Definition/Introduction
The National Quality Forum (NQF) is an independent, nonpartisan organization tasked with devising a national strategy to set standards for quality improvement and reporting in the United States healthcare industry. It is the first-ever public service organization explicitly focused on addressing the quality of healthcare. The NQF consists of more than 400 member bodies, including consumer organizations, private and public purchasers, hospitals, physicians, certifying and accreditation agencies, and other healthcare stakeholders.
The modern movement of “healthcare quality and improvement” as a distinct field of study in the United States began in 1966, with the development of conceptualizing healthcare in terms of structure, processes, and outcomes. In 1987, the Healthcare Financing Administration released the first-ever publically available hospital-specific mortality data. In the early 1990s, the National Committee on Quality Assurance used the Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set as a performance improvement tool to standardize evaluating and reporting quality improvement initiatives within individual health plans nationwide. However, perhaps the most influential event that ultimately led to the development of the NQF was a landmark 1999 Institute of Medicine (IOM) report, “To Err Is Human,” which persuasively tied healthcare quality to patient safety.[1][2][3]
There remained a growing focus on patient safety and healthcare quality over the ensuing years, including the founding of the NQF by syndication of private and non-profit organizations.
Evolution of NQF
Before the NQF, there was very little systematic information available on healthcare quality. Similarly, no framework existed for the measurement or reporting of quality metrics. As a result, developing an appropriate healthcare policy was difficult. One of the NQF’s first tasks was to establish a Strategic Framework Board which consisted of nine healthcare quality experts to 1) design a national strategy for quality measurement and reporting system; 2) set forth fair and transparent benchmarking; and 3) identify potential barriers and recommend possible solutions to successful implementation. With consistent and ongoing intensive review and involvement of multiple stakeholders, NQF-endorsed measures began to be considered the gold standard for healthcare quality measurement.[1]
Role of The NQF on Quality Improvement and Cost-effectiveness
The NQF’s focus on national quality measurement and reporting transformed the United States into a worldwide leader in addressing complex issues such as risk adjustment for severity of illness. Stakeholders, including physicians, patients, and healthcare organizations, have utilized NQF systems as initiatives to reduce healthcare costs by improving quality. The NQF’s approach fits in two discrete but complementary roles:
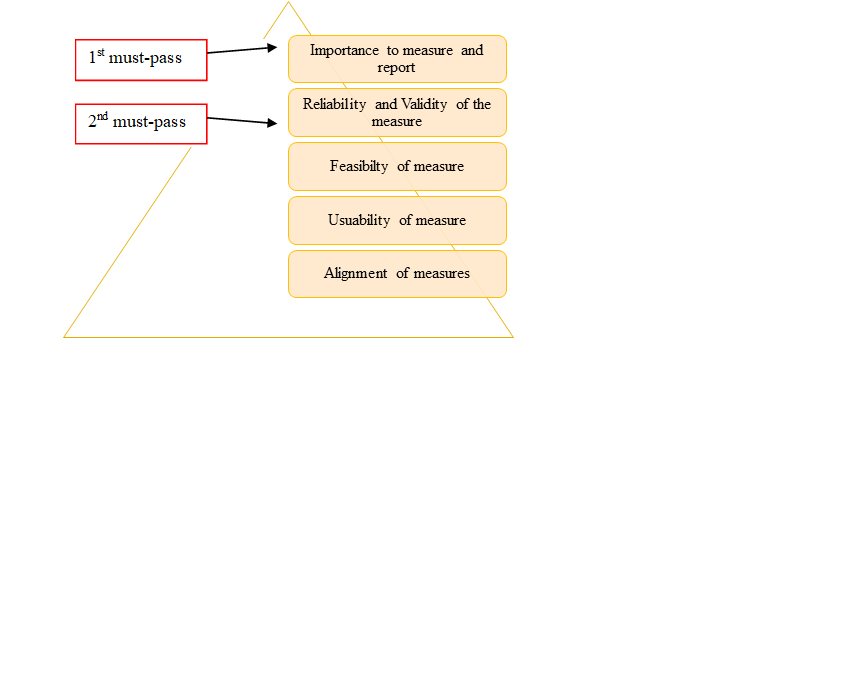
- Endorsing standardized performance measures: This approach involves pooling and prioritizing recommendations from various stakeholders such as the American Medical Association, the National Committee for Quality Assurance, Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services, and Joint Commission. The NQF uses distinct criteria to evaluate submitted metrics. Each proposed metric must meet the first and second criteria in the pyramid to be endorsed (Fig.1). In other words, an endorsed measure must demonstrate a high-impact health target or priority and must meet scientific standards. Also, measures should be relatively easy to use and tailor to specific healthcare settings with little burden. Hence, NQF endorsed measures are considered as a gold standard and granted privileged status in federal regulations.[1][4]
- Convene leaders in the public and private sectors to build consensus and guidelines regarding:
- Formulating priorities for National Quality Strategy on behalf of the US Department of Health and Human Services, with particular focus on access and affordability
- Quality measures selection to be used in federal public reporting and value-based programs
- Curtailing total healthcare costs by utilizing endorsed measures within varied programs