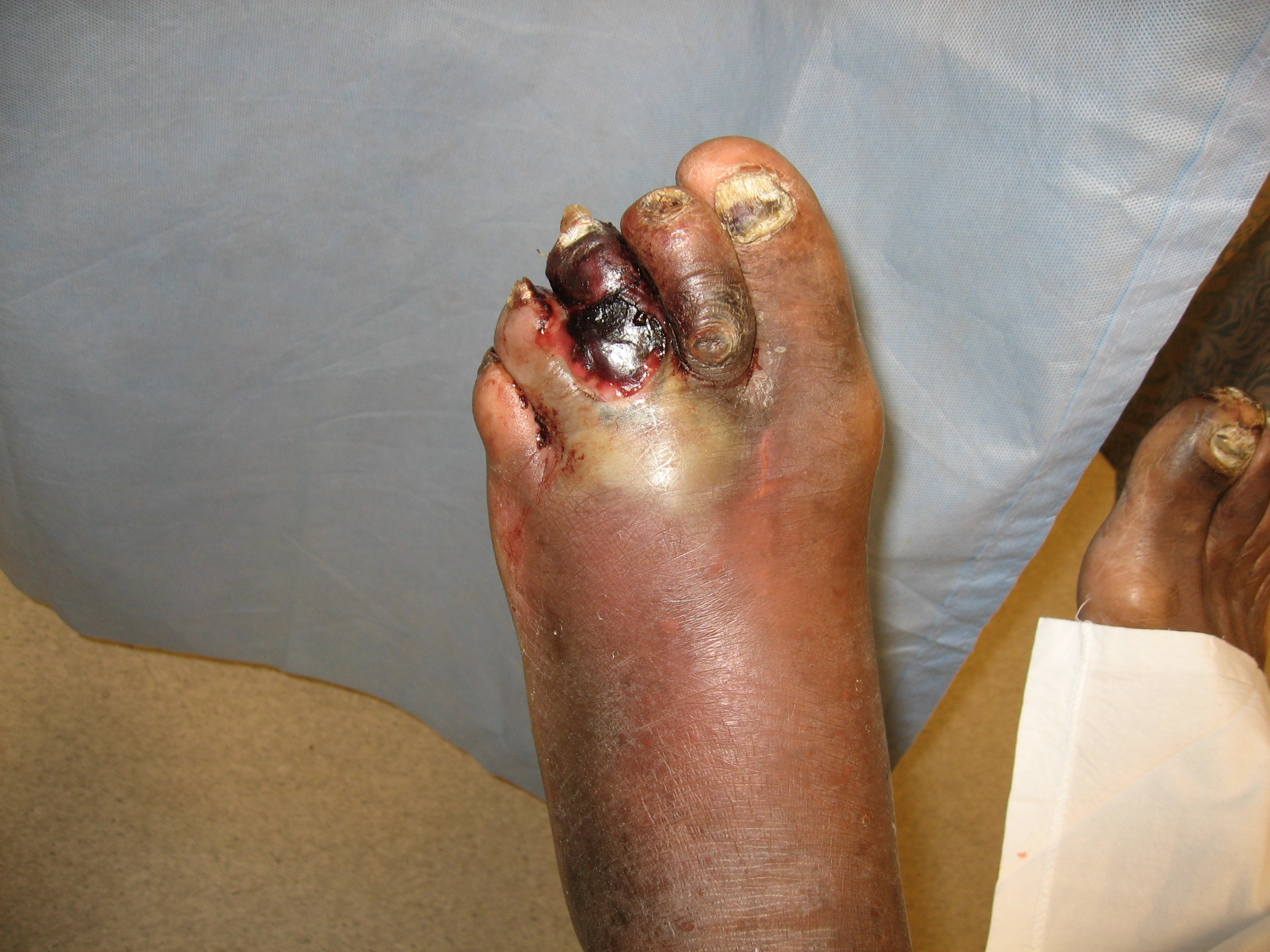
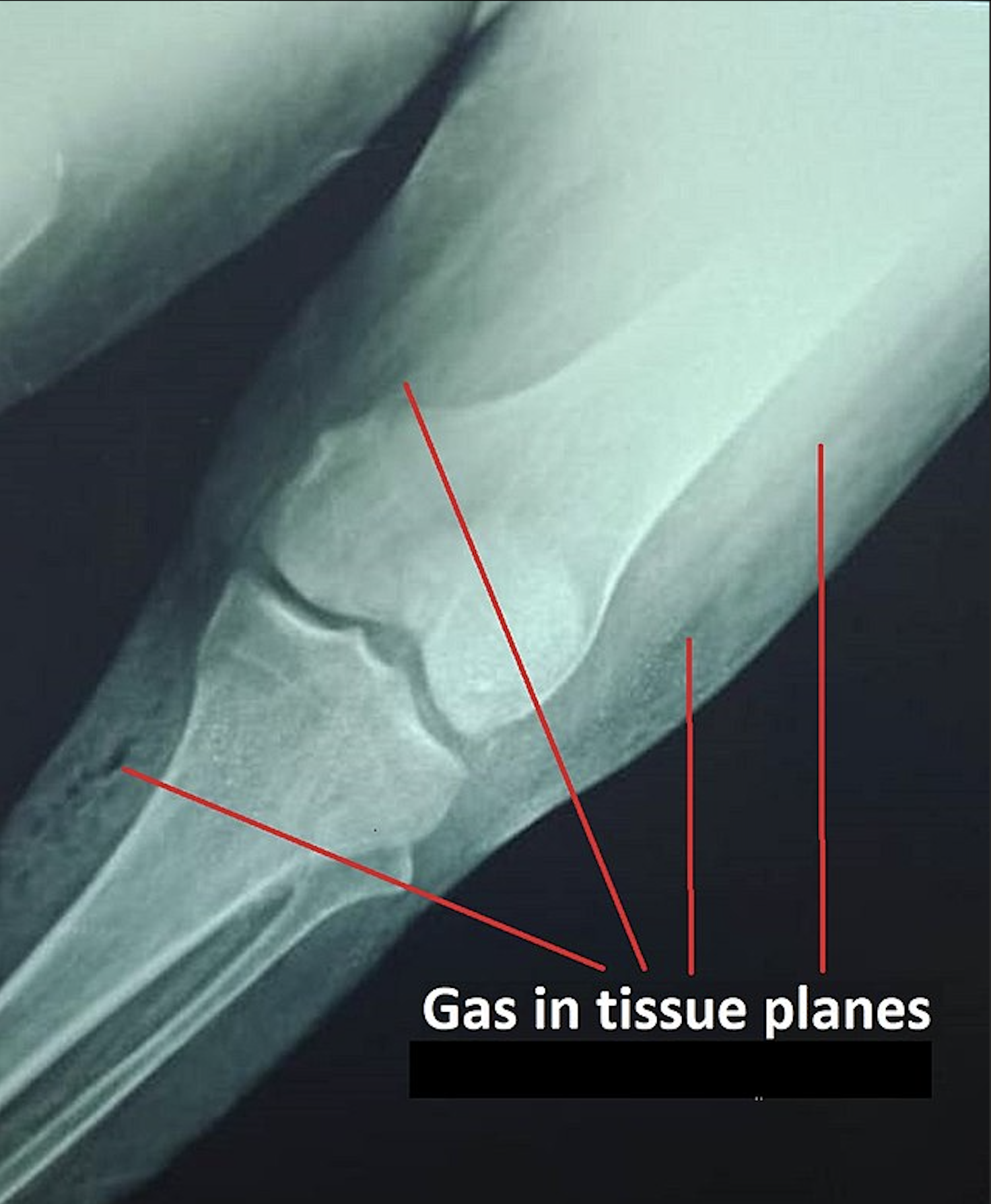
[1]
Takehara M. [Host Defense against Bacterial Infection and Bacterial Toxin-induced Impairment of Innate Immunity]. Yakugaku zasshi : Journal of the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan. 2018:138(10):1249-1253. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00102. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 30270267]
[2]
Stevens DL, Aldape MJ, Bryant AE. Life-threatening clostridial infections. Anaerobe. 2012 Apr:18(2):254-9. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2011.11.001. Epub 2011 Nov 20
[PubMed PMID: 22120198]
[3]
Huang YY, Lin CW, Yang HM, Hung SY, Chen IW. Survival and associated risk factors in patients with diabetes and amputations caused by infectious foot gangrene. Journal of foot and ankle research. 2018:11():1. doi: 10.1186/s13047-017-0243-0. Epub 2018 Jan 4
[PubMed PMID: 29312468]
[4]
Perkins TA, Bieniek JM, Sumfest JM. Solitary Candida albicans Infection Causing Fournier Gangrene and Review of Fungal Etiologies. Reviews in urology. 2014:16(2):95-8
[PubMed PMID: 25009452]
[5]
Dempsey A. Serious infection associated with induced abortion in the United States. Clinical obstetrics and gynecology. 2012 Dec:55(4):888-92. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0b013e31826fd8f8. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 23090457]
[6]
Stevens DL, Bryant AE. Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infections. The New England journal of medicine. 2017 Dec 7:377(23):2253-2265. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1600673. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 29211672]
[7]
Shindo Y, Dobashi Y, Sakai T, Monma C, Miyatani H, Yoshida Y. Epidemiological and pathobiological profiles of Clostridium perfringens infections: review of consecutive series of 33 cases over a 13-year period. International journal of clinical and experimental pathology. 2015:8(1):569-77
[PubMed PMID: 25755747]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[8]
Lehnhardt M,Homann HH,Daigeler A,Hauser J,Palka P,Steinau HU, Major and lethal complications of liposuction: a review of 72 cases in Germany between 1998 and 2002. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. 2008 Jun
[PubMed PMID: 18520866]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[9]
Takazawa K, Otsuka H, Nakagawa Y, Inokuchi S. Clinical Features of Non-clostridial Gas Gangrene and Risk Factors for In-hospital Mortality. The Tokai journal of experimental and clinical medicine. 2015 Sep 20:40(3):124-9
[PubMed PMID: 26369267]
[10]
Janik E, Ceremuga M, Saluk-Bijak J, Bijak M. Biological Toxins as the Potential Tools for Bioterrorism. International journal of molecular sciences. 2019 Mar 8:20(5):. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051181. Epub 2019 Mar 8
[PubMed PMID: 30857127]
[11]
Srivastava I, Aldape MJ, Bryant AE, Stevens DL. Spontaneous C. septicum gas gangrene: A literature review. Anaerobe. 2017 Dec:48():165-171. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2017.07.008. Epub 2017 Aug 2
[PubMed PMID: 28780428]
[12]
Crum-Cianflone NF. Infection and musculoskeletal conditions: Infectious myositis. Best practice & research. Clinical rheumatology. 2006 Dec:20(6):1083-97
[PubMed PMID: 17127198]
[13]
Carter GP, Cheung JK, Larcombe S, Lyras D. Regulation of toxin production in the pathogenic clostridia. Molecular microbiology. 2014 Jan:91(2):221-31
[PubMed PMID: 24563915]
[14]
Garcia NM, Cai J. Aggressive Soft Tissue Infections. The Surgical clinics of North America. 2018 Oct:98(5):1097-1108. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 Jul 29
[PubMed PMID: 30243450]
[15]
Roberts EJ, Martucci JA, Wu D. The Unusual Presence of Gas From a Puncture Wound: A Case Report. The Journal of foot and ankle surgery : official publication of the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons. 2018 Jul-Aug:57(4):785-789. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2017.11.003. Epub 2018 Mar 21
[PubMed PMID: 29571810]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[16]
Cristoferi G, Fabris G, Ronconi AM, Bozza F, Gallassi GC, Bucca D, Caria GM, Duodeci S. [Gas gangrene. Clinical considerations, prognosis and therapeutic prospects in our experience]. Journal de chirurgie. 1991 May:128(5):243-6
[PubMed PMID: 1880179]
[17]
Sarvari KP, Vasas B, Kiss I, Lazar A, Horvath I, Simon M, Peto Z, Urban E. Fatal Clostridium perfringens sepsis due to emphysematous gastritis and literature review. Anaerobe. 2016 Aug:40():31-4. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2016.03.011. Epub 2016 Mar 30
[PubMed PMID: 27036998]
[18]
Finsterer J, Hess B. Neuromuscular and central nervous system manifestations of Clostridium perfringens infections. Infection. 2007 Dec:35(6):396-405
[PubMed PMID: 18034207]
[19]
Nichols RL, Smith JW. Anaerobes from a surgical perspective. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 1994 May:18 Suppl 4():S280-6
[PubMed PMID: 8086576]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[20]
Shin SH, Park IK, Kang JW, Lee YS, Chung YG. Vacuum-Assisted Closure (VAC) Using Multiple Foam Pieces for Hidden Space Drainage through Less Exposure in Musculoskeletal Infections. The journal of hand surgery Asian-Pacific volume. 2018 Sep:23(3):369-376. doi: 10.1142/S242483551850039X. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 30282543]
[21]
Yang Z, Hu J, Qu Y, Sun F, Leng X, Li H, Zhan S. Interventions for treating gas gangrene. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2015 Dec 3:2015(12):CD010577. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010577.pub2. Epub 2015 Dec 3
[PubMed PMID: 26631369]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[22]
Devaney B, Frawley G, Frawley L, Pilcher DV. Necrotising soft tissue infections: the effect of hyperbaric oxygen on mortality. Anaesthesia and intensive care. 2015 Nov:43(6):685-92
[PubMed PMID: 26603791]
[23]
Bakker DJ. Clostridial myonecrosis (gas gangrene). Undersea & hyperbaric medicine : journal of the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society, Inc. 2012 May-Jun:39(3):731-7
[PubMed PMID: 22670554]
[24]
Mathieu D, Marroni A, Kot J. Tenth European Consensus Conference on Hyperbaric Medicine: recommendations for accepted and non-accepted clinical indications and practice of hyperbaric oxygen treatment. Diving and hyperbaric medicine. 2017 Mar:47(1):24-32. doi: 10.28920/dhm47.1.24-32. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 28357821]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[25]
Gacto-Sanchez P. Surgical treatment and management of the severely burn patient: Review and update. Medicina intensiva. 2017 Aug-Sep:41(6):356-364. doi: 10.1016/j.medin.2017.02.008. Epub 2017 Apr 26
[PubMed PMID: 28456441]
[26]
Pruskowski KA. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Antimicrobial Agents in Burn Patients. Surgical infections. 2021 Feb:22(1):77-82. doi: 10.1089/sur.2020.375. Epub 2020 Nov 6
[PubMed PMID: 33164665]
[27]
Ramos G, Cornistein W, Cerino GT, Nacif G. Systemic antimicrobial prophylaxis in burn patients: systematic review. The Journal of hospital infection. 2017 Oct:97(2):105-114. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2017.06.015. Epub 2017 Jun 16
[PubMed PMID: 28629932]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[28]
Barone M, Grani G, Ramundo V, Garritano T, Durante C, Falcone R. Fournier's gangrene during lenvatinib treatment: A case report. Molecular and clinical oncology. 2020 Jun:12(6):588-591. doi: 10.3892/mco.2020.2031. Epub 2020 Apr 10
[PubMed PMID: 32337042]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[29]
Chantre C, Foucher S, Le Hot H, Lefort H, Blatteau JÉ. [Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, a little-known discipline]. Revue de l'infirmiere. 2018 Jun-Jul:67(242):14-15. doi: 10.1016/j.revinf.2018.03.012. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 29907169]
[30]
Burman F. Low-pressure fabric hyperbaric chambers. South African medical journal = Suid-Afrikaanse tydskrif vir geneeskunde. 2019 Mar 29:109(4):12574. doi: 10.7196/SAMJ.2019.v109i4.13524. Epub 2019 Mar 29
[PubMed PMID: 31084683]
[31]
Heyboer M 3rd. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Side Effects - Where Do We Stand? The journal of the American College of Clinical Wound Specialists. 2016:8(1-3):2-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jccw.2018.01.005. Epub 2018 Feb 5
[PubMed PMID: 30276115]
[32]
Clark LA, Moon RE. Hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of life-threatening soft-tissue infections. Respiratory care clinics of North America. 1999 Jun:5(2):203-19
[PubMed PMID: 10333449]
[33]
Chernyadyev SA, Ufimtseva MA, Vishnevskaya IF, Bochkarev YM, Ushakov AA, Beresneva TA, Galimzyanov FV, Khodakov VV. Fournier's Gangrene: Literature Review and Clinical Cases. Urologia internationalis. 2018:101(1):91-97. doi: 10.1159/000490108. Epub 2018 Jun 27
[PubMed PMID: 29949811]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[34]
Chen SY, Fu JP, Wang CH, Lee TP, Chen SG. Fournier gangrene: a review of 41 patients and strategies for reconstruction. Annals of plastic surgery. 2010 Jun:64(6):765-9. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e3181ba5485. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 20407363]
[35]
McGinness K, Kurtz Phelan DH. Use of Viable Cryopreserved Umbilical Tissue for Soft Tissue Defects in Patients With Gas Gangrene: A Case Series. Wounds : a compendium of clinical research and practice. 2018 Apr:30(4):90-95
[PubMed PMID: 29718818]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[36]
Ingraham AM, Jung HS, Liepert AE, Warner-Hillard C, Greenberg CC, Scarborough JE. Effect of transfer status on outcomes for necrotizing soft tissue infections. The Journal of surgical research. 2017 Dec:220():372-378. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2017.06.006. Epub 2017 Sep 1
[PubMed PMID: 29180205]
[37]
Mills MK, Faraklas I, Davis C, Stoddard GJ, Saffle J. Outcomes from treatment of necrotizing soft-tissue infections: results from the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database. American journal of surgery. 2010 Dec:200(6):790-6; discussion 796-7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2010.06.008. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 21146022]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[38]
Roloff D. [Prerequisites for the transfer of patients with gas gangrene to a specialized facility]. Anaesthesiologie und Reanimation. 1991:16(1):49-58
[PubMed PMID: 2043237]
[39]
Sison-Martinez J, Hendriksen S, Cooper JS. Hyperbaric Treatment of Clostridial Myositis and Myonecrosis. StatPearls. 2024 Jan:():
[PubMed PMID: 29763178]