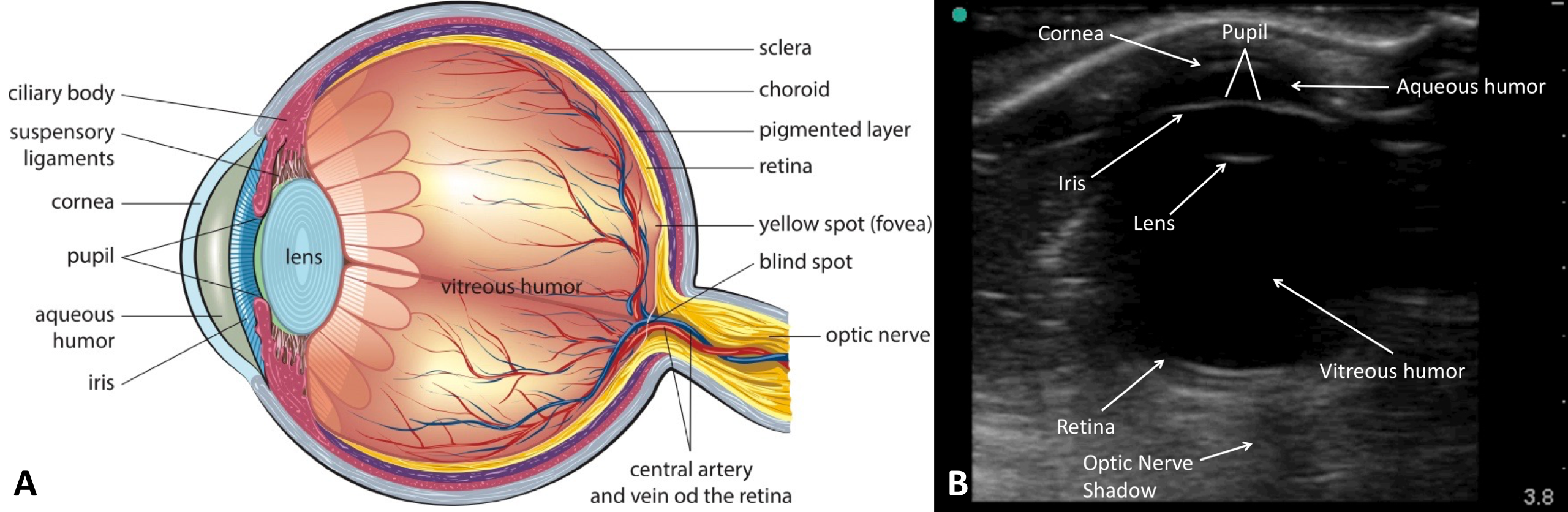
[1]
Roque PJ, Hatch N, Barr L, Wu TS. Bedside ocular ultrasound. Critical care clinics. 2014 Apr:30(2):227-41, v. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2013.10.007. Epub 2013 Dec 12
[PubMed PMID: 24606775]
[2]
Kilker BA, Holst JM, Hoffmann B. Bedside ocular ultrasound in the emergency department. European journal of emergency medicine : official journal of the European Society for Emergency Medicine. 2014 Aug:21(4):246-53. doi: 10.1097/MEJ.0000000000000070. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 24002686]
[3]
Woo MY, Hecht N, Hurley B, Stitt D, Thiruganasambandamoorthy V. Test characteristics of point-of-care ultrasonography for the diagnosis of acute posterior ocular pathology. Canadian journal of ophthalmology. Journal canadien d'ophtalmologie. 2016 Oct:51(5):336-341. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjo.2016.03.020. Epub 2016 Sep 3
[PubMed PMID: 27769323]
[4]
Chenkin J, Heslop CL, Atlin CR, Romano M, Jelic T. Bilateral Retinal Detachments Caused by Severe Preeclampsia Diagnosed with Point-of-Care Ultrasound. CJEM. 2016 Sep:18(5):395-8. doi: 10.1017/cem.2015.76. Epub 2015 Aug 19
[PubMed PMID: 26285683]
[5]
Shinar Z, Chan L, Orlinsky M. Use of ocular ultrasound for the evaluation of retinal detachment. The Journal of emergency medicine. 2011 Jan:40(1):53-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2009.06.001. Epub 2009 Jul 21
[PubMed PMID: 19625159]
[6]
Frasure SE, Saul T, Lewiss RE. Bedside ultrasound diagnosis of vitreous hemorrhage and traumatic lens dislocation. The American journal of emergency medicine. 2013 Jun:31(6):1002.e1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2013.02.013. Epub 2013 Apr 18
[PubMed PMID: 23602749]
[7]
Riccardi A, Siniscalchi C, Lerza R. Embolic Central Retinal Artery Occlusion Detected with Point-of-care Ultrasonography in the Emergency Department. The Journal of emergency medicine. 2016 Apr:50(4):e183-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2015.12.022. Epub 2016 Feb 12
[PubMed PMID: 26879704]
[8]
Marchese RF, Mistry RD, Binenbaum G, Liu GT, Scarfone RJ, Woodford AL, Chen AE. Identification of Optic Nerve Swelling Using Point-of-Care Ocular Ultrasound in Children. Pediatric emergency care. 2018 Aug:34(8):531-536. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000001046. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 28146012]
[9]
Kimberly HH, Shah S, Marill K, Noble V. Correlation of optic nerve sheath diameter with direct measurement of intracranial pressure. Academic emergency medicine : official journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine. 2008 Feb:15(2):201-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2007.00031.x. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 18275454]
[10]
Use of the sonographic diameter of optic nerve sheath to estimate intracranial pressure., Amini A,Kariman H,Arhami Dolatabadi A,Hatamabadi HR,Derakhshanfar H,Mansouri B,Safari S,Eqtesadi R,, The American journal of emergency medicine, 2013 Jan
[PubMed PMID: 22944553]
[11]
Xu W, Gerety P, Aleman T, Swanson J, Taylor J. Noninvasive methods of detecting increased intracranial pressure. Child's nervous system : ChNS : official journal of the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery. 2016 Aug:32(8):1371-86. doi: 10.1007/s00381-016-3143-x. Epub 2016 Jun 28
[PubMed PMID: 27351182]
[12]
Abu-Zidan FM, Balac K, Bhatia CA. Surgeon-performed point-of-care ultrasound in severe eye trauma: Report of two cases. World journal of clinical cases. 2016 Oct 16:4(10):344-350
[PubMed PMID: 27803918]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[13]
Engelbert PR, Palma JK. Petroleum Jelly: A Novel Medium for Ocular Ultrasound. The Journal of emergency medicine. 2015 Aug:49(2):172-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 May 23
[PubMed PMID: 26014760]
[14]
Blaivas M, Theodoro D, Sierzenski PR. A study of bedside ocular ultrasonography in the emergency department. Academic emergency medicine : official journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine. 2002 Aug:9(8):791-9
[PubMed PMID: 12153883]