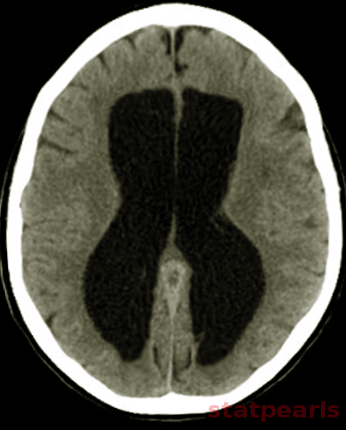
[1]
ADAMS RD, FISHER CM, HAKIM S, OJEMANN RG, SWEET WH. SYMPTOMATIC OCCULT HYDROCEPHALUS WITH "NORMAL" CEREBROSPINAL-FLUID PRESSURE.A TREATABLE SYNDROME. The New England journal of medicine. 1965 Jul 15:273():117-26
[PubMed PMID: 14303656]
[2]
Shprecher D, Schwalb J, Kurlan R. Normal pressure hydrocephalus: diagnosis and treatment. Current neurology and neuroscience reports. 2008 Sep:8(5):371-6
[PubMed PMID: 18713572]
[3]
Jaraj D, Rabiei K, Marlow T, Jensen C, Skoog I, Wikkelsø C. Prevalence of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurology. 2014 Apr 22:82(16):1449-54. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000342. Epub 2014 Mar 28
[PubMed PMID: 24682964]
[4]
Brean A, Fredø HL, Sollid S, Müller T, Sundstrøm T, Eide PK. Five-year incidence of surgery for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus in Norway. Acta neurologica Scandinavica. 2009 Nov:120(5):314-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2009.01250.x. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 19832773]
[5]
Tanaka N, Yamaguchi S, Ishikawa H, Ishii H, Meguro K. Prevalence of possible idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus in Japan: the Osaki-Tajiri project. Neuroepidemiology. 2009:32(3):171-5. doi: 10.1159/000186501. Epub 2008 Dec 19
[PubMed PMID: 19096225]
[6]
Krauss JK, Halve B. Normal pressure hydrocephalus: survey on contemporary diagnostic algorithms and therapeutic decision-making in clinical practice. Acta neurochirurgica. 2004 Apr:146(4):379-88; discussion 388
[PubMed PMID: 15057532]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[7]
Bradley WG Jr, Scalzo D, Queralt J, Nitz WN, Atkinson DJ, Wong P. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus: evaluation with cerebrospinal fluid flow measurements at MR imaging. Radiology. 1996 Feb:198(2):523-9
[PubMed PMID: 8596861]
[8]
Bateman GA. The reversibility of reduced cortical vein compliance in normal-pressure hydrocephalus following shunt insertion. Neuroradiology. 2003 Feb:45(2):65-70
[PubMed PMID: 12592485]
[9]
Stephensen H, Tisell M, Wikkelsö C. There is no transmantle pressure gradient in communicating or noncommunicating hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 2002 Apr:50(4):763-71; discussion 771-3
[PubMed PMID: 11904027]
[10]
Børgesen SE, Gjerris F. The predictive value of conductance to outflow of CSF in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain : a journal of neurology. 1982 Mar:105(Pt 1):65-86
[PubMed PMID: 7066675]
[11]
Edwards RJ, Dombrowski SM, Luciano MG, Pople IK. Chronic hydrocephalus in adults. Brain pathology (Zurich, Switzerland). 2004 Jul:14(3):325-36
[PubMed PMID: 15446589]
[12]
Owler BK, Pickard JD. Normal pressure hydrocephalus and cerebral blood flow: a review. Acta neurologica Scandinavica. 2001 Dec:104(6):325-42
[PubMed PMID: 11903086]
[13]
Tarkowski E, Tullberg M, Fredman P, Wikkelsö C. Normal pressure hydrocephalus triggers intrathecal production of TNF-alpha. Neurobiology of aging. 2003 Sep:24(5):707-14
[PubMed PMID: 12885578]
[14]
Li X, Miyajima M, Jiang C, Arai H. Expression of TGF-betas and TGF-beta type II receptor in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neuroscience letters. 2007 Feb 14:413(2):141-4
[PubMed PMID: 17194537]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[15]
Silverberg GD. Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH): ischaemia, CSF stagnation or both. Brain : a journal of neurology. 2004 May:127(Pt 5):947-8
[PubMed PMID: 15111447]
[16]
Bateman GA. Vascular compliance in normal pressure hydrocephalus. AJNR. American journal of neuroradiology. 2000 Oct:21(9):1574-85
[PubMed PMID: 11039334]
[17]
Greitz D. Radiological assessment of hydrocephalus: new theories and implications for therapy. Neurosurgical review. 2004 Jul:27(3):145-65; discussion 166-7
[PubMed PMID: 15164255]
[18]
Gleason PL, Black PM, Matsumae M. The neurobiology of normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery clinics of North America. 1993 Oct:4(4):667-75
[PubMed PMID: 8241789]
[19]
Corkill RG, Cadoux-Hudson TA. Normal pressure hydrocephalus: developments in determining surgical prognosis. Current opinion in neurology. 1999 Dec:12(6):671-7
[PubMed PMID: 10676746]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[20]
Malm J, Graff-Radford NR, Ishikawa M, Kristensen B, Leinonen V, Mori E, Owler BK, Tullberg M, Williams MA, Relkin NR. Influence of comorbidities in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus - research and clinical care. A report of the ISHCSF task force on comorbidities in INPH. Fluids and barriers of the CNS. 2013 Jun 10:10(1):22. doi: 10.1186/2045-8118-10-22. Epub 2013 Jun 10
[PubMed PMID: 23758953]
[21]
Cucca A, Biagioni MC, Sharma K, Golomb J, Gilbert RM, Di Rocco A, Fleisher JE. Comorbid Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus with Parkinsonism: A Clinical Challenge and Call for Awareness. Case reports in neurological medicine. 2018:2018():2513474. doi: 10.1155/2018/2513474. Epub 2018 Jan 21
[PubMed PMID: 29610690]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[22]
Jones HC, Klinge PM. Hydrocephalus 2008, 17-20th September, Hannover Germany: a conference report. Cerebrospinal fluid research. 2008 Dec 16:5():19. doi: 10.1186/1743-8454-5-19. Epub 2008 Dec 16
[PubMed PMID: 19087341]
[23]
Graff-Radford NR, Godersky JC. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Onset of gait abnormality before dementia predicts good surgical outcome. Archives of neurology. 1986 Sep:43(9):940-2
[PubMed PMID: 3741212]
[24]
Hashimoto M, Ishikawa M, Mori E, Kuwana N, Study of INPH on neurological improvement (SINPHONI). Diagnosis of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus is supported by MRI-based scheme: a prospective cohort study. Cerebrospinal fluid research. 2010 Oct 31:7():18. doi: 10.1186/1743-8454-7-18. Epub 2010 Oct 31
[PubMed PMID: 21040519]
[25]
Graff-Radford NR, Jones DT. Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Continuum (Minneapolis, Minn.). 2019 Feb:25(1):165-186. doi: 10.1212/CON.0000000000000689. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 30707192]
[26]
Kazui H, Miyajima M, Mori E, Ishikawa M, SINPHONI-2 Investigators. Lumboperitoneal shunt surgery for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (SINPHONI-2): an open-label randomised trial. The Lancet. Neurology. 2015 Jun:14(6):585-94. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00046-0. Epub 2015 Apr 28
[PubMed PMID: 25934242]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[27]
Lemcke J, Meier U, Müller C, Fritsch MJ, Kehler U, Langer N, Kiefer M, Eymann R, Schuhmann MU, Speil A, Weber F, Remenez V, Rohde V, Ludwig HC, Stengel D. Safety and efficacy of gravitational shunt valves in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a pragmatic, randomised, open label, multicentre trial (SVASONA). Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry. 2013 Aug:84(8):850-7. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-303936. Epub 2013 Mar 1
[PubMed PMID: 23457222]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[28]
Farahmand D,Sæhle T,Eide PK,Tisell M,Hellström P,Wikkelsö C, A double-blind randomized trial on the clinical effect of different shunt valve settings in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Journal of neurosurgery. 2016 Feb;
[PubMed PMID: 26315004]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[29]
Scholz R, Lemcke J, Meier U, Stengel D. Efficacy and safety of programmable compared with fixed anti-siphon devices for treating idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) in adults - SYGRAVA: study protocol for a randomized trial. Trials. 2018 Oct 17:19(1):566. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2951-6. Epub 2018 Oct 17
[PubMed PMID: 30333067]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[30]
Delwel EJ, de Jong DA, Dammers R, Kurt E, van den Brink W, Dirven CM. A randomised trial of high and low pressure level settings on an adjustable ventriculoperitoneal shunt valve for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: results of the Dutch evaluation programme Strata shunt (DEPSS) trial. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry. 2013 Jul:84(7):813-7. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-302935. Epub 2013 Feb 13
[PubMed PMID: 23408069]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[31]
Boon AJ, Tans JT, Delwel EJ, Egeler-Peerdeman SM, Hanlo PW, Wurzer HA, Avezaat CJ, de Jong DA, Gooskens RH, Hermans J. Dutch Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus Study: randomized comparison of low- and medium-pressure shunts. Journal of neurosurgery. 1998 Mar:88(3):490-5
[PubMed PMID: 9488303]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[32]
Tudor KI, Tudor M, McCleery J, Car J. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH). The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2015 Jul 29:2015(7):CD010033. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010033.pub2. Epub 2015 Jul 29
[PubMed PMID: 26222251]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[33]
Marmarou A, Bergsneider M, Klinge P, Relkin N, Black PM. The value of supplemental prognostic tests for the preoperative assessment of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 2005 Sep:57(3 Suppl):S17-28; discussion ii-v
[PubMed PMID: 16160426]
[34]
Kiefer M, Unterberg A. The differential diagnosis and treatment of normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Deutsches Arzteblatt international. 2012 Jan:109(1-2):15-25; quiz 26. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2012.0015. Epub 2012 Jan 9
[PubMed PMID: 22282714]
[35]
Pyykkö OT, Nerg O, Niskasaari HM, Niskasaari T, Koivisto AM, Hiltunen M, Pihlajamäki J, Rauramaa T, Kojoukhova M, Alafuzoff I, Soininen H, Jääskeläinen JE, Leinonen V. Incidence, Comorbidities, and Mortality in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. World neurosurgery. 2018 Apr:112():e624-e631. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.01.107. Epub 2018 Jan 31
[PubMed PMID: 29374607]
[36]
Vanhala V, Junkkari A, Korhonen VE, Kurki MI, Hiltunen M, Rauramaa T, Nerg O, Koivisto AM, Remes AM, Perälä J, Suvisaari J, Lehto SM, Viinamäki H, Soininen H, Jääskeläinen JE, Leinonen V. Prevalence of Schizophrenia in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 2019 Apr 1:84(4):883-889. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyy147. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 29741669]