Introduction
Plasma cells are differentiated B-lymphocyte white blood cells capable of secreting immunoglobulin or antibodies. They play a significant role in the adaptive immune response, being the main cells responsible for humoral immunity. Without their presence, an individual is said to have agammaglobulinemia and is highly susceptible to recurrent infection. Here, the hematopoietic lineage, structure, and function of plasma cells, along with the clinical presentations arising from improper plasma cell growth and development, are reviewed.
Function
After antigenic stimulation, plasma cells develop from antigen-activated B lymphocytes in lymphoid organs, such as the bone marrow, spleen, and lymph nodes. Blimp-1, IRF4, and XBP-1 transcription factors are known to be essential for the differentiation of mature B cells into plasma cells.[1][2] BLIMP-1 and XBP-1 are often viewed as key regulators of plasma cell differentiation, with Blimp-1 working upstream of XBP-1.[3][4][5][6] Plasma cell differentiation is also linked to the activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling pathway.[5][7] UPR activation aids in the plasma cell’s ability to adapt continually to an ever-changing milieu. However, the UPR’s function is still under investigation; the belief is that the UPR plays a role in monitoring immunoglobulin concertation and modulating or suppressing immunoglobulin secretion.[8]
The most immature blood cell of a plasma cell lineage is the plasmablast. Plasmablasts can proliferate and secrete small amounts of antibodies. The terminally differentiated or mature plasma cells are non-proliferating, are much larger than B cells, and can secrete large amounts of antibodies. During their lifespan of 2 to 3 days, they continuously synthesize and secrete antibodies with specificity for the antigen that stimulated the plasma cell precursor to proliferate and differentiate. Estimates are that a single plasma cell can secrete hundreds to thousands of antibody molecules per second, a remarkable measure of the power of the immune response for combating pathogens. Plasma cells, as antibody factories, are important contributors to humoral immunity.
Though the production and secretion of antibodies were long thought to be the sole functions of plasma cells, recent studies indicate plasma cell involvement in immune response regulation. Research has found that plasma cells inhibit the development of follicular T-helper cells within this capacity.[9] Mice devoid of plasma cells, via knock-out of the BLIMP-1 gene, expressed elevated levels of follicular T-helper cells, which, in turn, produce IL-21, a protein critical for the processes of affinity maturation, germinal center longevity and function, and B-lymphocyte terminal differentiation.[1][10] The elevated IL-21 resulting from lacking plasma cells could alter germinal center activity and fates or B-lymphocyte levels. In contrast, limited follicular T-helper cells and IL-21 appear to elevate a competitive milieu for active germinal center physiology, resulting in enhanced B-lymphocyte affinity and maturation. These findings suggest that an antigen-specific negative feedback loop exists, modulating plasma cell production, thus mitigating unnecessary and potentially pathological excess plasma cell numbers.[9][10]
Histochemistry and Cytochemistry
All plasma cells, albeit normal or malignant, are distinguished by their expression of CD38 and CD138.[11] The former catalyzes the synthesis and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose, resulting in the maintenance of intracellular calcium levels.[12] In contrast, CD138, syndecan-1, allows the plasma cell to attach to extracellular matrix proteins. Recent research has found that in addition to its role in plasma cell adhesion, CD138 plays a further role in acting as a co-receptor for epithelial growth factor (EGF), particularly in the context of multiple myeloma.[11][12] Though malignant plasma cells express CD38 and CD138 alongside their normal, non-malignant counterparts, a distinguishing characteristic unique to malignant plasma cells is the loss of CD19 expression alongside the possible aberrant expression of CD56, a marker characteristic of natural killer (NK) cells.[11][13] It bears mention, however, that not all myeloma cells express CD56.
An additional noteworthy marker of plasma cells is CD79a. The protein is critical in B-lymphocyte antigen signal transduction and overall B-lymphocyte development and stabilization.[14] Though CD79a is present in the cytoplasm of precursor B-lymphocytes and mature, differentiated plasma cells, its aberrant loss of expression has been noted in certain samples of plasma cell neoplasms.
Microscopy, Light
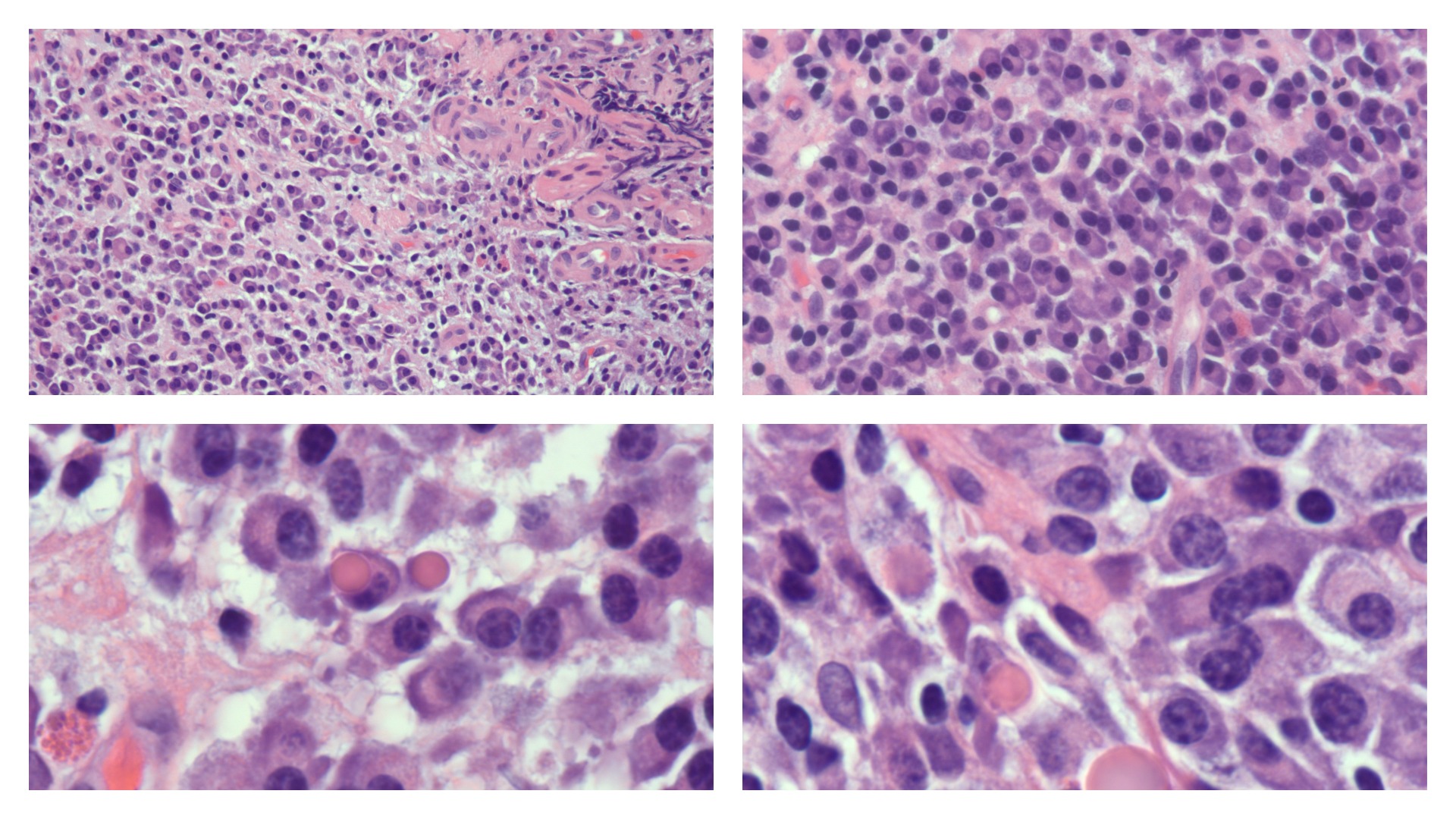
Plasma cells vary in size from 14 to 20 micrometers. They are round-to-ovoid cells containing abundant deep blue cytoplasm with a pale perinuclear area corresponding to the Golgi apparatus. They have a round, eccentrically placed nucleus with coarse chromatin arranged in a clock face (art wheel) pattern (see Image. Plasma Cells).[15] Most plasma cells are uninucleate; few are binucleate or multinucleate. They may contain cytoplasmic inclusions called Russell bodies or multiple spherical inclusions packed in their cytoplasm (Mott, grape, or morular cells). Russell bodies and the inclusions of Mott cells are dilated endoplasmic reticulum cisternae containing condensed immunoglobulins.
Microscopy, Electron
Electron microscopy reveals that the plasma cells contain an eccentric round nucleus with condensed chromatin and a well-developed nucleolus. The nuclear membrane-associated chromatin gives the nuclei of mature plasma cells a cartwheel appearance in histologic sections. The cytoplasm contains parallel arrays of rough endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasmic fibrils, and numerous polymorphic mitochondria. The cytoplasm also contains a Golgi complex immediately adjacent to the nucleus. Intracytoplasmic inclusions—elliptical, round, or needle-like crystalline—are present. A significant accumulation of immunoglobulins forms these inclusions.
Clinical Significance
Deviation from proper plasma cell proliferation can lead to a number of clinical pathologies, which are classified as plasma cell neoplasms and plasma cell immunodeficiency.
Plasma cell neoplasms are characteristically an aberrant proliferation of clonal plasma cells producing monoclonal, heavy-chain, class-switched immunoglobulin, referred to as M-protein.[16] Given the excessive proliferation and associated findings induced by such proliferation, plasma cell neoplasms can be classified into several specified pathological states. Determination of the extent of neoplasm involves a complete diagnostic evaluation, which includes the following specific tests and observations: complete CBC with differential; serum protein electrophoresis (to evaluate for M protein); immunofixation (to determine amount and type of immunoglobulin); serum-free light chain analysis; complete skeletal survey (to assess for the presence of lytic lesions); and a bone marrow biopsy (to determine the percentage of clonal plasma cells and potential cytogenetic analysis).[17]
Plasma Cell Neoplasms
MGUS
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, or MGUS, is the least severe manifestation of plasma cell neoplasm. MGUS classifies as a clonal population of plasma cells secreting immunoglobulin, though serum M-protein concentration does not exceed 3 g/dL.[18] Likewise, the clonal plasma cells do not exceed 10% of the bone marrow. Patients are often asymptomatic, and many patients with MGUS do not progress into malignancy. Research has shown that the prevalence of MGUS affects 1% to 2% of the population in the United States and Europe.[19] Men are more often affected than women, and the incidence increases with age. Further, research has identified a higher prevalence in individuals of African descent.[20]
Immunofixation studies of monoclonal proteins indicate that approximately 70% of MGUS cases are IgG, 15% are IgM, 12% are IgA, and 3% are biclonal.[21] Contingent on immunoglobulin type, MGUS is often classified into 2 main types with distinct potential clinical progression. Patients with IgM MGUS may progress to lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma or Waldenström macroglobulinemia. In contrast, the progression of non-IgM MGUS cases manifests as smoldering myeloma or multiple myeloma.
Smoldering Myeloma
As plasma cells continue to proliferate aberrantly, an individual may progress beyond the criteria of MGUS, a stage defined clinically as smoldering myeloma. In contrast to MGUS, serum M-protein levels are equal to or greater than 3 g/dL, and clonal plasma cells comprise 10% to 59% of the bone marrow.[18] By definition, a patient with smoldering myeloma does not present with CRAB lesions. CRAB lesions demonstrate calcium elevation, renal inefficacy, anemia, and bone disease (lytic lesion(s)). They are a potential manifestation seen in multiple myeloma, as explained in the following subsection.
Similar to MGUS, the criteria for smoldering myeloma manifest asymptomatically.[22] In contrast to MGUS, however, individuals with smoldering myeloma are significantly more likely to progress to the stage of symptomatic multiple myeloma: the rate of progression from smoldering myeloma to multiple myeloma is 10% annually for the first 5 years; 3% annually for the next 5 years; and 1% each year onward.[22]
Multiple Myeloma
The most severe presentation of plasma cell neoplasm is that of multiple myeloma. Though similar to smoldering myeloma in having serum M-protein concentrations of at least 3 g/dL, multiple myeloma criteria require the presence of at least 1 additional characteristic. Such include the presence of 1 or more CRAB lesions, bone marrow clonal plasma cells exceeding 60%, a serum-free light chain ratio equal to or greater than 100, and at least 1 focal lesion detected in MRI.[18]
Multiple myeloma represents approximately 10% of all hematopoietic neoplasms.[19] Symptoms vary from individual to individual and range from focal, non-specific signs to systemic involvement. Commonly presenting symptoms include anemia, usually normochromic and normocytic; bone pain, especially in the chest and back; renal failure (elevated creatinine); hypercalcemia; fatigue, infection, and weight loss.[19]Unfortunately, multiple myeloma is often incurable, ultimately resulting in death attributable to infection or renal failure. Median survival ranges from 2.5 to 5 years and is highly variable.
Other Plasma Cell Neoplasms
Amyloidosis is classified as the deposition of immunoglobulin light chain fibrils from clonal plasma cells, often of lambda composition. Such can occur independently or as sequelae of MGUS, smoldering myeloma, or multiple myeloma.[19] Deposition of amyloid fibrils most commonly occurs in the kidney, heart, nervous, and gastrointestinal systems. A positive Congo Red stain confirms the presence of amyloid, manifest by a red/pink color under light microscopy and fluorescing as apple-green birefringence when polarized. Additional plasma cell neoplasms include solitary plasmacytoma of bone and extraosseous plasmacytoma.
Plasma Cell Deficiencies
Counter to the preceding disorders, characterized by excessive plasma cells or their byproducts, common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) results from inadequate plasma cell numbers. Reduced levels of IgG, IgA, or IgM establish the diagnosis of the disorder.[23] Specifically, CVID is noted by an IgG level of < 400 mg/dL. The lack of immunoglobulin results in an increasingly significant susceptibility to bacterial infections. Further, individuals with CVID are prone to several chronic pathologies, including chronic lung disease, inflammatory bowel disease, autoimmune disorders, and lymphoid hyperplasia. As this diagnosis remains with an individual throughout his or her lifetime, antibody titer to common pathogens (ie, Haemophilus influenzae, MMR, varicella, and pneumococcus) should have consistent testing.[23] If IgG levels decrease beyond 200 mg/dL, immunoglobulin replacement therapy is recommended.
In addition to CVID, over 100 primary immunodeficiencies are attributable to improper B-lymphocyte development or function, including improper immunoglobulin production. X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is characterized by a mutant BTK gene (Bruton’s tyrosine kinase), inhibiting pre-B cell formation.[24] The result is a diminished number of mature B-lymphocytes, including plasma cells, and reduced immunoglobulin production and secretion. Given XLA’s inheritance, males are almost exclusively affected. In contrast, selective IgA deficiency (SIGAD), the most common primary immunodeficiency, affects males and females equally.[24] Though the specific mutation associated with SIGAD is not yet fully understood, the disease is known to present in a familial pattern, and the notion of multiple mutations causing SIGAD is under investigation. As implied in the name, patients with selective IgA deficiency lack IgA in the serum and mucosa; IgM and IgG levels are normal. Therefore, the condition appears due to improper isotype switching to IgA or improper IgA-secreting B cell maturation.[24] Given the sheer amount of additional primary immunodeficiencies attributable to B-lymphocytes and plasma cells, a continual understanding of these cells’ physiology is crucial for properly advancing the health sciences.