Continuing Education Activity
Balanoposthitis, a condition affecting the glans penis and prepuce, is prevalent among both pediatric and adult uncircumcised males, with a prevalence of up to 20%. It manifests as inflammation of the foreskin and the head of the penis, causing significant discomfort and morbidity. While often benign, it can result in complications if left untreated. The etiology typically involves factors like poor hygiene, skin irritants, infections, and sometimes even sexually transmitted diseases. However, in about a third of cases, a definitive cause remains elusive despite extensive testing. Initial management includes empiric treatments such as sitz baths, gentle cleaning, and topical therapy. Yet, failure of these measures may signal the need for further investigation into unusual infections or underlying malignancies. Early recognition and timely intervention play pivotal roles in mitigating the impact of balanoposthitis, highlighting the importance of proactive patient education regarding hygiene, safe sex practices, and regular check-ups.
Participating in the course on balanoposthitis provides clinicians with a comprehensive understanding of the condition, including its evaluation, identification, and consideration of potential differential diagnoses. Through this educational experience, healthcare professionals gain insights into tailored management strategies based on the underlying etiology, involving topical antifungal agents, antibiotics, or corticosteroids as appropriate. Furthermore, the course details the significance of patient education in preventing recurrence and improving outcomes. Collaborating with an interprofessional team is emphasized as it enhances patient care by integrating diverse perspectives and expertise. By fostering effective communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals, patient outcomes are optimized, complications are minimized, and overall quality of life is improved.
Objectives:
Identify the etiology and epidemiology of balanoposthitis to more easily recognize the typical patient who is affected and provide appropriate care.
Differentiate between balanoposthitis and other conditions with similar clinical presentations.
Determine and implement the specific treatment as determined by the etiology of balanoposthitis as part of the patient's care plan.
Implement effective collaboration and communication among interprofessional team members to improve treatment efficacy, prevent recurrence, and enhance quality of life for patients with balanoposthitis.
Introduction
Balanoposthitis is a relatively common condition affecting pediatric and adult men who are uncircumcised. This condition is an inflammation affecting the glans penis and prepuce. Many etiologies exist, but they can generally be classified as either infectious, irritative, or traumatic in origin. Balanoposthitis is separate and distinct from balanitis, which refers to inflammation of the glans penis, while posthitis refers to inflammation of the prepuce. This review focuses on balanoposthitis; see StatPearls' companion topic "Balanitis" for further information.[1]
At birth, the prepuce, commonly referred to as the foreskin, is attached by adhesions to the glans. These nonpathological adhesions are responsible for physiologic phimosis or decreased ability to retract the foreskin in neonates. These physiological neonatal adhesions and phimoses normally disappear by adolescence. Hsieh et al found that 17.1% of first-grade boys had physiologic phimosis, which decreased to 1.2% by seventh grade in a cohort of healthy children in Taiwan.[2] "Pathologic phimosis" refers to an inability to retract the foreskin secondary to scarring of the prepuce.[3]
Etiology
Poor hygiene is the most common underlying etiology of balanoposthitis, which commonly leads to nonspecific balanoposthitis. Other etiologies include infection, inflammatory skin diseases, trauma, chronic edematous conditions, and cancer. Patients with a history of frequent genital washing and recurrent problems are likely to have contact dermatitis. A specific underlying etiology cannot be determined in about one-third of patients with balanoposthitis.[4]
The most commonly identifiable etiology of balanoposthitis is infectious, with Candida albicans being the most frequently identified pathogen, followed by Streptococcus.[5] Infections with Candidal yeast are the most prevalent in children. They may also be associated with diaper rash in infants. Other infectious causes include Staphylococcus aureus, Group A Streptococcus, Bacteroides, Gardnerella, anaerobic bacteriae, syphilis, and human papillomavirus (HPV).[6][7][8]
Some inflammatory etiologies include contact dermatitis, reactive arthritis, and lichen sclerosus (balanitis xerotica obliterans.)[9] See StatPearls' companion topics "Lichen Sclerosus" and "Balanitis Xerotica Obliterans" for further information.[10][11] Reactions to antiseptic solutions used in patients performing intermittent self-catheterizations have been reported.[12] In older men, intertrigo, contact irritants, and fungal infections are common causes.
Epidemiology
Balanoposthitis is a relatively common condition affecting pediatric and adult patients. Prevalence in males of all ages is between 12% to 20%.[13] Pediatric patients most commonly present around ages 2 to 5 years; this is likely due to physiologic phimosis and hygiene habits. In adults, uncircumcised men with diabetes mellitus are at the highest risk, with a prevalence of around 35%.[14][15] Meta-analysis results have shown that circumcision decreases the prevalence of inflammatory conditions of the glans penis by 68%.
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiologic processes can vary widely depending on etiology. These can be infectious, autoimmune-mediated, secondary to trauma, or malignancy. Balanoposthitis can also be commonly provoked by irritants and allergens, causing non-specific inflammation leading to erythema and pruritis. Most cases of balanoposthitis commence with moisture such as urine, sweat, or smegma (the physiologic secretion from genital sebaceous glands and shed epithelial cells) becoming trapped within the preputial space secondary to adhesions, phimosis, or poor hygiene—creating a nidus for bacteria and fungi.
History and Physical
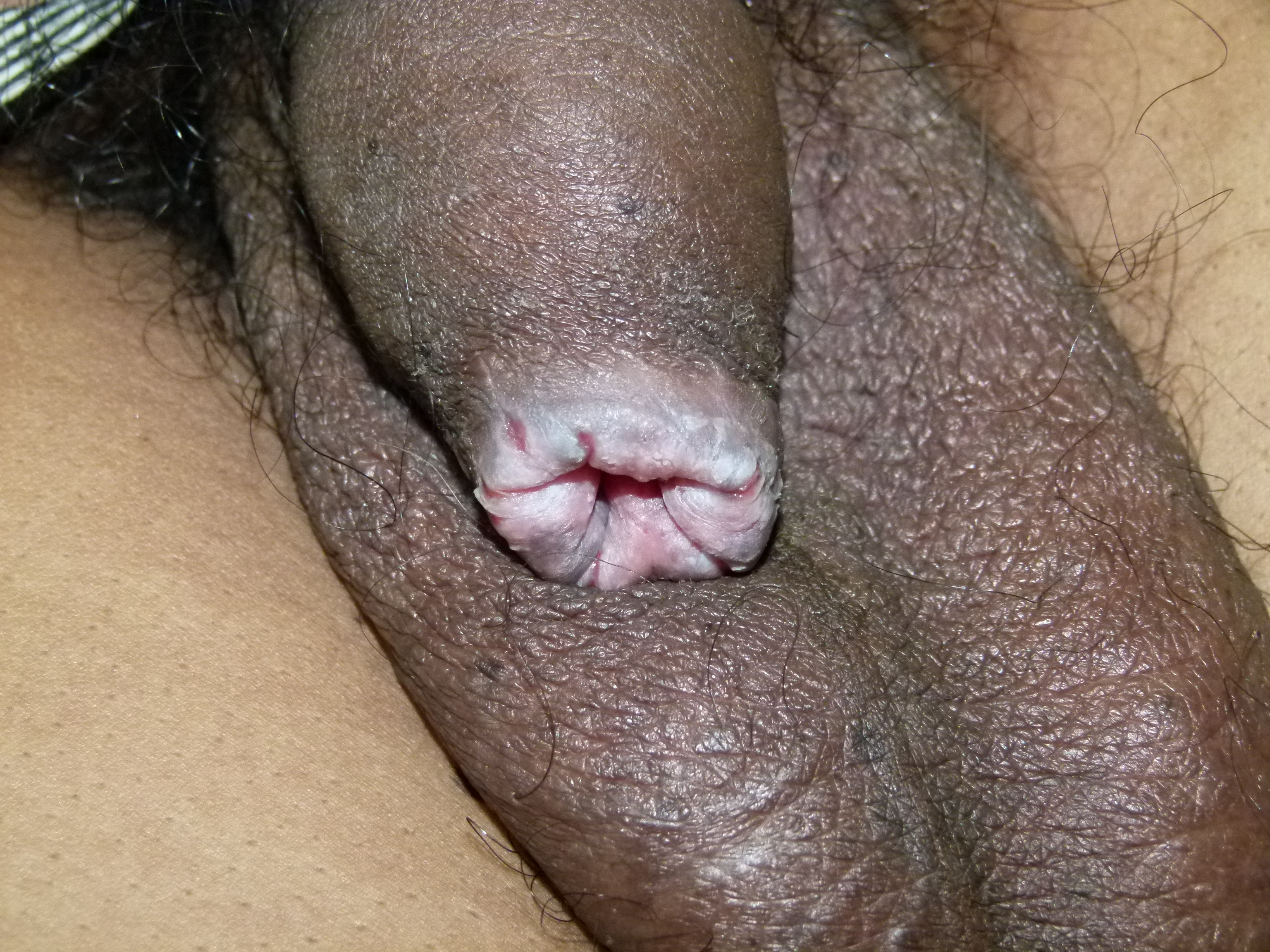
Balanoposthitis can present with penile pain, pruritus, discharge, erythema, rash, or inconsolable crying in infants. By definition, this condition only affects those who are uncircumcised. The typical finding on examination is a moist, erythematous, macular lesion on the glans and foreskin. Erythema is often noted and is sometimes described as blotchy. Small papules may also be present, which may sometimes appear eroded. Balanoposthitis may also present as a dull, dry, reddish plaque with a somewhat glazed or waxy appearance.[16] Areas of yellowish or even black discoloration may occasionally be present.
Balanoposthitis is more common in patients with poor genital hygiene and may present with or without phimosis. Depending on the underlying etiology and severity, the prepuce may be scarred, the patient may be unable to void, the stream may be weak, genital ulcers may be present, phimosis with or without skin splitting may occur, rashes may occur, urethral discharge may occur, and other lesions may be present.
Evaluation
In most cases of balanoposthitis, a thorough history and physical exam are sufficient for diagnosing and establishing a course of treatment. The history should elicit the duration of symptoms, hygiene habits, infectious exposures, potential allergens, and sexual practices. The physical examination should focus on the patient's general hygiene, presence of phimotic discharge, urethral discharge, urinary retention, erythema, edema, tenderness, scarring, inguinal lymphadenitis, testicular edema, or tenderness.
Physiologic preputial smegma can be confused with a urethral discharge. A true discharge is more exudative in appearance, may have a foul order, and may be associated with erythema and tenderness. Consider collecting fungal (Candida) and bacterial cultures from under the foreskin.[16] Culturing for group A beta-hemolytic Streptococcus may be indicated in adult and pediatric patients.
Penile ulcers, vesicles, urethral discharge, and other lesions point toward sexually transmitted infections as etiology and indicate the need for appropriate tests. If a sexually transmitted disease is suspected, cultures and swabs for nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) for gonorrhea and chlamydia should be performed and could provide a definitive diagnosis. Consider NAATs for Trichomonas vaginalis as well, especially in cases resistant to initial therapy.[16] If ulcers are present, consider NAATs or similar testing for herpes simplex virus, as well as testing for syphilis.
Children in whom there is no suspicion of sexual abuse and in the absence of lesions or discharge are manageable empirically without any further testing is not required. Otherwise, further evaluation should be guided by other symptoms and a history of exposures. In new cases of balanoposthitis, especially a fungal etiology in older children, an evaluation for diabetes must be necessary as this may be the first sign of hyperglycemia and glycosuria.[14] Although most cases will respond to hygiene improvements or empiric treatment, patients with symptoms that recur or are refractory to treatment after 4 weeks may warrant a biopsy to investigate the etiology and pathology further and possibly a circumcision.[16][17]
Treatment / Management
Most cases of balanoposthitis will respond to hygiene improvements or empiric treatment. Balanoposthitis treatment should optimally be based on identifying the specific causative agent. When that is impossible, empiric therapy based on the most likely etiology and general therapeutic principles should be used.
General empiric therapy for balanoposthitis typically includes:
- Avoiding the application or exposure of any known or potential irritants to the penis. For example, soap should not be used to clean under the foreskin, as even a gentle soap can be irritating. If soap must be used:
- Select one safe for babies, as it typically has fewer potentially irritating chemical ingredients.
- Avoid antibacterial soaps and those with fragrances and other unnecessary chemicals.
- Avoid potentially irritating agents, including detergents, perfumes, powdered talc, bubble baths, alcohol, adult or baby wipes, antiseptics, sexual lubricants, spermicides, moisturizers, ointments, and creams unless specifically recommended.
- Creams or ointments with parabens and neomycin should be avoided as these may cause an inflammatory reaction in some patients.
- Avoiding sexual activity is recommended until the balanoposthitis has entirely resolved.
- Cleaning the area is best done passively by sitting in a warm sitz bath 2 or 3 times a day, more often if the condition is severe. The sitz bath is also anti-inflammatory. A dilute salt solution is suggested.
- Cleaning beneath the foreskin may be gently and carefully done with a cotton swab and water, as needed.[18]
- If phimosis prevents access to the glans, gentle irrigation with warm water can be done with a small 5 or 8-French straight catheter or feeding tube placed through the lumen of the foreskin.[19]
- Review the proper hygiene of the foreskin; this skin should not be fully retracted for cleaning unless it is easily done and painless.
- Water should be used for routine cleaning, and the area should be thoroughly dried before the foreskin is replaced over the glans.
Topical empiric treatment of balanoposthitis includes antibiotics (bacitracin, metronidazole, mupiricin, or bacitracin/polymyxin B), antifungals (clotrimazole 1% cream), and low-potency (1% hydrocortisone) corticosteroids.[20][21] Metronidazole is effective for anaerobic bacteria, fungi, and protozoa.[22] Upon presentation, if phimosis is severe enough to cause urinary obstruction, the patient should be urgently catheterized. If unable to place a catheter, the patient may require more invasive interventions such as a dorsal slit. Circumcision can then be deferred until preputial edema and inflammation have subsided.[23][24]
Malignant and premalignant penile lesions, including Buschke-Lowenstein tumor (giant condyloma), cutaneous penile horn, leukoplakia, lichen sclerosus, and pseudoepitheliomatous keratotic and micaceous balanitis, are discussed in StatPearls' companion topic "Penile Cancer."[25] Penile intraepithelial neoplasia (formerly called Bowen disease, bowenoid papulosis, Erythroplasia of Querat, and squamous cell carcinoma in situ of the penis) are considered HPV-related premalignant lesions and are also discussed in StatPearls' companion topic "Penile Cancer."[25]
A Guideline for Treatment of Balanoposthitis of Specific Etiology
Amebiasis is a rare cause of balanoposthitis but should be suspected in cases resistant to initial antibiotic therapy, especially in men who have sex with men and those who are immunocompromised. The diagnosis is made by biopsy as the clinical presentation is nonspecific. The finding of trophozoites on microscopic examination of the biopsy specimen is diagnostic. Treatment is with metronidazole, but emetine (no longer made in the US due to its increased toxicity) may also be used in metronidazole failures.[26][27]
Anaerobic bacterial infections should be suspected in cases with erythema, edema, and a foul-smelling exudate or discharge. Superficial erosions may sometimes be seen. Lymphadenopathy may be present in severe cases. Diagnosis is made by culturing the exudate or discharge.
Mild cases can be treated with topical metronidazole, while more severe cases should receive oral antibiotics (metronidazole 400 mg to 500 mg twice a day or 15 to 35 mg/kg per day in divided doses) for 7 days. An acceptable alternate therapy is amoxicillin—clavulanic acid 250/125 mg 3 times daily or clindamycin (150 mg to 300 mg or 8 mg to 16 mg/kg/day 4 times daily) for 7 days.[16] Consider circumcision for recurrent or resistant cases.
Bacterial balanoposthitis should be suspected in intense erythema and a transudative or exudative preputial discharge. Definitive diagnosis is by culture. The degree of erythema, edema, or both is variable.[16] Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus are common causative aerobic bacteria. Mild cases can receive topical antibiotic therapy such as mupirocin 2% cream 3 times a day for 7 to 14 days. In severe cases or when phimosis prevents topical treatment, therapy should include at least 1 week of oral antibiotics, such as cephalexin or erythromycin, or as identified from cultures.[20] Cases with concomitant group A Streptococcal pharyngitis are treated as pharyngitis with a beta-lactam.
Balanitis circumscripta plasmacellularis (Zoon balanitis, plasma cell balanitis) is a benign condition that appears as well-demarcated, shiny (glazed), orange-reddish in color areas on the glans and inner surface of the foreskin. This is typically found with the symmetrical distribution of multiple tiny red spots and is often associated with other cutaneous pathologies.[16][28] The primary treatment is circumcision, but other therapies have been used, including the following:
- Circumcision (usually resolves and cures the lesion)
- General hygienic measures
- Laser ablation
- Topical antibiotic cream (Mupirocin 2% ointment) applied twice a day
- Topical calcineurin inhibitor cream (pimecrolimus 1%) is applied twice a day, but there is a possible risk of malignancy
- Topical high-potency steroids (clobetasone)
- Treatment of any underlying or associated dermatoses [29][30][31][32][33][34][35][36][37]
Candidal infections are the most commonly identified cause of balanoposthitis, particularly in children.[16] This condition is often associated with or secondary to diaper rash (dermatitis) in infants. See StatPearls' companion topic, "Diaper Dermatitis," for further information.[38] The classic description is an erythematous rash with satellite lesions tender to palpation. In adults, candidal balanoposthitis can be associated with diabetes mellitus, older age, immunosuppressive disorders, or the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics.[16][39] A potassium hydroxide (KOH) slide preparation can help visualize candida directly, facilitating the diagnosis, and a fungal culture can help with treatment. Candidal balanoposthitis can be treated with topical therapy, such as 7 days of 0.25% miconazole cream applied at each diaper change. Clotrimazole 1% or miconazole 2% cream is preferred in adults and is typically applied 2 times daily for 2 but no more than 4 weeks.[16]
Nystatin cream 100,000 u/gram 3 times daily for 2 weeks is also an option for the topical therapy of candidal balanoposthitis. A low-potency topical steroid cream (hydrocortisone 1%) twice a day can be added if there is significant inflammation. In severe cases, 150 mg of oral fluconazole may be used in addition to topical therapy.[16][40]
Circinate balanitis can occur in isolation, with the human immunodeficiency virus, or associated with reactive arthritis.[16] About 20% to 40% of uncircumcised men with reactive arthritis will develop circinate balanitis. The typical appearance is whitish-grayish pale macules with white margins on the glans, which may coalesce to form a single lesion with an irregular, white margin. This condition is usually associated with eye, joint, and skin problems, but these are not required.[16][41] See StatPearls' companion topic, "Reactive Arthritis," for further information.[41]
Screening for sexually transmitted infections, including syphilis, which can appear similarly, should be considered.[42][43] A positive human leukocyte antigen B27 blood test suggests a diagnosis of reactive arthritis.[41][44] Treatment includes managing any underlying conditions and using mild to moderate topical steroids, such as applying a thin layer of 1% hydrocortisone topically twice a day for 1 to 2 weeks.[16]
Fixed drug eruptions presenting on the penis are relatively uncommon. They appear after using certain medications, including tetracyclines, phenolphthalein, phenacetin, paracetamol, non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs, barbiturates, and sulfa drugs. They may also appear after intercourse with a sexual partner who is on one of these medications.[45][46][47] The lesions are generally described as round, erythematous patches that turn darker with or without associated edema and vesicles.[45] They most commonly occur in the genitals or oral mucosa.
Fixed drug eruptions resolve upon discontinuing the medication and return shortly to the same location if that medication is resumed. A drug challenge with the suspected offending agent can confirm the diagnosis, but the subsequent allergic reaction could be quite severe. Therefore, such a drug challenge should only be done after consultation with an allergist or dermatologist, where immediate treatment can be quickly administered. Appropriate skin testing is suggested before such a drug challenge.[16][48] Other than stopping the offending medication, a mild to moderate potency steroid cream (such as hydrocortisone 1%) can be applied in a thin layer twice daily for 1 to 2 weeks. Severe eruptions may rarely require systemic steroids.[16]
Irritative balanoposthitis is more common in patients presenting with atopic dermatitis and is often due to frequent or overly aggressive washing with soap.[9] This typically presents as mild erythema with or without pruritus. Most cases can be appropriately managed by avoiding strong soaps and applying emollients such as petroleum jelly multiple times daily. Potential allergens such as latex condom use, lubricants, and detergents used in underwear should be investigated and avoided. Topical hydrocortisone 1% is a treatment option, applying a thin layer of cream twice daily for 1 to 2 weeks.
Lichen planus is an inflammatory skin disorder with an idiopathic etiology that is thought to be a T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease related to hepatitis C and various drugs such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta-blockers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and thiazide diuretics. The typical presentation is purplish plaques or scales with well-defined margins appearing on the penile exterior epithelium. However, mucosal surfaces can show annular or erosive lesions.[16][49] The exterior epithelial dermatoses will usually resolve spontaneously after 18 months. However, the mucosal lesions tend to be intermittent and recurrent.[16] Lichen planus is considered benign and will only develop premalignant characteristics extremely rarely.[50] Initial therapy usually involves high-potency topical steroids. However, calcineurin inhibitor creams can also be used. Cyclosporine may be considered in erosive lesions.[16][49][51][52][53][54][55][56] Steroids and circumcision may be considered in severe cases.[16][56][57]
Lichen sclerosus is an inflammatory skin condition of the male genitalia that is exacerbated by extended contact with urine in uncircumcised males.[58] This is a common cause or contributing factor in childhood balanoposthitis. Contributing and predisposing factors include anatomical male genital abnormalities (hypospadias), obesity, and urological surgical procedures.[16] The condition does occur in men circumcised as neonates but is quite rare.
Lichen sclerosus typically begins as an itchy area of white discoloration on the mucosal surface of the foreskin or the glans. These areas may initially appear mottled or diffuse, but they tend to coalesce. As the condition progresses, the skin loses elasticity, becoming sore and somewhat brittle.[59] Typical symptoms include adhesions around the corona, changes in the coronal sulcus (dull or effaced), frenulum abnormalities (bunching, effacement, or hyperkeratosis), hemorrhagic blisters, hyperpigmentation of preputial skin edges or meatus, itching, lichenoid or Zoonoid inflammation, meatal stenosis or thickening, post-void dribbling, scarring, skin splitting, soreness, and urinary problems.[10][11][16][60]
Lichen sclerosus is associated with urethral strictures, meatal stenosis, phimosis, paraphimosis, and penile intraepithelial neoplasia; this is one of the predisposing conditions most closely associated with penile cancer (the other is HPV.)[11][16] A biopsy is suggested as lichen sclerosus is closely related to squamous cell carcinoma.[59]
Treatment includes:
- High-potency (clobetasone) topical steroid cream applications twice a day for up to 30 days. If not successful or recurrent, circumcision is recommended instead of prolonged or intermittent topical steroid use (Use cautiously in patients with a history of genital warts, as this may prompt a relapse.)
- Regular application of a topical skin barrier to urine (petroleum jelly)
- Removal of any genital jewellery
- Washing without using irritating soap
- Weight loss
- Meatotomy or meatal dilation
- Circumcision, particularly for intractable or recurrent cases [16][59]
Lichen sclerosus is reviewed in more detail in StatPearls' companion topics "Lichen Sclerosus" and "Balanitis Xerotica Obliterans."[10][11]
Nonspecific balanoposthitis is the most common type in children, usually secondary to poor hygiene. Some preputial discharge may be present on a physical exam, but there should be no urethral drainage, ulcers, or discrete lesions. An assessment for urethral discharge is done by milking the urethra from the base of the penis to the glans.
The diagnosis is generally one of exclusion, as patients typically do not respond to antifungal creams or high-potency topical steroids and have negative tests for bacteria, candida, chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes simplex, HPV, syphilis, and trichomonas. Histological examination of biopsy specimens is nonspecific.
Treatment involves gently cleaning the area 2 to 3 times daily. If physiologic phimosis is present, forceful prepuce retraction should be avoided. In patients able to easily retract the foreskin, clean the area gently with a cotton swab. After commencing a proper hygiene routine, symptoms usually resolve within 5 to 7 days. If not, definitive therapy would be a circumcision.[16]
Sexually transmitted infections may present with urethral drainage when milking the penis from the penile base. This finding should prompt evaluation and treatment for sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea and chlamydia.[18] In children, sexual abuse should be considered in the presence of a urethral discharge or the finding of a sexually transmitted infection.
Neisseria gonorrhea or Chlamydia trachomatis can receive treatment with a single dose of ceftriaxone 250 mg intramuscularly and a single oral 1-gram dose of azithromycin. A painless ulcer may indicate a syphilis infection, which can be treated with benzathine penicillin G 50,000 units/kg up to a maximum of 2.4 million units once delivered via intramuscular injection. Trichomonas vaginalis can be diagnosed from NAAT testing. Treatment is usually with metronidazole 2 grams in a single oral dose.[61][62]
Viral balanoposthitis would include herpes simplex virus and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Herpes simplex presents as an erythematous base with overlying vesicles that may rupture. The diagnosis is made by NAAT or similar testing. A first episode is treated with oral acyclovir for 7 to 10 days. Recurrent episodes will require a 5-day treatment protocol.[63][64] Human papillomavirus can present as diffuse erythema. Lichenification, genital warts, and irregular borders suggest an HPV infection, which can be seen in association with balanoposthitis. Applying a gauze pad with 5% acetic acid solution to the penis for 3-5 minutes will cause any HPV-infected tissues to turn white. This technique is considered a very sensitive and specific test for HPV-affected skin.[65] Treatment includes topical podophyllotoxin 0.5% gel twice daily for 3 days, repeated weekly for up to 4 weeks. Alternative topical treatments include imiquimod (a topical immune response cream) 3 times weekly, sinecatechins 15% ointment, trichloracetic acid, and oral isotretinoin (an oral medication typically used for acne).[66] Surgery, laser therapy, photodynamic therapy, and cryotherapy may also be used in selected cases. See StatPearls' companion topic, "Genital Warts," for further information.[66] Circumcision should be considered for intractable and recurrent cases.[16]
Differential Diagnosis
The most critical differential diagnosis for balanoposthitis is squamous cell carcinoma of the penis. Squamous cell carcinoma intially presents as a painless, asymmetrical, irregular ulcer or nodule, which may become painful or tender in later stages.[25] A definitive diagnosis requires a biopsy. For more information on squamous cell carcinoma of the penis, see StatPearls' companion topic "Penile Cancer" for further information.[25]
Penile intraepithelial neoplasia is most often associated with HPV.[25] For more information on penile intraepithelial neoplasia, see StatPearls' companion topic "Penile Cancer" for further information.[25]
Additional considerations for the differential diagnosis of balanoposthitis:
- Balanitis
- Balanitis circumscripta plasmacellularis (Zoon balanitis, plasma cell balanitis)
- Circinate balanitis
- Contact dermatitis
- Diaper dermatitis
- Discoid (nummular) eczema
- Fixed drug eruption
- Human papillomavirus
- Intertrigo
- Lichen planus
- Lichen sclerosus, also known as balanitis xerotica obliterans
- Mondor phlebitis (disease) of the penis
- Penile intraepithelial neoplasia (Bowen disease, bowenoid papulosis, Erythroplasia of Queryat, squamous cell carcinoma in situ)
- Psoriasis
- Reactive arthritis
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- Urethritis
Prognosis
The prognosis for balanoposthitis is generally quite good. Most patients without a clear infectious etiology will respond to changes in hygiene and empiric therapy with emollients within one to two weeks.[67] However, about one in ten of those patients' symptoms will recur, requiring further evaluation and more targeted management.[9]
Complications
Patients with symptoms that recur or are refractory to four weeks of treatment and present with associated pathologic phimosis or urinary obstruction should be considered for a biopsy to investigate the condition further. Circumcision or a 1 cm wedge biopsy of the affected area is necessary for a pathologic diagnosis and histologic grade. Refractory cases may represent cancerous or precancerous lesions, including balanitis xerotica obliterans, amebiasis, or squamous cell carcinoma.[68][69] Clinicians may miss these without histopathologic examination.[70]
Deterrence and Patient Education
The clinician and other healthcare staff must educate and provide guidance to patients and families regarding appropriate preputial hygiene; this intervention can be preventative as well as therapeutic in most cases of balanoposthitis.
Proper preputial hygiene involves gentle cleaning of the area 2 to 3 times daily. If physiologic phimosis is present, forceful prepuce retraction should be avoided. In patients able to retract the foreskin, the area can be cleaned with a cotton swab. Strong or scented soaps are also not recommended, as they irritate the male genitalia.
Investigating other possible irritants and providing guidance on how to avoid them can also significantly improve symptoms.
Circumcision is considered a prophylactic measure for balanoposthitis.[13][16][71]
Pearls and Other Issues
Prevention
Balanoposthitis can be prevented by first establishing proper hygiene habits, including routine washing of the area, avoiding forceful retraction of the foreskin, aggressive scrubbing or cleaning under the prepuce in young boys with physiologic phimosis, and avoiding strong soaps and detergents.
Another way to prevent balanoposthitis is circumcision. Although controversy exists regarding recommendations for circumcising neonates, research shows it prevents penile dermatosis, urinary tract infections, penile cancer, and sexually transmitted infections such as HIV, HPV, and syphilis.[69][72][73] See StatPearls' companion topic "Circumcision" for further information.[73]
Conflicting literature exists regarding whether circumcision prevents balanitis compared to balanoposthitis in uncircumcised patients.[72][74] However, meta-analysis data has shown that inflammatory conditions of the glans penis have a 3.1 times higher prevalence in uncircumcised males.[75]
Avoiding high-risk sexual behavior may help prevent balanoposthitis by decreasing the risk of sexually transmitted infections such as syphilis, herpes simplex virus, and human papillomavirus, which can contribute to balanoposthitis.
Disposition
Most patients without a clear infectious etiology will respond to changes in hygiene and empiric therapy with emollients within one to two weeks. About one in ten of those patients' symptoms will recur, and they need further evaluation and more targeted management.[9] Cases that do not resolve or improve with standard therapy after 30 days should be considered for further evaluation, such as NAAT testing for herpes and trichomonas, as well as candidal cultures and a serum syphilis screening test. If these are all negative, a biopsy or circumcision should be considered for possible malignancy, amebiasis (Entamoeba histolytica), etc. Patients with symptoms that recur or are refractory to four weeks of treatment and present with associated pathologic phimosis or urinary obstruction will need a biopsy and/or circumcision.
A biopsy is warranted to investigate refractory cases further, as an underlying malignancy or pre-malignant lesion may be present.[16] Such lesions could include squamous cell carcinoma, Erythroplasia of Queryat, Bowen disease, or penile intraepithelial neoplasia.[25][68][69] These may often be missed without histopathologic examination.[25][70]
A circumcision or a 1 cm wedge biopsy of the affected area should be performed to obtain a pathologic diagnosis and histologic grade.[69]
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
When managing balanoposthitis, an interprofessional approach to healthcare can positively impact patient outcomes and safety. A strong communication network is imperative for a strong healthcare team. Detailed documentation can improve communication and avoid redundant testing, unnecessary antibiotics, and loss of follow-up.
Communication with nurses can help them further clarify patient education, hygienic care, prescriptions, and the importance of follow-up. Pharmacists can be involved in verifying proper dosing and mode of administration for patients and compatibility with other medications. They review prescriptions, check for drug interactions, and counsel patients and their families.
Early urological consultation and treatment may be needed in refractory or urgent cases to minimize complications.
The patients themselves must be considered a part of the interprofessional healthcare team, which includes primary care physicians, pediatricians, general and pediatric urologists, dermatologists, infectious disease specialists, nurses, and pharmacists.
Providing the patient and his family with a clear explanation of the diagnosis, likely causes, treatment options, possible complications, the importance of close follow-up, and detailed home management instructions can also have a positive impact on compliance, overall patient care, outcomes, and the patients quality of life.