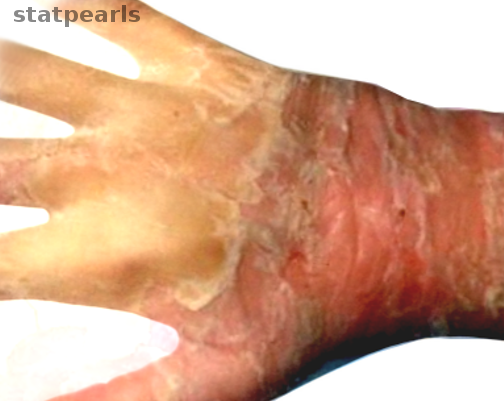
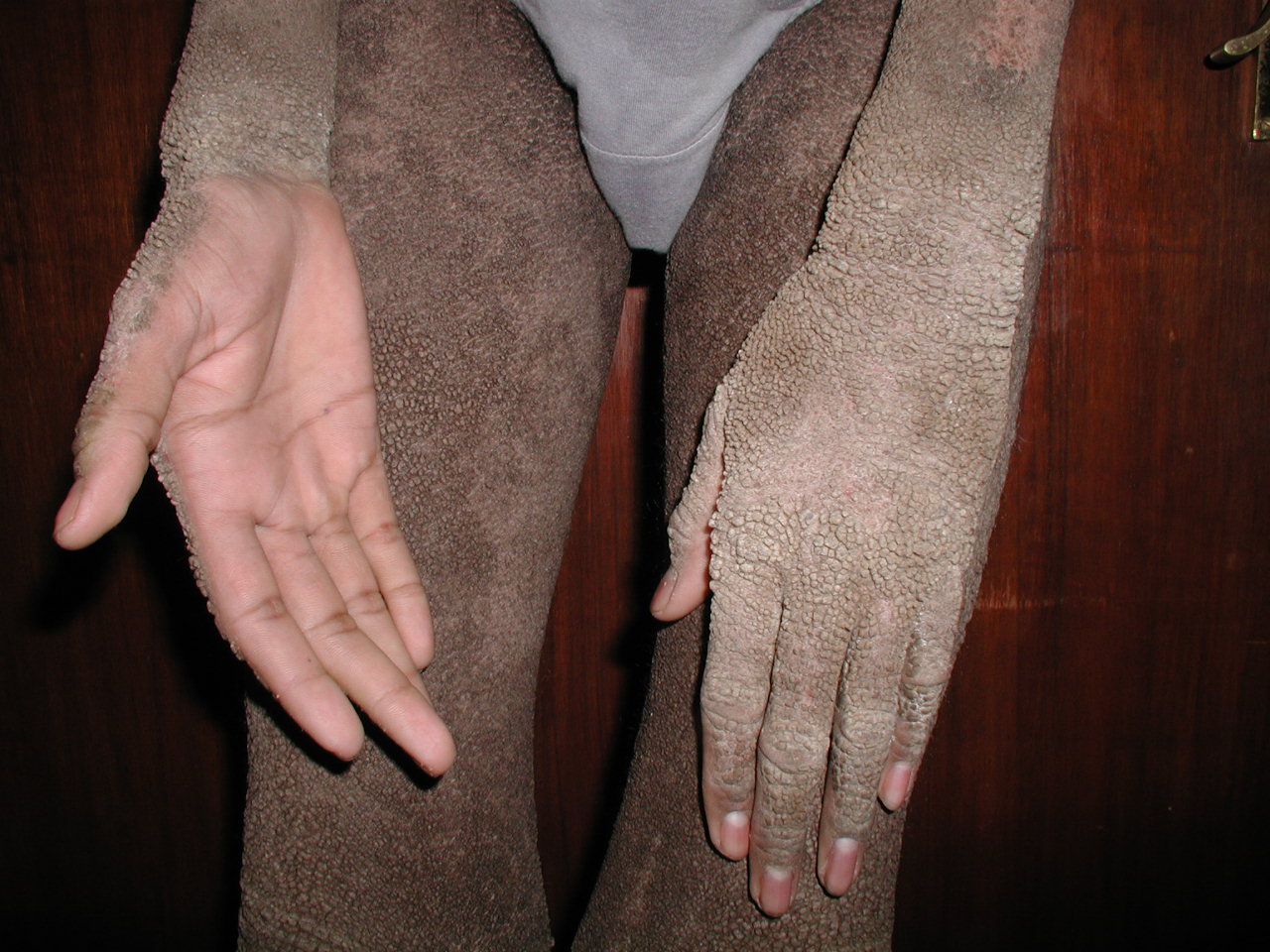
[1]
Peter Rout D, Nair A, Gupta A, Kumar P. Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis: clinical update. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology. 2019:12():333-344. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S166849. Epub 2019 May 8
[PubMed PMID: 31190940]
[2]
Covaciu C, Castori M, De Luca N, Ghirri P, Nannipieri A, Ragone G, Zambruno G, Castiglia D. Lethal autosomal recessive epidermolytic ichthyosis due to a novel donor splice-site mutation in KRT10. The British journal of dermatology. 2010 Jun:162(6):1384-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09665.x. Epub 2010 Mar 10
[PubMed PMID: 20302579]
[3]
Oji V, Tadini G, Akiyama M, Blanchet Bardon C, Bodemer C, Bourrat E, Coudiere P, DiGiovanna JJ, Elias P, Fischer J, Fleckman P, Gina M, Harper J, Hashimoto T, Hausser I, Hennies HC, Hohl D, Hovnanian A, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Jacyk WK, Leachman S, Leigh I, Mazereeuw-Hautier J, Milstone L, Morice-Picard F, Paller AS, Richard G, Schmuth M, Shimizu H, Sprecher E, Van Steensel M, Taïeb A, Toro JR, Vabres P, Vahlquist A, Williams M, Traupe H. Revised nomenclature and classification of inherited ichthyoses: results of the First Ichthyosis Consensus Conference in Sorèze 2009. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2010 Oct:63(4):607-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2009.11.020. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 20643494]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[4]
Chipev CC, Korge BP, Markova N, Bale SJ, DiGiovanna JJ, Compton JG, Steinert PM. A leucine----proline mutation in the H1 subdomain of keratin 1 causes epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Cell. 1992 Sep 4:70(5):821-8
[PubMed PMID: 1381288]
[5]
Ishida-Yamamoto A, McGrath JA, Judge MR, Leigh IM, Lane EB, Eady RA. Selective involvement of keratins K1 and K10 in the cytoskeletal abnormality of epidermolytic hyperkeratosis (bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma). The Journal of investigative dermatology. 1992 Jul:99(1):19-26
[PubMed PMID: 1376754]
[6]
Virtanen M, Smith SK, Gedde-Dahl T Jr, Vahlquist A, Bowden PE. Splice site and deletion mutations in keratin (KRT1 and KRT10) genes: unusual phenotypic alterations in Scandinavian patients with epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 2003 Nov:121(5):1013-20
[PubMed PMID: 14708600]
[7]
Irvine AD, McLean WH. Human keratin diseases: the increasing spectrum of disease and subtlety of the phenotype-genotype correlation. The British journal of dermatology. 1999 May:140(5):815-28
[PubMed PMID: 10354017]
[8]
Müller FB, Huber M, Kinaciyan T, Hausser I, Schaffrath C, Krieg T, Hohl D, Korge BP, Arin MJ. A human keratin 10 knockout causes recessive epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Human molecular genetics. 2006 Apr 1:15(7):1133-41
[PubMed PMID: 16505000]
[9]
Tsubota A, Akiyama M, Kanitakis J, Sakai K, Nomura T, Claudy A, Shimizu H. Mild recessive bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma due to a previously unidentified homozygous keratin 10 nonsense mutation. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 2008 Jul:128(7):1648-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5701257. Epub 2008 Jan 24
[PubMed PMID: 18219278]
[10]
DiGiovanna JJ, Bale SJ. Clinical heterogeneity in epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Archives of dermatology. 1994 Aug:130(8):1026-35
[PubMed PMID: 8053700]
[11]
Paller AS, Syder AJ, Chan YM, Yu QC, Hutton E, Tadini G, Fuchs E. Genetic and clinical mosaicism in a type of epidermal nevus. The New England journal of medicine. 1994 Nov 24:331(21):1408-15
[PubMed PMID: 7526210]
[13]
Fuchs E, Coulombe P, Cheng J, Chan YM, Hutton E, Syder A, Degenstein L, Yu QC, Letai A, Vassar R. Genetic bases of epidermolysis bullosa simplex and epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 1994 Nov:103(5 Suppl):25S-30S
[PubMed PMID: 7525738]
[14]
Nelson WG, Sun TT. The 50- and 58-kdalton keratin classes as molecular markers for stratified squamous epithelia: cell culture studies. The Journal of cell biology. 1983 Jul:97(1):244-51
[PubMed PMID: 6190820]
[15]
Roop DR, Huitfeldt H, Kilkenny A, Yuspa SH. Regulated expression of differentiation-associated keratins in cultured epidermal cells detected by monospecific antibodies to unique peptides of mouse epidermal keratins. Differentiation; research in biological diversity. 1987:35(2):143-50
[PubMed PMID: 2450799]
[16]
Syder AJ, Yu QC, Paller AS, Giudice G, Pearson R, Fuchs E. Genetic mutations in the K1 and K10 genes of patients with epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Correlation between location and disease severity. The Journal of clinical investigation. 1994 Apr:93(4):1533-42
[PubMed PMID: 7512983]
[17]
Chen PJ, Li CX, Wen J, Peng YS, Zeng K, Zhang SQ, Tian X, Zhang XB. S159P mutation of keratin 10 gene causes severe form of epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV. 2016 Oct:30(10):e102-e104. doi: 10.1111/jdv.13345. Epub 2015 Sep 15
[PubMed PMID: 26373619]
[18]
DiGiovanna JJ, Bale SJ. Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis: applied molecular genetics. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 1994 Mar:102(3):390-4
[PubMed PMID: 7509838]
[19]
Lacour M, Mehta-Nikhar B, Atherton DJ, Harper JI. An appraisal of acitretin therapy in children with inherited disorders of keratinization. The British journal of dermatology. 1996 Jun:134(6):1023-9
[PubMed PMID: 8763418]