differentiation of Dermatofibroma and Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. Turk patoloji dergisi. 2017:1(1):223-227. doi: 10.5146/tjpath.2017.01402. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 28832078]
[31]
Magro G. Differential Diagnosis of Benign Spindle Cell Lesions. Surgical pathology clinics. 2018 Mar:11(1):91-121. doi: 10.1016/j.path.2017.09.005. Epub 2017 Dec 9
[PubMed PMID: 29413661]
[32]
Remstein ED, Arndt CA, Nascimento AG. Plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor: clinicopathologic analysis of 22 cases. The American journal of surgical pathology. 1999 Jun:23(6):662-70
[PubMed PMID: 10366148]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[33]
Abrams JS, Tait N, Silva H, Eisenberger M, Van Echo DA, Olver IN, Aisner J. Phase II trial of N-methylformamide in advanced renal cancer. American journal of clinical oncology. 1989 Feb:12(1):41-2
[PubMed PMID: 2912020]
[34]
Ochoa CE, Joseph RW. Desmoplastic melanoma: a brief review and the efficacy of immunotherapy. Expert review of anticancer therapy. 2019 Mar:19(3):205-207. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2019.1574573. Epub 2019 Feb 4
[PubMed PMID: 30686076]
[35]
Gregorian C, Nakashima J, Dry SM, Nghiemphu PL, Smith KB, Ao Y, Dang J, Lawson G, Mellinghoff IK, Mischel PS, Phelps M, Parada LF, Liu X, Sofroniew MV, Eilber FC, Wu H. PTEN dosage is essential for neurofibroma development and malignant transformation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009 Nov 17:106(46):19479-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0910398106. Epub 2009 Oct 21
[PubMed PMID: 19846776]
[36]
Spurlock G, Knight SJ, Thomas N, Kiehl TR, Guha A, Upadhyaya M. Molecular evolution of a neurofibroma to malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) in an NF1 patient: correlation between histopathological, clinical and molecular findings. Journal of cancer research and clinical oncology. 2010 Dec:136(12):1869-80. doi: 10.1007/s00432-010-0846-3. Epub 2010 Mar 15
[PubMed PMID: 20229272]
[37]
Gesundheit B, Parkin P, Greenberg M, Baruchel S, Senger C, Kapelushnik J, Smith C, Klement GL. The role of angiogenesis in the transformation of plexiform neurofibroma into malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Journal of pediatric hematology/oncology. 2010 Oct:32(7):548-53. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0b013e3181e887c7. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 20686424]
[38]
Schaefer IM, Fletcher CD. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) arising in diffuse-type neurofibroma: clinicopathologic characterization in a series of 9 cases. The American journal of surgical pathology. 2015 Sep:39(9):1234-41. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000447. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 25929351]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[39]
Garozzo D. Peripheral nerve tumors in neurofibromatosis 1: An overview on management and indications for surgical treatment in our experience. Neurology India. 2019 Jan-Feb:67(Supplement):S38-S44. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.250697. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 30688231]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence