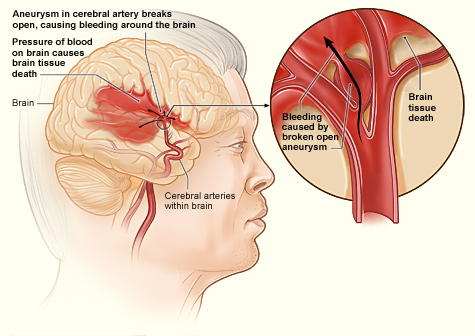
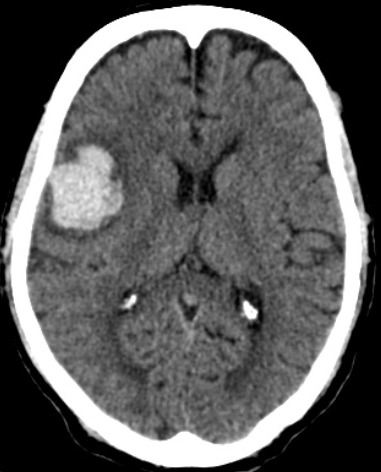
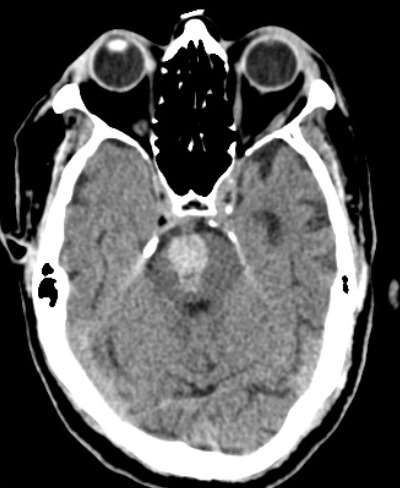
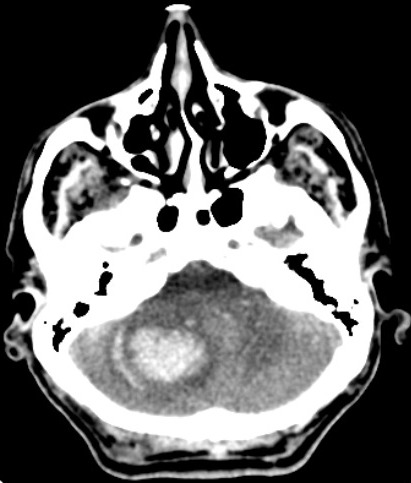
[1]
Chen S, Zeng L, Hu Z. Progressing haemorrhagic stroke: categories, causes, mechanisms and managements. Journal of neurology. 2014 Nov:261(11):2061-78. doi: 10.1007/s00415-014-7291-1. Epub 2014 Mar 5
[PubMed PMID: 24595959]
[2]
Kitagawa K. Blood pressure management for secondary stroke prevention. Hypertension research : official journal of the Japanese Society of Hypertension. 2022 Jun:45(6):936-943. doi: 10.1038/s41440-022-00908-1. Epub 2022 Apr 18
[PubMed PMID: 35437312]
[3]
Castello JP, Pasi M, Kubiszewski P, Abramson JR, Charidimou A, Kourkoulis C, DiPucchio Z, Schwab K, Anderson CD, Gurol ME, Greenberg SM, Rosand J, Viswanathan A, Biffi A. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Depression Among Intracerebral Hemorrhage Survivors. Stroke. 2022 Feb:53(2):523-531. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.035488. Epub 2021 Sep 30
[PubMed PMID: 34587793]
[4]
Ojaghihaghighi S, Vahdati SS, Mikaeilpour A, Ramouz A. Comparison of neurological clinical manifestation in patients with hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke. World journal of emergency medicine. 2017:8(1):34-38. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2017.01.006. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 28123618]
[5]
An SJ, Kim TJ, Yoon BW. Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Clinical Features of Intracerebral Hemorrhage: An Update. Journal of stroke. 2017 Jan:19(1):3-10. doi: 10.5853/jos.2016.00864. Epub 2017 Jan 31
[PubMed PMID: 28178408]
[6]
Magid-Bernstein J, Girard R, Polster S, Srinath A, Romanos S, Awad IA, Sansing LH. Cerebral Hemorrhage: Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Future Directions. Circulation research. 2022 Apr 15:130(8):1204-1229. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319949. Epub 2022 Apr 14
[PubMed PMID: 35420918]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[7]
Aronowski J, Zhao X. Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral hemorrhage: secondary brain injury. Stroke. 2011 Jun:42(6):1781-6. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.596718. Epub 2011 Apr 28
[PubMed PMID: 21527759]
[8]
Matsuyama T, Okuchi K, Seki T, Higuchi T, Murao Y. Perimesencephalic nonaneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage caused by physical exertion. Neurologia medico-chirurgica. 2006 Jun:46(6):277-81; discussion 281-2
[PubMed PMID: 16794347]
[9]
Coelho LG, Costa JM, Silva EI. Non-aneurysmal spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage: perimesencephalic versus non-perimesencephalic. Revista Brasileira de terapia intensiva. 2016 Jun:28(2):141-6. doi: 10.5935/0103-507X.20160028. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 27410409]
[10]
Fekadu G, Chelkeba L, Kebede A. Risk factors, clinical presentations and predictors of stroke among adult patients admitted to stroke unit of Jimma university medical center, south west Ethiopia: prospective observational study. BMC neurology. 2019 Aug 7:19(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12883-019-1409-0. Epub 2019 Aug 7
[PubMed PMID: 31390995]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[11]
Kushner MJ, Bressman SB. The clinical manifestations of pontine hemorrhage. Neurology. 1985 May:35(5):637-43
[PubMed PMID: 3990963]
[12]
Hakimi R, Garg A. Imaging of Hemorrhagic Stroke. Continuum (Minneapolis, Minn.). 2016 Oct:22(5, Neuroimaging):1424-1450
[PubMed PMID: 27740983]
[13]
Smith EE, Rosand J, Greenberg SM. Hemorrhagic stroke. Neuroimaging clinics of North America. 2005 May:15(2):259-72, ix
[PubMed PMID: 16198939]
[14]
Kazui S, Minematsu K, Yamamoto H, Sawada T, Yamaguchi T. Predisposing factors to enlargement of spontaneous intracerebral hematoma. Stroke. 1997 Dec:28(12):2370-5
[PubMed PMID: 9412616]
[15]
Broderick JP, Brott TG, Duldner JE, Tomsick T, Huster G. Volume of intracerebral hemorrhage. A powerful and easy-to-use predictor of 30-day mortality. Stroke. 1993 Jul:24(7):987-93
[PubMed PMID: 8322400]
[16]
Macellari F, Paciaroni M, Agnelli G, Caso V. Neuroimaging in intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2014 Mar:45(3):903-8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.003701. Epub 2014 Jan 14
[PubMed PMID: 24425128]
[17]
Becker KJ, Baxter AB, Bybee HM, Tirschwell DL, Abouelsaad T, Cohen WA. Extravasation of radiographic contrast is an independent predictor of death in primary intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 1999 Oct:30(10):2025-32
[PubMed PMID: 10512902]
[18]
Delgado Almandoz JE, Romero JM. Advanced CT imaging in the evaluation of hemorrhagic stroke. Neuroimaging clinics of North America. 2011 May:21(2):197-213, ix. doi: 10.1016/j.nic.2011.01.001. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 21640295]
[19]
Siddiqui FM, Bekker SV, Qureshi AI. Neuroimaging of hemorrhage and vascular defects. Neurotherapeutics : the journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics. 2011 Jan:8(1):28-38. doi: 10.1007/s13311-010-0009-x. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 21274683]
[20]
Hemphill JC 3rd, Greenberg SM, Anderson CS, Becker K, Bendok BR, Cushman M, Fung GL, Goldstein JN, Macdonald RL, Mitchell PH, Scott PA, Selim MH, Woo D, American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, Council on Clinical Cardiology. Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2015 Jul:46(7):2032-60. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000069. Epub 2015 May 28
[PubMed PMID: 26022637]
[21]
Schlunk F, Kuthe J, Harmel P, Audebert H, Hanning U, Bohner G, Scheel M, Kleine J, Nawabi J. Volumetric accuracy of different imaging modalities in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. BMC medical imaging. 2022 Jan 15:22(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00735-3. Epub 2022 Jan 15
[PubMed PMID: 35033012]
[22]
Berlit P. Diagnosis and treatment of cerebral vasculitis. Therapeutic advances in neurological disorders. 2010 Jan:3(1):29-42. doi: 10.1177/1756285609347123. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 21180634]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[23]
Lapchak PA, Araujo DM. Advances in hemorrhagic stroke therapy: conventional and novel approaches. Expert opinion on emerging drugs. 2007 Sep:12(3):389-406
[PubMed PMID: 17874968]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[24]
Qureshi AI, Palesch YY, Martin R, Novitzke J, Cruz-Flores S, Ehtisham A, Ezzeddine MA, Goldstein JN, Hussein HM, Suri MF, Tariq N, Antihypertensive Treatment of Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage Study Investigators. Effect of systolic blood pressure reduction on hematoma expansion, perihematomal edema, and 3-month outcome among patients with intracerebral hemorrhage: results from the antihypertensive treatment of acute cerebral hemorrhage study. Archives of neurology. 2010 May:67(5):570-6. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.61. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 20457956]
[25]
Anderson CS, Huang Y, Arima H, Heeley E, Skulina C, Parsons MW, Peng B, Li Q, Su S, Tao QL, Li YC, Jiang JD, Tai LW, Zhang JL, Xu E, Cheng Y, Morgenstern LB, Chalmers J, Wang JG, INTERACT Investigators. Effects of early intensive blood pressure-lowering treatment on the growth of hematoma and perihematomal edema in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: the Intensive Blood Pressure Reduction in Acute Cerebral Haemorrhage Trial (INTERACT). Stroke. 2010 Feb:41(2):307-12. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.561795. Epub 2009 Dec 31
[PubMed PMID: 20044534]
[26]
Mayer SA, Brun NC, Begtrup K, Broderick J, Davis S, Diringer MN, Skolnick BE, Steiner T, FAST Trial Investigators. Efficacy and safety of recombinant activated factor VII for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. The New England journal of medicine. 2008 May 15:358(20):2127-37. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0707534. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 18480205]
[27]
Gigliotti MJ, Srikanth S, Cockroft KM. Patterns of prophylactic anticonvulsant use in spontaneous intracerebral and subarachnoid hemorrhage: results of a practitioner survey. Neurological sciences : official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology. 2022 Mar:43(3):1873-1877. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05588-2. Epub 2021 Sep 8
[PubMed PMID: 34495437]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[28]
Mendelow AD, Gregson BA, Fernandes HM, Murray GD, Teasdale GM, Hope DT, Karimi A, Shaw MD, Barer DH, STICH investigators. Early surgery versus initial conservative treatment in patients with spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral haematomas in the International Surgical Trial in Intracerebral Haemorrhage (STICH): a randomised trial. Lancet (London, England). 2005 Jan 29-Feb 4:365(9457):387-97
[PubMed PMID: 15680453]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[29]
Hattori N, Katayama Y, Maya Y, Gatherer A. Impact of stereotactic hematoma evacuation on activities of daily living during the chronic period following spontaneous putaminal hemorrhage: a randomized study. Journal of neurosurgery. 2004 Sep:101(3):417-20
[PubMed PMID: 15352598]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[30]
Mould WA, Carhuapoma JR, Muschelli J, Lane K, Morgan TC, McBee NA, Bistran-Hall AJ, Ullman NL, Vespa P, Martin NA, Awad I, Zuccarello M, Hanley DF, MISTIE Investigators. Minimally invasive surgery plus recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator for intracerebral hemorrhage evacuation decreases perihematomal edema. Stroke. 2013 Mar:44(3):627-34. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000411. Epub 2013 Feb 7
[PubMed PMID: 23391763]
[31]
Morgan T, Awad I, Keyl P, Lane K, Hanley D. Preliminary report of the clot lysis evaluating accelerated resolution of intraventricular hemorrhage (CLEAR-IVH) clinical trial. Acta neurochirurgica. Supplement. 2008:105():217-20
[PubMed PMID: 19066112]
[32]
Moussa WM, Khedr W. Decompressive craniectomy and expansive duraplasty with evacuation of hypertensive intracerebral hematoma, a randomized controlled trial. Neurosurgical review. 2017 Jan:40(1):115-127. doi: 10.1007/s10143-016-0743-6. Epub 2016 May 27
[PubMed PMID: 27235128]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[33]
Takeuchi S, Wada K, Nagatani K, Otani N, Mori K. Decompressive hemicraniectomy for spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurgical focus. 2013 May:34(5):E5. doi: 10.3171/2013.2.FOCUS12424. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 23634924]
[34]
Kellner CP, Connolly ES Jr. Neuroprotective strategies for intracerebral hemorrhage: trials and translation. Stroke. 2010 Oct:41(10 Suppl):S99-102. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.597476. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 20876519]
[35]
Laskowitz DT, Kolls BJ. Neuroprotection in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2010 Oct:41(10 Suppl):S79-84. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.595090. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 20876512]
[36]
Lin J, Cai C, Xie Y, Yi L. Acute glycemic variability and mortality of patients with acute stroke: a meta-analysis. Diabetology & metabolic syndrome. 2022 May 10:14(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00826-9. Epub 2022 May 10
[PubMed PMID: 35538585]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[37]
Linn J, Brückmann H. Differential diagnosis of nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage. Klinische Neuroradiologie. 2009 Mar:19(1):45-61. doi: 10.1007/s00062-009-8036-x. Epub 2009 May 15
[PubMed PMID: 19636678]
[38]
Hemphill JC 3rd, Bonovich DC, Besmertis L, Manley GT, Johnston SC. The ICH score: a simple, reliable grading scale for intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2001 Apr:32(4):891-7
[PubMed PMID: 11283388]
[39]
Trevisi G, Caccavella VM, Scerrati A, Signorelli F, Salamone GG, Orsini K, Fasciani C, D'Arrigo S, Auricchio AM, D'Onofrio G, Salomi F, Albanese A, De Bonis P, Mangiola A, Sturiale CL. Machine learning model prediction of 6-month functional outcome in elderly patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurgical review. 2022 Aug:45(4):2857-2867. doi: 10.1007/s10143-022-01802-7. Epub 2022 May 6
[PubMed PMID: 35522333]
[40]
Balami JS, Buchan AM. Complications of intracerebral haemorrhage. The Lancet. Neurology. 2012 Jan:11(1):101-18. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70264-2. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 22172625]
[41]
Putaala J, Lehto M, Meretoja A, Silvennoinen K, Curtze S, Kääriäinen J, Koivunen RJ, Kaste M, Tatlisumak T, Strbian D. In-hospital cardiac complications after intracerebral hemorrhage. International journal of stroke : official journal of the International Stroke Society. 2014 Aug:9(6):741-6. doi: 10.1111/ijs.12180. Epub 2013 Sep 12
[PubMed PMID: 24025067]