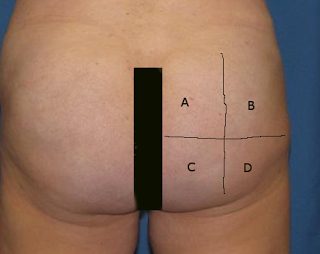
[1]
Shaw H. Intramuscular injection. Nursing standard (Royal College of Nursing (Great Britain) : 1987). 2015 Oct 7:30(6):61-2. doi: 10.7748/ns.30.6.61.s48. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 26443178]
[2]
Nicoll LH, Hesby A. Intramuscular injection: an integrative research review and guideline for evidence-based practice. Applied nursing research : ANR. 2002 Aug:15(3):149-62
[PubMed PMID: 12173166]
[3]
Dincer B, Yildirim D. The effect of vibration stimulation on intramuscular injection pain and patient satisfaction: Single-blind, randomised controlled study. Journal of clinical nursing. 2021 Jun:30(11-12):1615-1622. doi: 10.1111/jocn.15715. Epub 2021 Mar 1
[PubMed PMID: 33590594]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[4]
Soliman E, Ranjan S, Xu T, Gee C, Harker A, Barrera A, Geddes J. A narrative review of the success of intramuscular gluteal injections and its impact in psychiatry. Bio-design and manufacturing. 2018:1(3):161-170. doi: 10.1007/s42242-018-0018-x. Epub 2018 Jul 27
[PubMed PMID: 30546922]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[5]
Nakajima Y, Fujii T, Mukai K, Ishida A, Kato M, Takahashi M, Tsuda M, Hashiba N, Mori N, Yamanaka A, Ozaki N, Nakatani T. Anatomically safe sites for intramuscular injections: a cross-sectional study on young adults and cadavers with a focus on the thigh. Human vaccines & immunotherapeutics. 2020:16(1):189-196. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1646576. Epub 2019 Aug 23
[PubMed PMID: 31403356]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[6]
Rishovd A. Pediatric intramuscular injections: guidelines for best practice. MCN. The American journal of maternal child nursing. 2014 Mar-Apr:39(2):107-12; quiz 113-4. doi: 10.1097/NMC.0000000000000009. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 24201242]
[7]
Sisson H. Aspirating during the intramuscular injection procedure: a systematic literature review. Journal of clinical nursing. 2015 Sep:24(17-18):2368-75. doi: 10.1111/jocn.12824. Epub 2015 Apr 14
[PubMed PMID: 25871949]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[8]
Sepah Y, Samad L, Altaf A, Halim MS, Rajagopalan N, Javed Khan A. Aspiration in injections: should we continue or abandon the practice? F1000Research. 2014:3():157. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.1113.3. Epub 2014 Jul 10
[PubMed PMID: 28344770]
[9]
Jung Kim H, Hyun Park S. Sciatic nerve injection injury. The Journal of international medical research. 2014 Aug:42(4):887-97. doi: 10.1177/0300060514531924. Epub 2014 Jun 11
[PubMed PMID: 24920643]
[10]
Cook IF. Best vaccination practice and medically attended injection site events following deltoid intramuscular injection. Human vaccines & immunotherapeutics. 2015:11(5):1184-91. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1017694. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 25868476]
[11]
Warren BL. Intramuscular injection angle: evidence for practice? Nursing praxis in New Zealand inc. 2002 Jul:18(2):42-51
[PubMed PMID: 12238797]
[12]
Al Awaidy S, Bawikar S, Duclos P. Safe injection practices in a primary health care setting in Oman. Eastern Mediterranean health journal = La revue de sante de la Mediterranee orientale = al-Majallah al-sihhiyah li-sharq al-mutawassit. 2006:12 Suppl 2():S207-16
[PubMed PMID: 17361692]
[13]
Rodger MA, King L. Drawing up and administering intramuscular injections: a review of the literature. Journal of advanced nursing. 2000 Mar:31(3):574-82
[PubMed PMID: 10718876]
[14]
Sivri Bilgen B, Balcı S. The Effect on Pain of Buzzy® and ShotBlocker® during the Administration of Intramuscular Injections to Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2019 Aug:49(4):486-494. doi: 10.4040/jkan.2019.49.4.486. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 31477677]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[15]
Yilmaz G, Alemdar DK. Using Buzzy, Shotblocker, and Bubble Blowing in a Pediatric Emergency Department to Reduce the Pain and Fear Caused by Intramuscular Injection: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of emergency nursing. 2019 Sep:45(5):502-511. doi: 10.1016/j.jen.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 Jun 27
[PubMed PMID: 31257044]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[16]
Bilge S, Aydin A, Gun C, Aldinc H, Acar YA, Yaylaci S, Cinar O, Balci V. Comparison of the efficacy of ShotBlocker and cold spray in reducing intramuscular injection-related pain in adults. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Saudi medical journal. 2019 Oct:40(10):996-1002. doi: 10.15537/smj.2019.10.24322. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 31588477]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[17]
Yildirim D, Dinçer B. Shotblocker Use in Emergency Care: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Advanced emergency nursing journal. 2021 Jan-Mar 01:43(1):39-47. doi: 10.1097/TME.0000000000000330. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 33952876]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[18]
Zengin M, Yayan EH. A Comparison of Two Different Tactile Stimulus Methods on Reducing Pain of Children During Intramuscular Injection: A Randomized Controlled Study. Journal of emergency nursing. 2022 Mar:48(2):167-180. doi: 10.1016/j.jen.2021.10.006. Epub 2021 Dec 22
[PubMed PMID: 34952709]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[19]
Sridharan K, Sivaramakrishnan G. Pharmacological interventions for reducing pain related to immunization or intramuscular injection in children: A mixed treatment comparison network meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Journal of child health care : for professionals working with children in the hospital and community. 2018 Sep:22(3):393-405. doi: 10.1177/1367493518760735. Epub 2018 Feb 27
[PubMed PMID: 29486590]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[20]
Cassidy KL, Reid GJ, McGrath PJ, Smith DJ, Brown TL, Finley GA. A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of the EMLA patch for the reduction of pain associated with intramuscular injection in four to six-year-old children. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway : 1992). 2001 Nov:90(11):1329-36
[PubMed PMID: 11808908]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[21]
Kashaninia Z, Sajedi F, Rahgozar M, Noghabi FA. The effect of Kangaroo Care on behavioral responses to pain of an intramuscular injection in neonates. Journal for specialists in pediatric nursing : JSPN. 2008 Oct:13(4):275-80
[PubMed PMID: 19238715]
[22]
Öztürk D, Baykara ZG, Karadag A, Eyikara E. The effect of the application of manual pressure before the administration of intramuscular injections on students' perceptions of postinjection pain: a semi-experimental study. Journal of clinical nursing. 2017 Jun:26(11-12):1632-1638. doi: 10.1111/jocn.13530. Epub 2016 Nov 24
[PubMed PMID: 27535654]
[23]
Basak T, Demirtas A, Yorubulut SM. Virtual reality and distraction cards to reduce pain during intramuscular benzathine penicillin injection procedure in adults: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of advanced nursing. 2021 May:77(5):2511-2518. doi: 10.1111/jan.14782. Epub 2021 Feb 19
[PubMed PMID: 33608955]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[24]
Canbulat Şahiner N, Türkmen AS. The Effect of Distraction Cards on Reducing Pain and Anxiety During Intramuscular Injection in Children. Worldviews on evidence-based nursing. 2019 Jun:16(3):230-235. doi: 10.1111/wvn.12359. Epub 2019 Apr 17
[PubMed PMID: 30997744]
[25]
Sahebkar M, Khosrojerdi A, Rad M, Stewart JJ, Rastaghi S, Assarroudi A. Evaluation of the effect of selecting gluteal injection site on the pain injection based on anthropometric indices and body shape pattern: A randomised controlled trial study. Journal of clinical nursing. 2021 Jun:30(11-12):1556-1563. doi: 10.1111/jocn.15703. Epub 2021 Feb 25
[PubMed PMID: 33559212]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[26]
Kara D, Yapucu Güneş Ü. The effect on pain of three different methods of intramuscular injection: A randomized controlled trial. International journal of nursing practice. 2016 Apr:22(2):152-9. doi: 10.1111/ijn.12358. Epub 2014 Jul 11
[PubMed PMID: 25039702]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[27]
Mitchell JR, Whitney FW. The effect of injection speed on the perception of intramuscular injection pain. A clinical update. AAOHN journal : official journal of the American Association of Occupational Health Nurses. 2001 Jun:49(6):286-92
[PubMed PMID: 11760527]
[28]
Taddio A, Ilersich AL, Ipp M, Kikuta A, Shah V, HELPinKIDS Team. Physical interventions and injection techniques for reducing injection pain during routine childhood immunizations: systematic review of randomized controlled trials and quasi-randomized controlled trials. Clinical therapeutics. 2009:31 Suppl 2():S48-76. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.07.024. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 19781436]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[29]
Hall LM, Ediriweera Y, Banks J, Nambiar A, Heal C. Cooling to reduce the pain associated with vaccination: A systematic review. Vaccine. 2020 Dec 3:38(51):8082-8089. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.11.005. Epub 2020 Nov 11
[PubMed PMID: 33189429]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[30]
Ayinde O, Hayward RS, Ross JDC. The effect of intramuscular injection technique on injection associated pain; a systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS one. 2021:16(5):e0250883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250883. Epub 2021 May 3
[PubMed PMID: 33939726]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[31]
Nahm FS, Lee PB, Park SY, Kim YC, Lee SC, Shin HY, Lee CJ. Pain from intramuscular vaccine injection in adults. Revista medica de Chile. 2012 Feb:140(2):192-7. doi: 10.4067/S0034-98872012000200007. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 22739948]
[32]
Mansoor F, Hamid S, Mir T, Abdul Hafiz R, Mounts A. Incidence of traumatic injection neuropathy among children in Pakistan. Eastern Mediterranean health journal = La revue de sante de la Mediterranee orientale = al-Majallah al-sihhiyah li-sharq al-mutawassit. 2005 Jul:11(4):798-804
[PubMed PMID: 16700396]
[33]
Donaldson C, Green J. Using the ventrogluteal site for intramuscular injections. Nursing times. 2005 Apr 19-25:101(16):36-8
[PubMed PMID: 15871375]
[34]
Small SP. Preventing sciatic nerve injury from intramuscular injections: literature review. Journal of advanced nursing. 2004 Aug:47(3):287-96
[PubMed PMID: 15238123]
[35]
Shoemaker S. Preventing Shoulder Injury Related to Vaccine Administration. The American journal of nursing. 2021 Jun 1:121(6):45-47. doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000753660.62075.69. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 34009164]
[36]
Nakajima Y, Mukai K, Takaoka K, Hirose T, Morishita K, Yamamoto T, Yoshida Y, Urai T, Nakatani T. Establishing a new appropriate intramuscular injection site in the deltoid muscle. Human vaccines & immunotherapeutics. 2017 Sep 2:13(9):2123-2129. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1334747. Epub 2017 Jun 12
[PubMed PMID: 28604191]
[37]
Chan VO, Colville J, Persaud T, Buckley O, Hamilton S, Torreggiani WC. Intramuscular injections into the buttocks: are they truly intramuscular? European journal of radiology. 2006 Jun:58(3):480-4
[PubMed PMID: 16495027]
[38]
White S, Goodwin J, Behan L. Nurses' Use of Appropriate Needle Sizes When Administering Intramuscular Injections. Journal of continuing education in nursing. 2018 Nov 1:49(11):519-525. doi: 10.3928/00220124-20181017-09. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 30376144]
[39]
Ozen O, Gunaydin M, Tosun A, Coskun ZU, Aytekin K, Takir S. Assessment rate of true dorsogluteal intramuscular drug injection using ultrasonography. Pakistan journal of medical sciences. 2019 Jul-Aug:35(4):1132-1137. doi: 10.12669/pjms.35.4.313. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 31372156]
[40]
Dayananda L, Belaval VV, Raina A, Chandana R. Intended intramuscular gluteal injections: are they truly intramuscular? Journal of postgraduate medicine. 2014 Apr-Jun:60(2):175-8. doi: 10.4103/0022-3859.132334. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 24823517]
[41]
Strohfus P, Palma S, Wallace CT. Dorsogluteal intramuscular injection depth needed to reach muscle tissue according to body mass index and gender: A systematic review. Journal of clinical nursing. 2022 Oct:31(19-20):2943-2958. doi: 10.1111/jocn.16126. Epub 2021 Nov 17
[PubMed PMID: 34791732]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[42]
Herraiz-Adillo Á, Martínez-Vizcaíno V, Pozuelo-Carrascosa DP. Aspiration before intramuscular vaccines injection, should the debate continue? Enfermeria clinica (English Edition). 2022 Jan-Feb:32(1):65-66. doi: 10.1016/j.enfcle.2021.10.002. Epub 2022 Jan 22
[PubMed PMID: 35078751]
[43]
Thomas CM, Mraz M, Rajcan L. Blood Aspiration During IM Injection. Clinical nursing research. 2016 Oct:25(5):549-59. doi: 10.1177/1054773815575074. Epub 2015 Mar 17
[PubMed PMID: 25784149]
[44]
Erkoc Hut A, Yazici ZA. Glass particle contamination threat in nursing practice: A pilot study. Journal of advanced nursing. 2021 Jul:77(7):3189-3191. doi: 10.1111/jan.14847. Epub 2021 Apr 14
[PubMed PMID: 33855755]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[45]
Chiannilkulchai N, Kejkornkaew S. Safety concerns with glass particle contamination: improving the standard guidelines for preparing medication injections. International journal for quality in health care : journal of the International Society for Quality in Health Care. 2021 Jun 23:33(2):. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzab091. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 34101800]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[46]
Preston ST, Hegadoren K. Glass contamination in parenterally administered medication. Journal of advanced nursing. 2004 Nov:48(3):266-70
[PubMed PMID: 15488040]
[47]
Noyes J. An explanation of the differences between expert and novice performance in the administration of an intramuscular injection of an analgesic agent to a patient in pain. Journal of advanced nursing. 1995 Oct:22(4):800-7
[PubMed PMID: 8708202]
[48]
Cassista J, Payne-Gagnon J, Martel B, Gagnon MP. Applying Theory to Understand and Modify Nurse Intention to Adhere to Recommendations regarding the Use of Filter Needles: An Intervention Mapping Approach. Nursing research and practice. 2014:2014():356153. doi: 10.1155/2014/356153. Epub 2014 Jul 10
[PubMed PMID: 25120927]