Continuing Education Activity
Thoracic empyema is an infectious process defined by frank pus in the pleural space. Due to the high mortality associated with this condition, health professionals should be cognizant of the multifactorial pathogenesis, different stages of the disease, and treatment modalities available. Rapid diagnosis is essential to successful treatment and patient survival. Treatment aims at combining medical and surgical interventions that target eradication of the infection and ensure adequate lung re-expansion. This activity reviews the evaluation and treatment of thoracic empyemas and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and treating patients with this condition.
Objectives:
Identify the etiology of empyema, including risk factors associated with common medical conditions and bacteriology.
Outline the pathophysiology of empyema, including the different stages of the disease.
Review the medical and surgical treatment options available for empyema.
Explain a well-coordinated, interprofessional team approach to provide effective care to patients affected by thoracic empyema.
Introduction
Thoracic empyema, an infectious process defined by frank pus in the pleural space, has been recognized since the time of Hippocrates and historically carries a considerably high mortality.[1] Empyema is a complex entity with multifactorial pathogenesis and etiology, and clinicians should be mindful in recognizing different stages of the disease.[2] Rapid diagnosis is essential to successful treatment and patient survival. Treatment aims at combining medical and surgical interventions that target the source of infection and ensure adequate lung re-expansion.
Etiology
Risk Factors
A significant proportion of pleural space infections present as complications in community- or hospital-acquired pneumonia.[1] Other causes include penetrating chest trauma, thoracic surgery, esophageal rupture, pulmonary tuberculosis, lung abscess, bronchiectasis, subphrenic abscess, and osteomyelitis of ribs. Independent risk factors for empyema development include:[3][4][5]
- Age under 60 years old
- Poor oral hygiene
- Disorders with a predisposition to aspiration (seizure, alcohol use disorder, central nervous system disease)
- IV drug misuse
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular disease
- Liver cirrhosis
- Other immunocompromised states (HIV infection, malignancy)
One prospective observational study found six risk factors associated with patients admitted with community-acquired pneumonia who subsequently developed empyema, including albumin less than 30 g/L, sodium below 130 mmol/L, platelet count greater than 400 X 109, C-reactive protein over 100 mg/L, and a history of alcohol use or intravenous drug use disorders.[6]
Bacteriology
Aerobic Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species and Gram-negative bacteria, including Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, and Klebsiella pneumoniae, were the predominant microorganisms in community-acquired empyema.[7] However, recent literature suggests that anaerobes and staphylococcal species have replaced S. pneumoniae as the major pathogen in surgically treated empyemas. Also, anaerobic isolates were found in higher incidence in CAP than previously reported.[8] Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and gram negatives, including Pseudomonas and Enterobacteriaceae, are pathogens commonly seen in hospital-acquired empyema. Anaerobes are slow growing organisms that notoriously yield negative culture media. Therefore, broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage with anaerobic coverage is warranted.
Fungal empyema is a clinical entity that is rare but carries a high mortality. One single center retrospective analysis isolated Candida and Aspergillus species from 65 critically ill patients w/ variable comorbidities, including malignancy. The majority of these cases were nosocomial infections or had concomitant fungemia.[9]
Epidemiology
In the United States, the incidence of parapneumonic empyema is estimated to be 6 cases per 100000. In-hospital mortality in the adult population (over 65 years of age) is approximately 16.1%.[10]
Pathophysiology
Approximately 60 years ago, The American Thoracic Society first described the evolution of empyema as a continuous process that subdivides into three stages.
Exudative stage - initial bacterial infection causes an acute inflammatory response between the pulmonary parenchyma and visceral pleural. Proinflammatory cytokines cause increased capillary permeability, leading to an influx of neutrophil-rich fluid into the pleural space. This exudative fluid is usually free-flowing, resolves with appropriate antibiotic treatment, and does not warrant invasive drainage.
Fibrinopurulent and Loculated stage—In the absence of appropriate treatment, the effusion can become complicated by the deposition of fibrin clots and membranes, resulting in isolated collections of fluid in the pleural space. At this stage, bacteriology usually becomes positive, and the effusion warrants antimicrobials and drainage.
Chronic Organizational stage - if not drained, fibroblasts coalesce to form a thick pleural peel between the visceral and parietal pleura. This peel can ultimately encase the underlying lung parenchyma and complicate the clinical course by inhibiting adequate gas exchange, trapped lung, or chronic forms of empyema.[11]
History and Physical
Clinical presentation can be multifactorial and varies based on underlying comorbidities, the timing of clinical presentation, and the causative microorganism. Patients with empyema generally present late in the clinical course with untreated pneumonia or mismanaged complicated pleural effusions. Common clinical features of empyema are nonspecific and similar to bacterial pneumonia. Symptoms include cough, dyspnea, fever, and/or pleuritic chest pain.
On physical exam, dullness to percussion and decreased breath sounds can be appreciated but are not particularly diagnostic of empyema. Therefore, imaging may be necessary in any patient with suspected parapneumonic effusion.
Evaluation
Imaging
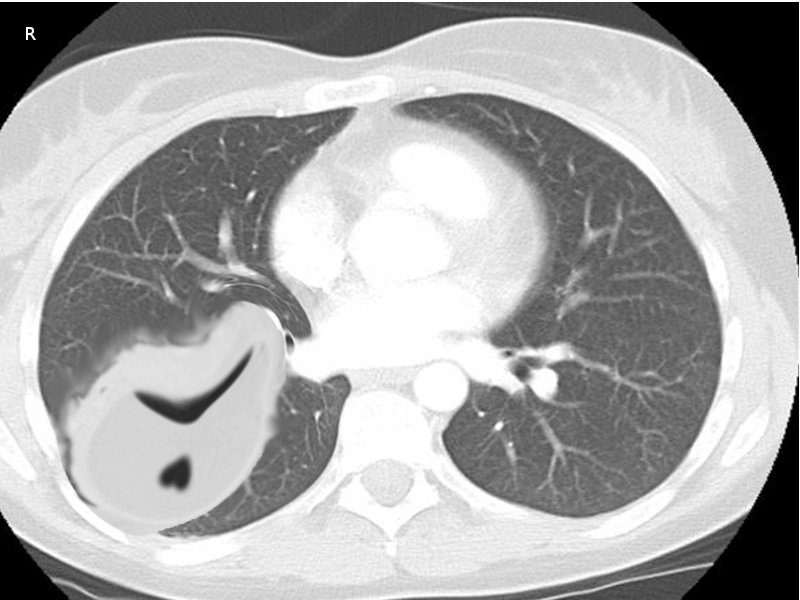
Chest imaging is a fundamental step in the diagnosis and management of empyema. Despite advances in imaging modalities, plain radiographs still serve as a great screening tool for pleural effusions in patients with pneumonia. Typically, a unilateral, markedly asymmetric pleural effusion with blunting of the costophrenic angle can be appreciated. Smaller volume effusions are detectable with a lateral view X-ray. Decubitus views can be obtained to assess for layering and help quantify an existing effusion. However, ultrasonography and computed tomography (CT) scanning have greater sensitivity for fluid detection and provide additional information for determining the extent and nature of the pleural infection.[12] Ultrasound is useful in providing an accessible, radiation-free method of visualizing free versus loculated pleural effusions. One series published in Thorax, 2017, showed ultrasound had better sensitivity for diagnosing pleural effusion when compared to plain radiographs.[13] CT scan with intravenous contrast is optimal and has a high diagnostic yield for empyema. The “split pleura” sign is a radiologic finding with a high diagnostic value for empyema. Enhancement and thickening of both the visceral and parietal pleura on CT scan with separation by pleural fluid over 30 mm is highly suggestive of a complicated parapneumonic effusion amenable to drainage.[14]
Thoracocentesis
The recommendation is for diagnostic fluid sampling via thoracentesis in all patients with pleural effusions with greater than 2 cm depth on lateral decubitus film or computed tomography associated with a pneumonic illness, recent chest trauma, surgery, or features of ongoing sepsis.[12][13] Frank pus in the pleural space invariably necessitates surgical drainage. However, if there is uncertainty whether a turbid fluid is infected, a pH less than 7.2 measured via a blood gas analyzer warrants an invasive procedure for drainage.[14] Polymorphonucleocyte predominance, low glucose, and LDH over 1000 on biochemical analysis of pleural fluid support the diagnosis of empyema. Furthermore, fluid culture data should be used to guide appropriate antimicrobial therapy. Research shows that culture yield can be increased significantly if the pleural fluid gets injected into blood culture bottles immediately after aspiration.[15]
Other Tests
Blood cultures are necessary for any patient with empyema. Although generally nondiagnostic, they can help identify causative pathogens and identify bacteremia if the results are positive.
Treatment / Management
In 2000, the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) published clinical practice guidelines on the medical and surgical approach to effusions and empyema. The risk of poor outcome was directly related to the following three variables: pleural space anatomy, pleural fluid bacteriology, and pleural fluid chemistry. Per ACCP consensus, categories 1 and 2 involve effusions in the exudative stage, are free-flowing, and carry the lowest risk for adverse outcomes. Category 3 defines complicated effusions in the fibrinopurulent stage and can be larger, free-flowing, or loculated and carry a moderate risk for poor outcomes. Empyema, category 4, carries the highest risk for poor outcomes.[16] The goals of therapy for empyema include eradication of the infection via antimicrobials and pleural drainage via tube thoracostomy with or without adjuvant intrapleural medications, video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS), or by open thoracostomy and decortication.
Antimicrobials
For most patients with suspected or confirmed empyema, empiric broad-spectrum antibiotics are necessary. Initiation should not delay pending diagnostic procedures. Antimicrobials should be tailored to target pathogens based on geographic epidemiology, antibiotic resistance patterns, mode of acquisition (aspiration, trauma), and whether the affected patient presents from a community versus a healthcare setting.
-
Community-acquired empyema—The antibiotic regimen should target common pathogens of the oropharynx, including aerobic Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species and anaerobes. Appropriate antibiotics include third-generation cephalosporins, metronidazole, or a beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor combination.
- Hospital-acquired empyema - As well as covering typical organisms and anaerobes, antimicrobial therapy should be directed at providing coverage for MRSA and Pseudomonas. Reasonable options include Vancomycin plus metronidazole and an antipseudomonal cephalosporin. Vancomycin plus piperacillin/tazobactam, a broad spectrum beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor, provides both anaerobic and antipseudomonal activity.
Caution should be taken with the use of aminoglycosides due to poor pleural penetration and, therefore, are not the recommendation in the treatment of empyema.[17] Duration of antibiotics is generally recommended for 2 to 6 weeks (intravenous followed by oral), depending on the degree of infection and clinical response to therapy.[18]
Tube Thoracostomy
Under radiologic guidance, chest tube placement is the least invasive and most common non-surgical modality for empyema. Optimal thoracostomy tube size has been a controversial topic amongst chest physicians. The traditional dogma was a large bore (greater than 22 French) thoracostomy tube was more suitable for draining the viscous purulent fluid of empyemas. However, recent literature has shown no significant mortality benefit or delay in surgery between large-bore (greater than 20 French) versus small-bore chest tubes (less than 20 French).[19][20] Clinically, the location of the chest tube is more relevant than its size, as mal-positioning is often the cause of treatment failure. COnfirmation of adequate positioning should be via plain film or chest CT within the first 24 hours. Most chest tubes are left in place until the drainage is less than 50 ml in 24 hours or if there is proof of lung re-expansion on chest radiography.
The use of adjunctive intrapleural medications is controversial. The data regarding isolated use of fibrinolytic drugs (streptokinase, tissue plasminogen activator (TPA), and urokinase) has been underwhelming and has shown no profound benefit in patient outcomes or need for surgical intervention. In contrast, combination therapy of fibrinolytic agents and mucolytics, particularly TPA–DNase therapy, improved fluid drainage for patients with pleural infection and reduced the frequency of surgical referral and the duration of the hospital stay. Despite such positive outcomes, there was no change in mortality.[19]
Recently, a new intrapleural irrigation approach using saline lavage has reported benefits for patients with empyema. The Pleural Irrigation Trial (PIT) found radiographic improvement after three days in empyema patients receiving saline irrigation via tube thoracostomy vs. standard of care. A smaller retrospective study comparing saline flushes plus urokinase versus saline alone found decreased chest tube duration and use of fibrinolytics. Although researchers noted no mortality benefit, more extensive randomized studies are needed to confirm the benefits of this inexpensive, well-tolerated therapy.[20]
VATS
Surgical consultation should be a consideration when drainage via tube thoracostomy fails or in multi-loculated empyema. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) is a minimally invasive surgical technique that allows for direct visualization and evacuation of the infected pleural space. Although the appropriate timing of VATS is unclear, it has been documented to have superior outcomes when compared to tube thoracostomy for the treatment of advanced-stage empyema in terms of postoperative morbidity, complications, and length of hospital stay.[21]
Open Thoracostomy and Decortication
Persistent empyema refractory to standard therapies, including VATS, should be considered for open window thoracostomy (OWT) with prolonged chest tube drainage or decortication. Acute empyema can have long-term consequences despite adequate therapeutic interventions. Pleural scarring and fibrosis can lead to adhesions, decreased lung compliance, and a restrictive lung disease pattern. A decortication is an option for lung re-expansion if symptoms persist 6 months after empyema resolution.
Differential Diagnosis
- Pneumonia (community, healthcare-acquired, aspiration)
- Hemothorax
- Chylothorax
- Pulmonary infarct
Prognosis
Empyema carries a poor prognosis if not treated early and aggressively from the time of diagnosis. Although most patients recover, clinical outcomes remain poor, with one in five patients requiring surgery and 20% dying within the first year of diagnosis. There is a 1.5 times increase in negative outcomes in the frail, older patients, and immunocompromised population.
Complications
Complications of empyema can be secondary to the underlying disease process, and patients may succumb to worsening sepsis, septic shock, or death. Complications can also arise from incomplete drainage due to tube malposition or malfunction. This complication can lead to pneumothorax, bronchopleural fistulas, and pleural fibrosis with subsequent trapped lung. One rare complication, empyema necessitans, refers to the extension and subsequent dissection into the subcutaneous tissue of the chest wall.[22]
Deterrence and Patient Education
Parapneumonic effusions can progress to empyema if not treated appropriately from the time of symptom onset. There is often a delay in the diagnosis of pleural effusion. Clinicians should have a high index of suspicion of empyema in patients with pneumonia, persistent fever, and elevated inflammatory markers who have failed conservative antibiotic therapy. Patients should also be informed to seek medical attention if they notice a decline in their respiratory status, pleuritic chest pain, or refractory fever in the setting of a known pneumatic process despite antimicrobials.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The management of empyema can be challenging and complex. Coordination of care across multiple disciplines is necessary, functioning as a cohesive interprofessional team, to optimize positive patient outcomes. Since therapeutic options for empyema involve medical and surgical intervention, the involvement of several specialists is prudent in improving morbidity and mortality. The American Association for Thoracic Surgery (ATS), British Thoracic Society (BTS), and American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) have published comprehensive, evidence-based guidelines to help guide healthcare professionals in their treatment of empyema. ATS and BTS guidelines provide a concise approach to appropriate antibiotic use, sampling, and analysis via thoracentesis, tube thoracostomy drainage for frank empyema, and prompt surgical referral if patients are not improving. BTS guidelines recommend the early involvement of a chest physician or thoracic surgeon in the care of patients requiring tube thoracostomy. These highly skilled physicians can help identify surgical candidates early, assess thoracic surgical risk, manage potential complications associated with invasive procedures, and involve their cardiothoracic surgeon colleagues when appropriate.[23] The American Association for Thoracic Surgery (ATS) guidelines support the involvement of infectious disease specialists to help guide antibiotic stewardship.[24] ACCP guidelines focus on the management of empyema and the risk of poor outcomes without adequate therapy.[16] Despite overwhelming evidence from multiple expert panels, the strength of quality evidence is lacking. Further research is warranted across medical and surgical specialties to develop an optimal treatment strategy that improves morbidity and mortality. [Level I]
In addition to the specialists, other members of the interprofessional healthcare team need to collaborate to optimize patient outcomes for empyema patients. Nurses will provide post-surgical care and can report to the team regarding patient progress. Nursing is also on the front lines for adverse drug reactions, and can contact the pharmacist if necessary for guidance, then reach out to the managing physician. Pharmacists can perform medication reconciliation, alert the prescribing clinicians regarding potential drug interactions, and verify dosing and antimicrobial coverage. All these disciplines must collaborate across interprofessional lines as a team for optimal patient treatment. [Level 5]