Continuing Education Activity
Aflatoxins are metabolites produced by toxigenic strains of molds, mainly Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus, which grow in soil, hay, decaying vegetation, and grains. Aflatoxin is produced by fungal action during food production, harvest, storage, and processing. Dietary exposure to aflatoxins may result in severe toxic and carcinogenic outcomes in humans and animals. Aflatoxin toxicity may result in nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, convulsions, and other signs of acute liver injury. Long-term exposure also leads to various complications like growth retardation, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. This activity describes the evaluation and management of aflatoxin toxicity and reviews the role of the interprofessional team in managing patients with this condition.
Objectives:
Describe the epidemiology of aflatoxin toxicity.
Outline the typical presentation of a patient with aflatoxin toxicity.
Explain the treatment options for patients with aflatoxin toxicity.
Review the importance of improving care coordination among the interprofessional team to enhance care coordination for patients affected by aflatoxin toxicity.
Introduction
Aflatoxins are metabolites produced by toxigenic strains of molds, mainly Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus, which grow in soil, hay, decaying vegetation, and grains. Aflatoxin toxicity occurs due to acute or chronic exposure to aflatoxin. The term "aflatoxin" is derived from the name Aspergillus flavus. It was named around 1960 after its discovery as the source of a disease in turkey called turkey X disease.[1] It was also observed as the cause of cancer in rainbow trout fed on peanut and cottonseed meals.
Dietary exposure to aflatoxins may result in severe toxic and carcinogenic outcomes in humans and animals. The symptoms and biomarkers of exposure, production, and metabolism of aflatoxin and methods to reduce aflatoxin toxicity have been widely investigated over the last 50 years.[2] Studies have mostly focused on humans, agricultural animals, or laboratory model species and have identified species-specific aspects of aflatoxin toxicity.[3][4][3]
Aflatoxins form one of the major groupings of mycotoxins. Aflatoxin is produced by fungal action during the production, harvest, storage, and processing of food and feed. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it an unavoidable contaminant of foods. Aflatoxin exposure can cause nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and convulsions acutely, and its chronic exposure can also lead to complications like hepatotoxicity, immunotoxicity, and teratogenicity. Aflatoxin is one of the major causes of hepatocellular carcinoma in developing countries.[5]
Different types of aflatoxin, such as aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) and aflatoxin B2 (AFB2), are produced by both A. flavus and A. parasiticus. AFB1 is believed to be the most potent among all aflatoxins. Aflatoxin M1 (AFM1) is found in the fermentation broth of A. parasiticus, but it and aflatoxin M2 are also developed when an infected liver metabolizes AFB1 and AFB2. AFM1 can be transmitted by milk.[6]
AFB1 and AFM1 have been classified as group 1 and group 2B human carcinogens by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC).[7][8]
Etiology
Around 25% of the world's crop is affected by mycotoxin, most of which is aflatoxin. They are regularly found in improperly stored cassava, cottonseed, chili pepper, maize, wheat, millet, peanut, rice, sesame, sunflower seed, and many spices. Crops can be contaminated in two phases:
- Aspergillus species infect crops during growth and development.
- Contamination can build during storage or transport with exposure to warm and humid conditions or severe drought.
Animals fed on contaminated feed can pass aflatoxin metabolism products into eggs, milk products, and meat, and thus humans can be exposed.[8]
Structural derivatives of difurocoumarin and aflatoxins are commonly produced by strains of A. flavus, A. parasiticus, and A. minus. Furthermore, many other Aspergilli, such as Emericella teleomorphs, have aflatoxigenic capabilities. Named according to their green or blue color under UV light, there are four primary aflatoxins. Of these, AFB is the most mutagenic, the most hepatotoxic, and the most prevalent worldwide.[9]
The following is a concise list of all the risk factors that can lead to aflatoxin exposure in humans and livestock:
- Contaminated feed (corn, cottonseed, peanuts, sorghum, figs, tree nuts, and spices)[10]
- Stress from drought or insect damage[11]
- Warm and humid conditions
- Temperatures near 30 C (86 F)
- Substrate, CO levels, time, and other environmental factors
Epidemiology
Around 4.5 billion people in developing countries are exposed to largely uncontrolled amounts of aflatoxin.[8] Children are particularly affected by aflatoxin exposure. It is associated with growth stunting, development delays, and liver damage, ultimately leading to liver cancer. Many reports show an association between growth stunting and aflatoxin exposure in children.[12][13] Also, epidemiological studies are underway to establish a causal relationship between growth stunting and aflatoxin exposure. Adults have a higher tolerance for aflatoxin exposure than children, though they remain at risk. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a well-established sequela of aflatoxin exposure, and 4.6% to 28.2% of all global cases of HCC can be caused by aflatoxin. Around 25% of all high-dose acute exposures may cause death.[14][15][16]
Pathophysiology
Evidence shows that the dose and duration of aflatoxin exposure significantly affect toxicology. Exposure to large doses, known as acute aflatoxicosis, can lead to critical illness and death. High-level exposure produces acute hepatic necrosis, resulting in sequelae of cirrhosis or HCC afterward. Acute liver failure manifests as fever, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, bleeding, digestion problems, edema, malabsorption, mental changes, and coma.
Exposure to chronic sublethal doses has nutritional and immunologic effects, mainly contributing to DNA alkylation by aflatoxin B1. Irrespective of the dose, all exposures have a cumulative effect on cancer risk. The carcinogenic effect of aflatoxin metabolites is via intercalation into DNA and the alkylation of the bases by epoxide moiety. This results in mutations in the p53 gene, an essential gene in preventing cell cycle progression in instances of DNA mutations or signaling of the programmed cell death (apoptosis).[16][17][18]
Evaluating the results of human exposure to aflatoxin requires considering various facts. Firstly, not all ingested aflatoxin is biologically significant; a proportion of consumed aflatoxin is detoxified. The relationship between DNA-relevant exposure and carcinogenesis is understood well enough to estimate the results of changing the concentration of aflatoxins in food for the risk to humans.[19] Secondly, other aspects of the diet could significantly define the consequence of aflatoxin ingestion. Dietary intake of antioxidant vitamins (vitamins A, C, and E) can influence aflatoxin toxicity.[20] Thirdly, the extent of biological exposure is influenced by infections, such as the hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus.
Histopathology
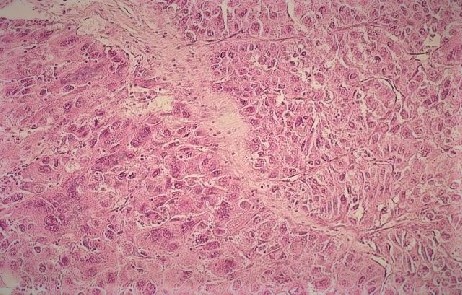
The liver is the main organ affected by the toxic effects of aflatoxin. Histopathologic changes in acute hepatotoxicity due to aflatoxin toxicity are fatty changes in hepatocytes, acute hemorrhagic necrosis, and bile duct proliferation. Also, chronic aflatoxin exposure may present with histopathologic features of cirrhosis, such as nodular degeneration and fibrosis leading to distortion of the hepatic architecture and HCC, which are well-vascularized tumors with wide trabeculae, small cell changes, vascular invasion, prominent acinar pattern, atypia, mitotic activity, and absence of Kupffer cells.[16][21][10] See Image. Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Toxicokinetics
The most common route of entry of aflatoxin into the human body is ingestion. After entry, it is metabolized by microsomal mixed-function oxidase (MFO) enzymes in the liver to reactive epoxide intermediate. MFO is an enzyme of the CYP450 superfamily. This epoxide intermediate (8,9-epoxide) is responsible for DNA mutation. The predominant mutation has been identified as the G→T transversion in codon 249 of the p53 tumor suppressor gene. This epoxide can bind to other macromolecules like RNA and proteins, causing cellular dysregulation. It is also responsible for inhibiting proteins, RNA, and DNA synthesis. Another pathway to toxicity is glutathione depletion and subsequent toxicity from reactive oxygen species. Other pathways of carcinogenesis, catalyzed by prostaglandin H (PGH) synthase and lipid peroxidase (LPO), are under study.
Another pathway of aflatoxin metabolism is by microsomal biotransformation of AFB1 by hydroxylation. It leads to the formation of less toxic and non-polar metabolites like AFM1 and aflatoxin Q1 (AFQ1). Also, enzymatic and non-enzymatic action on AFB1 can produce a dialdehyde form. Aflatoxin dialdehyde is acted upon by aflatoxin aldehyde reductase (AFAR) and excreted through urine as dialcohol. It can also bind proteins, mostly albumin.[7][17][18][22]
History and Physical
Whenever aflatoxin toxicity is suspected, a thorough history regarding the patient's dietary habits, similar complaints in family and community, the patient's occupation, and environmental exposure should be assessed. Health implications from aflatoxin toxicity depend on several factors ranging from the dose and duration of exposure to a person's gender, age, health, immunity, environmental factors, and diet. Patients with aflatoxin toxicity can have a range of non-specific signs and symptoms; however, the most prominent features are those of hepatotoxicity. Adults generally have a good tolerance to aflatoxin, and children have higher mortality. Children tend to have severe malnutrition secondary to aflatoxin toxicity.[23]
Acute toxicity results when someone consumes a high level of aflatoxins in a very short time. The most common signs and symptoms are:
- Nausea
- Yellowing of skin and sclera (icterus)
- Itching
- Vomiting
- Bleeding
- Abdominal pain
- Lethargy
- Edema
- Convulsions
- Coma
- Death
Chronic toxicity occurs through consuming small amounts of aflatoxins over a prolonged period. Chronic exposure to aflatoxin can result in the following:
- Impaired growth and development, especially in children
- Immunosuppression
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (weight loss, abdominal mass, anorexia, vomiting, nausea, bleeding, psychosis, etc.)[8][10]
Maternal exposure to aflatoxin is associated with a higher occurrence of preterm birth and late-term miscarriage.[24]
Evaluation
An evaluation of a suspected case of aflatoxin toxicity can be done by measuring the aflatoxin level in food consumed by the patient or the aflatoxin metabolites in the patient's body.
Some popular methods to detect aflatoxin exposure in food and feed are:
- Thin-layer chromatography (TLC)[25]
- High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
- Liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy (LCMS)
- Enzyme-linked immune-sorbent assay (ELISA)[26]
ELISA using AFB1-lysine (metabolite of AFB1) concentration in the patient blood can help detect aflatoxin.
Other techniques are used to detect levels of aflatoxin in the human body. One method is the measurement of the AFB-guanine adduct in the urine of patients.[27] This technique measures only recent exposure during the past 24 hours. Due to the varying half-life of this product, its level may vary from time to time based on diet. Therefore it is not ideal for assessment of long-term exposure. Measuring AFB-albumin adduct level in the blood serum is another method to detect aflatoxin exposure over a long period.
Additionally, the assessment of liver function test include prothrombin time (PT), international normalized ratio (INR), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), albumin, bilirubin, aspartate transaminase, and alanine transaminase. Imaging the liver using ultrasonography and CT-scan may help further study liver involvement.
Other tests include the basic metabolic panel, complete blood count, and renal function, depending on patient presentation and features.[8][28][29]
Treatment / Management
Acute aflatoxicosis has no known antidote, and removal of the contaminated food and replacement with an uncontaminated food source may help stop further poisoning. The management is mainly focused on symptomatic and supportive care. Meeting optimum dietary requirements with the help of supplementation may aid recovery. Largely, the focus of management should be on symptomatic control. Acute symptoms, such as fever, nausea, vomiting, and convulsions, should be carefully addressed. If signs and symptoms suggest acute liver failure, it must be recognized early, and subsequent care should follow in a critical care setting.[30][31]
Once hepatocellular carcinoma develops, there are several treatment options.[32] These include:
- Surgical resection
- Resection + ablation
- Orthotopic liver transplantation
- Thermal ablation
- Percutaneous alcohol (ethanol) injection
- Transarterial embolization
- Chemoembolization
- Radiotherapy
- Systemic chemotherapy + radioembolization
Differential Diagnosis
Aflatoxin toxicity is characterized by its toxic effects on the liver. So the presenting symptoms are similar to other causes of liver injury.
The list of differential diagnoses of acute aflatoxicosis is as follows:
- Drug intoxication (acetaminophen, tetracycline, halothane, isoniazid, ecstasy)
- Amanita species poisoning
- Infection (hepatitis-A/B/C/D/E, cytomegalovirus, Ebstein Barr virus)
- Immunological (autoimmune hepatitis)
- Metabolic (alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, Wilson disease)
- Veno-occlusive diseases[30][31]
Prognosis
The prognosis of aflatoxin toxicity depends upon the dosage and duration of exposure, nutritional status, immunity, and health. Acute exposure may cause nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, which may warrant symptomatic treatment only. Acute high-dose intoxication can be fatal in children. Chronic exposure to low-dose aflatoxin can lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, which are irreversible disease conditions with high morbidity and mortality.
Complications
Acute intoxication with a high dose of aflatoxin may result in fulminant hepatic failure and rhabdomyolysis. Chronic exposure to aflatoxin may result in liver cirrhosis and ultimately lead to hepatocellular carcinoma. Also, gall bladder carcinoma is associated with chronic toxicity.
In children, aflatoxin exposure is associated with growth stunting, nutrition deficiencies, and impaired development.[16][30]
Deterrence and Patient Education
Aflatoxin toxicity has important impacts on agriculture, livestock, and human health. Providing knowledge to the public about aflatoxin toxicity will help to ensure food safety and decrease the incidence of aflatoxin-related health problems. Aflatoxins are found in various kinds of cereal, oilseeds, spices, nuts, and animal products. Therefore, patients should be wise in their selection of food products. In addition, farmers should keep an eye on possible aflatoxin contamination during crops' growth, harvesting, storage, and transportation.
The public should be informed about early signs of aflatoxin toxicity and encouraged to seek medical help without delay. Some studies have shown that a regular diet consisting of apiaceous vegetables, such as celery, carrots, parsley, and parsnips, may help reduce the carcinogenic effects of aflatoxin.[33]
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The management and mitigation of aflatoxin toxicity encompass a wide range of professionals, such as farmers, agriculture engineers, food technicians, veterinary physicians, and other health professionals. Protecting food from aflatoxin is a significant step in limiting the health impacts of aflatoxin. Health professionals should be aware of the prevalence of aflatoxin toxicity and food practices in the region in which they live. Exposure in a patient warrants a food checkup of the patient and the family and community. This process helps trace the source of exposure and limits its effect.
The majority of presenting cases of aflatoxin toxicity are late presentations after chronic exposures. Aflatoxin toxicity is one of the major causes of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in developing countries. Acute high-dose exposures are rare, and most severe cases occur in children. Recognition of this condition throughout multiple contact points in the healthcare system is imperative. An interprofessional healthcare team is critical to successfully identifying and managing these toxicities. High-dose acute intoxication may require admission and close monitoring as life-threatening fulminant hepatitis will need intensive care support.[8][16] [Level 5]