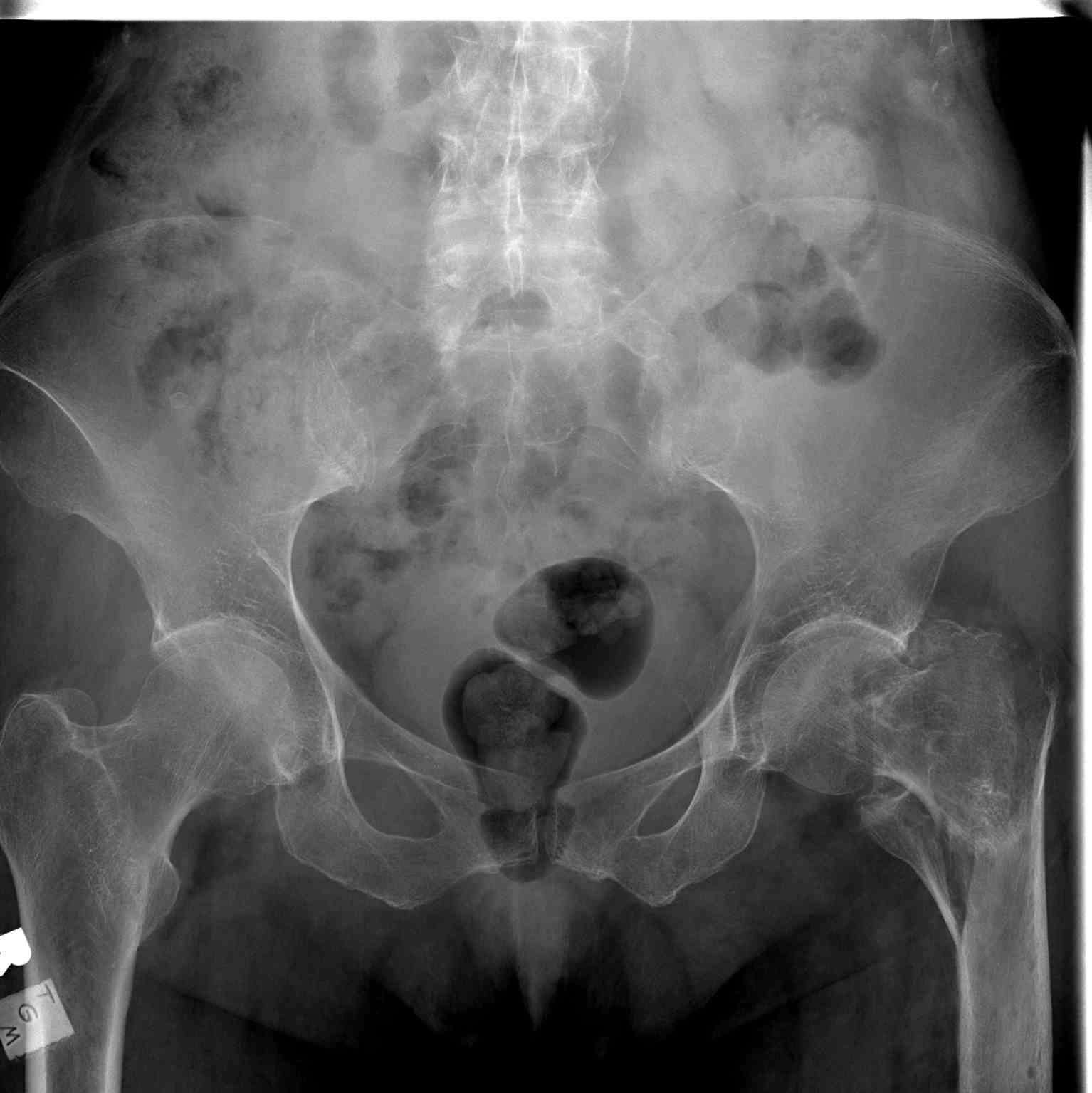
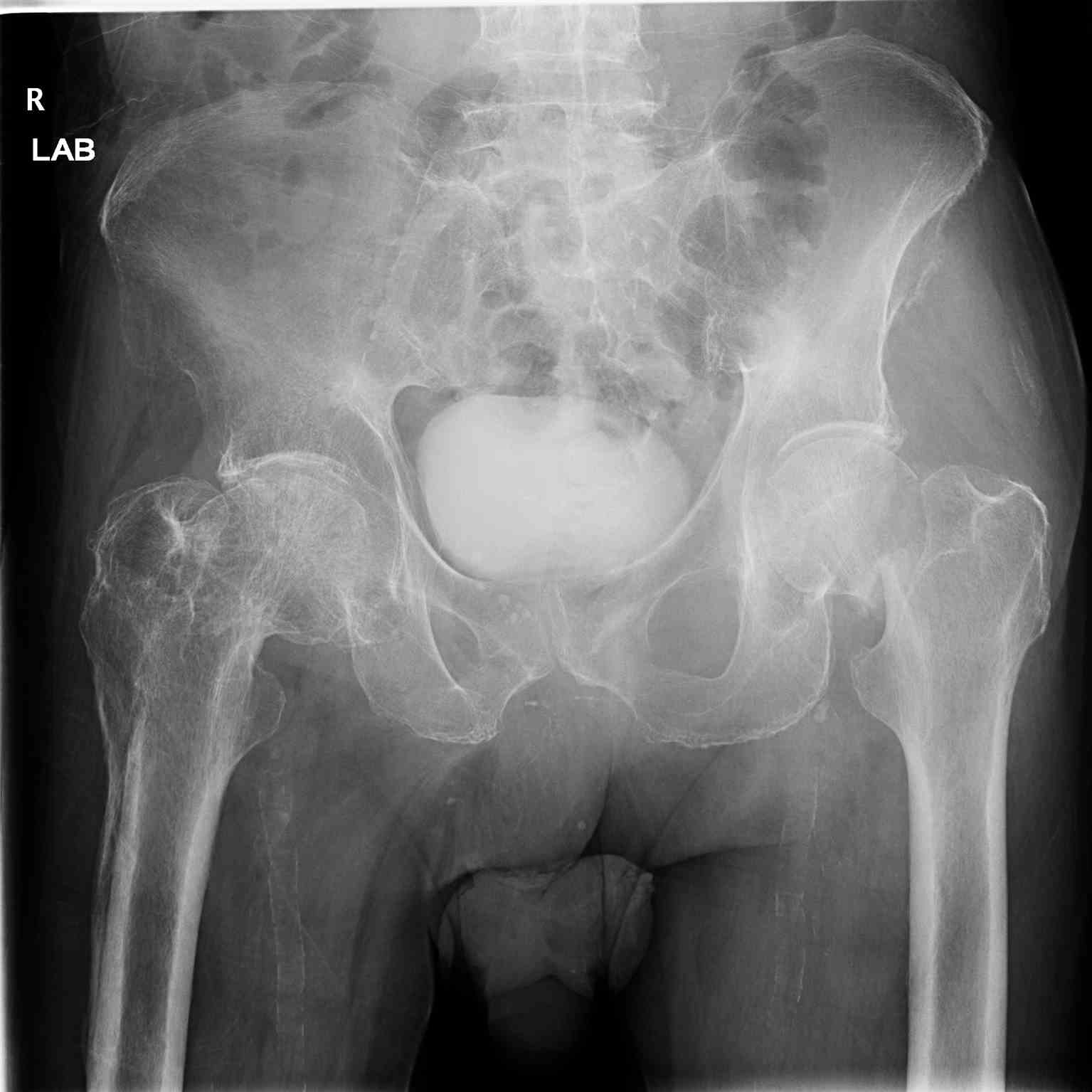
[1]
Deandrea S, Lucenteforte E, Bravi F, Foschi R, La Vecchia C, Negri E. Risk factors for falls in community-dwelling older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epidemiology (Cambridge, Mass.). 2010 Sep:21(5):658-68. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181e89905. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 20585256]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[3]
Gullberg B, Johnell O, Kanis JA. World-wide projections for hip fracture. Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA. 1997:7(5):407-13
[PubMed PMID: 9425497]
[4]
Dhanwal DK,Dennison EM,Harvey NC,Cooper C, Epidemiology of hip fracture: Worldwide geographic variation. Indian journal of orthopaedics. 2011 Jan;
[PubMed PMID: 21221218]
[5]
Brauer CA, Coca-Perraillon M, Cutler DM, Rosen AB. Incidence and mortality of hip fractures in the United States. JAMA. 2009 Oct 14:302(14):1573-9. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1462. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 19826027]
[6]
Youm T, Koval KJ, Zuckerman JD. The economic impact of geriatric hip fractures. American journal of orthopedics (Belle Mead, N.J.). 1999 Jul:28(7):423-8
[PubMed PMID: 10426442]
[7]
Mosk CA, Mus M, Vroemen JP, van der Ploeg T, Vos DI, Elmans LH, van der Laan L. Dementia and delirium, the outcomes in elderly hip fracture patients. Clinical interventions in aging. 2017:12():421-430. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S115945. Epub 2017 Mar 10
[PubMed PMID: 28331300]
[8]
Deleanu B,Prejbeanu R,Tsiridis E,Vermesan D,Crisan D,Haragus H,Predescu V,Birsasteanu F, Occult fractures of the proximal femur: imaging diagnosis and management of 82 cases in a regional trauma center. World journal of emergency surgery : WJES. 2015
[PubMed PMID: 26587053]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[9]
Foex BA, Russell A. BET 2: CT versus MRI for occult hip fractures. Emergency medicine journal : EMJ. 2018 Oct:35(10):645-647. doi: 10.1136/emermed-2018-208093.3. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 30249714]
[10]
Bartonícek J. Pauwels' classification of femoral neck fractures: correct interpretation of the original. Journal of orthopaedic trauma. 2001 Jun-Jul:15(5):358-60
[PubMed PMID: 11433141]
[11]
van Embden D, Roukema GR, Rhemrev SJ, Genelin F, Meylaerts SA. The Pauwels classification for intracapsular hip fractures: is it reliable? Injury. 2011 Nov:42(11):1238-40. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2010.11.053. Epub 2010 Dec 13
[PubMed PMID: 21146815]
[12]
Kazley JM,Banerjee S,Abousayed MM,Rosenbaum AJ, Classifications in Brief: Garden Classification of Femoral Neck Fractures. Clinical orthopaedics and related research. 2018 Feb
[PubMed PMID: 29389800]
[13]
Pedersen SJ, Borgbjerg FM, Schousboe B, Pedersen BD, Jørgensen HL, Duus BR, Lauritzen JB, Hip Fracture Group of Bispebjerg Hospital. A comprehensive hip fracture program reduces complication rates and mortality. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2008 Oct:56(10):1831-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2008.01945.x. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 19054201]
[14]
Downie S, Joss J, Sripada S. A prospective cohort study investigating the use of a surgical planning tool to improve patient fasting times in orthopaedic trauma. The surgeon : journal of the Royal Colleges of Surgeons of Edinburgh and Ireland. 2019 Apr:17(2):80-87. doi: 10.1016/j.surge.2018.05.003. Epub 2018 Jun 18
[PubMed PMID: 29929769]
[15]
Ylinenvaara SI, Elisson O, Berg K, Zdolsek JH, Krook H, Hahn RG. Preoperative urine-specific gravity and the incidence of complications after hip fracture surgery: A prospective, observational study. European journal of anaesthesiology. 2014 Feb:31(2):85-90. doi: 10.1097/01.EJA.0000435057.72303.0e. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 24145802]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[16]
Smith I,Kranke P,Murat I,Smith A,O'Sullivan G,Søreide E,Spies C,in't Veld B, Perioperative fasting in adults and children: guidelines from the European Society of Anaesthesiology. European journal of anaesthesiology. 2011 Aug
[PubMed PMID: 21712716]
[17]
Callear J, Shah K. Analgesia in hip fractures. Do fascia-iliac blocks make any difference? BMJ quality improvement reports. 2016:5(1):. doi: 10.1136/bmjquality.u210130.w4147. Epub 2016 Jan 14
[PubMed PMID: 26893899]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[18]
van de Ree CLP, De Jongh MAC, Peeters CMM, de Munter L, Roukema JA, Gosens T. Hip Fractures in Elderly People: Surgery or No Surgery? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Geriatric orthopaedic surgery & rehabilitation. 2017 Sep:8(3):173-180. doi: 10.1177/2151458517713821. Epub 2017 Jul 7
[PubMed PMID: 28835875]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[19]
Khan SK, Kalra S, Khanna A, Thiruvengada MM, Parker MJ. Timing of surgery for hip fractures: a systematic review of 52 published studies involving 291,413 patients. Injury. 2009 Jul:40(7):692-7. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2009.01.010. Epub 2009 May 18
[PubMed PMID: 19450802]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[20]
HIP ATTACK Investigators. Accelerated surgery versus standard care in hip fracture (HIP ATTACK): an international, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet (London, England). 2020 Feb 29:395(10225):698-708. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30058-1. Epub 2020 Feb 9
[PubMed PMID: 32050090]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[21]
Davison JN, Calder SJ, Anderson GH, Ward G, Jagger C, Harper WM, Gregg PJ. Treatment for displaced intracapsular fracture of the proximal femur. A prospective, randomised trial in patients aged 65 to 79 years. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume. 2001 Mar:83(2):206-12
[PubMed PMID: 11284567]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[22]
Keating JF, Grant A, Masson M, Scott NW, Forbes JF. Displaced intracapsular hip fractures in fit, older people: a randomised comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty. Health technology assessment (Winchester, England). 2005 Oct:9(41):iii-iv, ix-x, 1-65
[PubMed PMID: 16202351]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[23]
Johansson T, Jacobsson SA, Ivarsson I, Knutsson A, Wahlström O. Internal fixation versus total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures: a prospective randomized study of 100 hips. Acta orthopaedica Scandinavica. 2000 Dec:71(6):597-602
[PubMed PMID: 11145387]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[24]
Bray TJ, Smith-Hoefer E, Hooper A, Timmerman L. The displaced femoral neck fracture. Internal fixation versus bipolar endoprosthesis. Results of a prospective, randomized comparison. Clinical orthopaedics and related research. 1988 May:(230):127-40
[PubMed PMID: 3365885]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[25]
Frihagen F, Nordsletten L, Madsen JE. Hemiarthroplasty or internal fixation for intracapsular displaced femoral neck fractures: randomised controlled trial. BMJ (Clinical research ed.). 2007 Dec 15:335(7632):1251-4
[PubMed PMID: 18056740]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[26]
Sikorski JM, Barrington R. Internal fixation versus hemiarthroplasty for the displaced subcapital fracture of the femur. A prospective randomised study. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume. 1981:63-B(3):357-61
[PubMed PMID: 7263746]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[27]
Macaulay W, Nellans KW, Iorio R, Garvin KL, Healy WL, Rosenwasser MP, DFACTO Consortium. Total hip arthroplasty is less painful at 12 months compared with hemiarthroplasty in treatment of displaced femoral neck fracture. HSS journal : the musculoskeletal journal of Hospital for Special Surgery. 2008 Feb:4(1):48-54. doi: 10.1007/s11420-007-9061-4. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 18751862]
[28]
Hedbeck CJ, Enocson A, Lapidus G, Blomfeldt R, Törnkvist H, Ponzer S, Tidermark J. Comparison of bipolar hemiarthroplasty with total hip arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: a concise four-year follow-up of a randomized trial. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume. 2011 Mar 2:93(5):445-50. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.00474. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 21368076]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[29]
Metcalfe D, Judge A, Perry DC, Gabbe B, Zogg CK, Costa ML. Total hip arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for independently mobile older adults with intracapsular hip fractures. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2019 May 17:20(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-2590-4. Epub 2019 May 17
[PubMed PMID: 31101041]
[30]
HEALTH Investigators, Bhandari M, Einhorn TA, Guyatt G, Schemitsch EH, Zura RD, Sprague S, Frihagen F, Guerra-Farfán E, Kleinlugtenbelt YV, Poolman RW, Rangan A, Bzovsky S, Heels-Ansdell D, Thabane L, Walter SD, Devereaux PJ. Total Hip Arthroplasty or Hemiarthroplasty for Hip Fracture. The New England journal of medicine. 2019 Dec 5:381(23):2199-2208. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1906190. Epub 2019 Sep 26
[PubMed PMID: 31557429]
[31]
Yang B, Lin X, Yin XM, Wen XZ. Bipolar versus unipolar hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures in the elder patient: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. European journal of orthopaedic surgery & traumatology : orthopedie traumatologie. 2015 Apr:25(3):425-33. doi: 10.1007/s00590-014-1565-2. Epub 2014 Dec 5
[PubMed PMID: 25476243]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[32]
Hedbeck CJ, Blomfeldt R, Lapidus G, Törnkvist H, Ponzer S, Tidermark J. Unipolar hemiarthroplasty versus bipolar hemiarthroplasty in the most elderly patients with displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomised, controlled trial. International orthopaedics. 2011 Nov:35(11):1703-11. doi: 10.1007/s00264-011-1213-y. Epub 2011 Feb 8
[PubMed PMID: 21301830]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[33]
Lin FF, Chen YF, Chen B, Lin CH, Zheng K. Cemented versus uncemented hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trails. Medicine. 2019 Feb:98(8):e14634. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014634. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 30813202]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[34]
Cserháti P, Kazár G, Manninger J, Fekete K, Frenyó S. Non-operative or operative treatment for undisplaced femoral neck fractures: a comparative study of 122 non-operative and 125 operatively treated cases. Injury. 1996 Oct:27(8):583-8
[PubMed PMID: 8994566]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[35]
Parker MJ, White A, Boyle A. Fixation versus hemiarthroplasty for undisplaced intracapsular hip fractures. Injury. 2008 Jul:39(7):791-5. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2008.01.011. Epub 2008 Apr 14
[PubMed PMID: 18407277]
[36]
Fixation using Alternative Implants for the Treatment of Hip fractures (FAITH) Investigators. Fracture fixation in the operative management of hip fractures (FAITH): an international, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet (London, England). 2017 Apr 15:389(10078):1519-1527. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30066-1. Epub 2017 Mar 3
[PubMed PMID: 28262269]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[37]
Shehata MSA, Aboelnas MM, Abdulkarim AN, Abdallah AR, Ahmed H, Holton J, Consigliere P, Narvani AA, Sallam AA, Wimhurst JA, Imam MA. Sliding hip screws versus cancellous screws for femoral neck fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European journal of orthopaedic surgery & traumatology : orthopedie traumatologie. 2019 Oct:29(7):1383-1393. doi: 10.1007/s00590-019-02460-0. Epub 2019 Jun 5
[PubMed PMID: 31165917]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[38]
Ahrengart L, Törnkvist H, Fornander P, Thorngren KG, Pasanen L, Wahlström P, Honkonen S, Lindgren U. A randomized study of the compression hip screw and Gamma nail in 426 fractures. Clinical orthopaedics and related research. 2002 Aug:(401):209-22
[PubMed PMID: 12151898]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[39]
Li AB, Zhang WJ, Wang J, Guo WJ, Wang XH, Zhao YM. Intramedullary and extramedullary fixations for the treatment of unstable femoral intertrochanteric fractures: a meta-analysis of prospective randomized controlled trials. International orthopaedics. 2017 Feb:41(2):403-413. doi: 10.1007/s00264-016-3308-y. Epub 2016 Oct 8
[PubMed PMID: 27722824]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[40]
Zhang Y, Zhang S, Wang S, Zhang H, Zhang W, Liu P, Ma J, Pervaiz N, Wang J. Long and short intramedullary nails for fixation of intertrochanteric femur fractures (OTA 31-A1, A2 and A3): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthopaedics & traumatology, surgery & research : OTSR. 2017 Sep:103(5):685-690. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2017.04.003. Epub 2017 May 22
[PubMed PMID: 28546048]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[41]
Baumgaertner MR, Curtin SL, Lindskog DM, Keggi JM. The value of the tip-apex distance in predicting failure of fixation of peritrochanteric fractures of the hip. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume. 1995 Jul:77(7):1058-64
[PubMed PMID: 7608228]
[42]
Park SY, Yang KH, Yoo JH, Yoon HK, Park HW. The treatment of reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures with the intramedullary hip nail. The Journal of trauma. 2008 Oct:65(4):852-7. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e31802b9559. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 18849802]
[43]
Ekström W, Karlsson-Thur C, Larsson S, Ragnarsson B, Alberts KA. Functional outcome in treatment of unstable trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures with the proximal femoral nail and the Medoff sliding plate. Journal of orthopaedic trauma. 2007 Jan:21(1):18-25
[PubMed PMID: 17211264]
[44]
Rahme DM, Harris IA. Intramedullary nailing versus fixed angle blade plating for subtrochanteric femoral fractures: a prospective randomised controlled trial. Journal of orthopaedic surgery (Hong Kong). 2007 Dec:15(3):278-81
[PubMed PMID: 18162669]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[45]
Sadowski C, Lübbeke A, Saudan M, Riand N, Stern R, Hoffmeyer P. Treatment of reverse oblique and transverse intertrochanteric fractures with use of an intramedullary nail or a 95 degrees screw-plate: a prospective, randomized study. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume. 2002 Mar:84(3):372-81
[PubMed PMID: 11886906]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[46]
Cheng SY, Levy AR, Lefaivre KA, Guy P, Kuramoto L, Sobolev B. Geographic trends in incidence of hip fractures: a comprehensive literature review. Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA. 2011 Oct:22(10):2575-86. doi: 10.1007/s00198-011-1596-z. Epub 2011 Apr 12
[PubMed PMID: 21484361]
[47]
Tsang C, Boulton C, Burgon V, Johansen A, Wakeman R, Cromwell DA. Predicting 30-day mortality after hip fracture surgery: Evaluation of the National Hip Fracture Database case-mix adjustment model. Bone & joint research. 2017 Sep:6(9):550-556. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.69.BJR-2017-0020.R1. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 28947603]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[48]
Nijmeijer WS, Folbert EC, Vermeer M, Slaets JP, Hegeman JH. Prediction of early mortality following hip fracture surgery in frail elderly: The Almelo Hip Fracture Score (AHFS). Injury. 2016 Oct:47(10):2138-2143. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2016.07.022. Epub 2016 Jul 20
[PubMed PMID: 27469403]
[49]
Dyer SM,Crotty M,Fairhall N,Magaziner J,Beaupre LA,Cameron ID,Sherrington C, A critical review of the long-term disability outcomes following hip fracture. BMC geriatrics. 2016 Sep 2;
[PubMed PMID: 27590604]
[50]
Mackay DC, Harrison WJ, Bates JH, Dickenson D. Audit of deep wound infection following hip fracture surgery. Journal of the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh. 2000 Feb:45(1):56-9
[PubMed PMID: 10815382]
[51]
Carpintero P, Caeiro JR, Carpintero R, Morales A, Silva S, Mesa M. Complications of hip fractures: A review. World journal of orthopedics. 2014 Sep 18:5(4):402-11. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v5.i4.402. Epub 2014 Sep 18
[PubMed PMID: 25232517]
[52]
Carson JL, Terrin ML, Noveck H, Sanders DW, Chaitman BR, Rhoads GG, Nemo G, Dragert K, Beaupre L, Hildebrand K, Macaulay W, Lewis C, Cook DR, Dobbin G, Zakriya KJ, Apple FS, Horney RA, Magaziner J, FOCUS Investigators. Liberal or restrictive transfusion in high-risk patients after hip surgery. The New England journal of medicine. 2011 Dec 29:365(26):2453-62. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1012452. Epub 2011 Dec 14
[PubMed PMID: 22168590]
[53]
Kanis JA, Johansson H, Oden A, Dawson-Hughes B, Melton LJ 3rd, McCloskey EV. The effects of a FRAX revision for the USA. Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA. 2010 Jan:21(1):35-40. doi: 10.1007/s00198-009-1033-8. Epub 2009 Aug 25
[PubMed PMID: 19705047]