Definition/Introduction
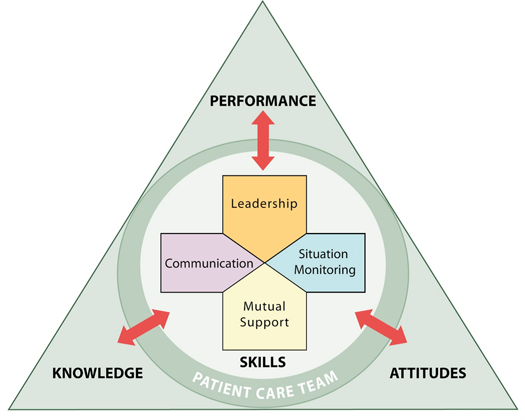
Collaboration has become an essential competency in the national and global plan for quality improvement. There is a need to transform a culture of avoidance and isolation that continues to cause medical errors and lower patient outcomes. A necessary strategy is to improve interrelationships and interactions between health care providers (HCP) and their teams in the clinical setting.
Collaboration is a function of evidenced-based care in managing the complexity of patient care. As an academic and professional requirement, its full potential in patient care management should attain full realization. Implementation will reverse the increasing disparities in patient outcomes stemming from inadequate knowledge, skills, and thinking. As a vital element of patient safety and quality services, collaboration should be measured and monitored for effectiveness. For the determination of satisfactory benchmarks, performance should be intentional and routinely conducted by all HCP's in the clinical setting. For this reason, HCP's must train to perform collaboratively as a clinical competency.
The conceptual framework for collaboration is interprofessional.[1] The concept provides structural, functional and analytical elements that define collaboration as a clinical competency. Interprofessionality embodies processes for building relationships, communication, and other problem-solving strategies for patient safety. Interprofessional education (IPE) is a field of study for interprofessional collaboration.