Continuing Education Activity
An atrioventricular block is a loss of the regular function of the cardiac electroconductive pathways linking the sinoatrial node (SA node) and the ventricles via conduction through the atrioventricular node (AV node). Third-degree AV block indicates a complete loss of communication between the atria and the ventricles. Without appropriate conduction through the AV node, the SA node cannot act to control the heart rate, and cardiac output can be diminished secondary to loss of coordination of the atria and the ventricles. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of patients with third-degree atrioventricular block and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating, monitoring, and treating patients with this condition.
Objectives:
- Describe when a third-degree atrioventricular block should be in the differential diagnosis.
- Summarize the reversible and irreversible causes of third-degree atrioventricular block.
- Explain treatment considerations for patients with third-degree atrioventricular block.
- Review the importance of the interprofessional team in monitoring and evaluating patients in a third-degree atrioventricular block.
Introduction
An atrioventricular block is a loss of the regular function of the cardiac electroconductive pathways linking the sinoatrial node (SA node) and the ventricles via conduction through the atrioventricular node (AV node). Third-degree AV block indicates a complete loss of communication between the atria and the ventricles. Without appropriate conduction through the AV node, the SA node cannot act to control the heart rate, and cardiac output can diminish secondary to loss of coordination of the atria and the ventricles. The condition can be fatal if not promptly treated. Most patients will require a permanent pacemaker. Temporary pacing may be considered on a case-to-case basis while a permanent pacemaker is awaited.
Etiology
The underlying cause of AV blocks is varied and the same for all degrees of blocks. These causes include idiopathic fibrosis and underlying chronic cardiac diseases such as structural heart disease, acute ischemic heart disease, medication toxicity, nodal ablation, electrolyte abnormalities, and post-operative heart block, such as after surgical or transcatheter aortic valve replacement.[1] Additional causes of AV block include Lyme disease and some systemic diseases such as collagen vascular disorders, amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Drugs associated with third-degree heart block include:
- Antiarrhythmics from all four classes
- Digoxin
An anterior wall MI with an intranodal complete heart block is a life-threatening condition. About 5 to 10% of patients with an inferior wall MI will develop a complete heart block, which may resolve within 2 to 48 hours. In general, a complete heart block after an acute MI is rare. AV blocks may accompany right coronary artery occlusion and most resolve after revascularization.
AV block can occur after open-heart surgery, septal alcohol infusion, and percutaneous coronary interventions. After aortic valve surgery, complete heart block is more commonly seen in female patients and those with annular calcification.
Epidemiology
Although AV blocks are fairly common, third-degree AV block is relatively rare.[2] The incidence in the general population appears to be low, approximately 0.02% to 0.04%.[3] Given the etiology of the disease, the incidence among the apparently healthy and presumptively asymptomatic individuals is as low as 0.001%.[4] Similarly, as one looks at people with a greater disease burden, the incidence increases with a study of patients in the Veterans Health Administration, demonstrating an incidence of 1.1% in those with diabetes mellitus and 0.6% in those with hypertension.[5]
Pathophysiology
Under its regular function, the AV node receives an impulse from the SA node. That impulse gets delayed in the AV node, assuring the contraction cycle in the atria is complete before a contraction begins in the ventricles. From the AV node, the electrical impulse passes through the His-Purkinje system to activate ventricular contraction. When there is a pathological delay in the AV nodal conduction, it is visualized on an electrocardiogram as an alteration in the PR interval. These delays present in the form of AV blocks, which are of first, second, and third-degree.
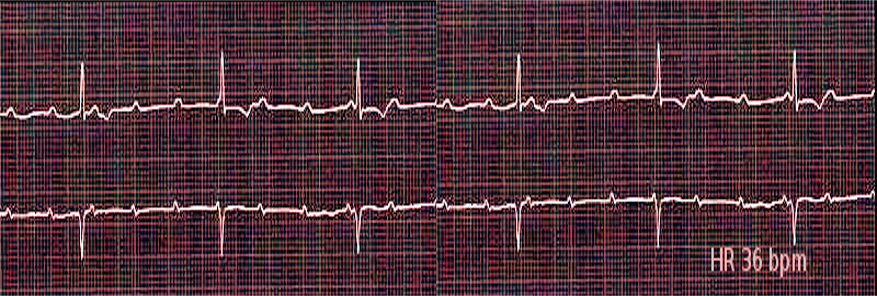
The third-degree block is also known as complete heart block. As the name implies, no impulses from the SA node get conducted to the ventricles, leading to a complete atrioventricular dissociation. The SA node continues its activity at a set rhythm, but the ventricles activate through an escape rhythm that can be mediated by either the AV node (junctional escape), one of the fascicles (fascicular escape), or by ventricular myocytes themselves (ventricular escape rhythm).[1]
The heart rate will typically be less than 45 to 50 beats/min, and most patients will be hemodynamically unstable. This rhythm is unresponsive to atropine and exercise.
History and Physical
Patients with third-degree blocks can have varying clinical presentations. Rarely are patients asymptomatic. Usually, they may present with generalized fatigue, tiredness, chest pain, shortness of breath, presyncope, or syncope. They may have significant hemodynamic instability and can be obtunded. The patient's status at the time of presentation can vary depending on the concurrent disease and the rate of the escape rhythm. Patients with complete AV-block accompanying an acute myocardial infarction often have ischemic symptoms of chest pain or dyspnea. The past medical history will often include the presence of cardiovascular disease and/or its risk factors, including diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking, etc.
The physical exam is usually remarkable for bradycardia. JVP examination often demonstrates cannon A-waves owing to the simultaneous contraction of the atria and ventricles. Thus a very large pressure wave is felt up against the vein. Especially with heart rates below 40/min, patients might also present with features consistent with decompensated heart failure, respiratory distress, and hypoprofusion, such as diaphoresis, tachypnea, altered mental status, retraction, cool skin, and decreased capillary refill.
The presence of any new murmurs should be noted as a strong association exists between complete AV block and cardiomyopathies, mitral calcification, aortic calcification, or endocarditis. If there is coexistent heart failure evidenced by S gallop, peripheral edema, or hepatomegaly, then immediate pacing is a crucial part of management.
Attention should be paid to any signs of infection or skin rashes, such as rheumatic fever, Lyme disease, and endocarditis, which cause heart blocks.
Evaluation
Patients with complete heart block might present in significant distress. After stabilizing the patient, the most important component of the evaluation is the electrocardiogram. The electrocardiogram will have completely independent atrial and ventricular activity with no relation between the P wave and the QRS complex. The atrial rate, demonstrated by the P wave, should be faster than the ventricular rate, as demonstrated by the QRS complex. Depending on the location of the block, the QRS complex might be a narrow morphology (junctional escape QRS complex) or a wide morphology (ventricular escape QRS complex). An ECG should also have an evaluation for signs of ischemia. A basic metabolic panel should be obtained to correct electrolyte abnormalities and to evaluate and correct the glucose, which might be low in beta-blocker toxicity. Troponin should also be evaluated and trended to check for myocardial infarction. In patients who take digoxin, a digoxin level must be obtained to exclude digoxin toxicity. A chest radiograph and complete blood count are necessary to evaluate for concomitant diseases.
Treatment / Management
The initial management of bradycardic patients that are symptomatic usually begins with the use of intravenous atropine as per the advanced cardiac life support recommendations. Unfortunately, atropine acts at the AV node and, as such, is rarely effective in raising the heart rate in patients with complete heart block. Subsequently, medical options for treating symptomatic bradycardia include dopamine and epinephrine, but both may serve as a temporary supporting measure only and might also be unsuccessful in improving the patient's heart rate in third-degree AV block. Often patients with third-degree heart block will require pacing. Transcutaneous pacing is more rapid, although both electrical and mechanical capture must be assured.
If transcutaneous pacing is not successful, a transvenous pacemaker may be required on a case-by-case basis. A cardiologist/electrophysiologist consultation for placing a permanent pacemaker is most appropriate in stable patients. Pacing may not be successful if underlying diseases causing the heart block do not receive treatment; this is particularly true in drug toxicity. Although the clinician might attempt pacing in these patients, the priority should be to treat the underlying cause.
The patients with Mobitz II block, high-degree AV block, and third-degree AV block require urgent admission for cardiac monitoring, further evaluation, consideration of a backup temporary cardiac pacing on a case-to-case basis, and eventually, the insertion of a permanent pacemaker. There is modest evidence and strong clinical consensus that patients with persistent second or third-degree AV block must receive permanent cardiac pacing therapy. The evidence is modest, and the consensus is weak for patients who have persistent bifascicular block (with or without underlying first-degree AV block) associated with transient AV block or with prolongation of PR interval.
Use of an urgent or emergent temporary transvenous pacemaker should not be a "knee-jerk" reaction to the presence of a second-degree, high grade or third-degree AV block. It should be considered after a careful evaluation of the risk-benefit ratio in clinical settings, consideration of hemodynamic stability (as gauged by the evaluation of systolic blood pressure and the degree and duration of the patient's clinical symptoms), level of AV block and presence of the type of escape rhythm. Complications are very common in patients treated with the placement of a temporary transvenous pacemaker. The complications are not just related to the implant itself but also related to the care post-implant, including the change of position of the lead, change of capture threshold, pacer malfunction, faulty programming, and/or battery depletion of the pacer box. Complications may also be related to accidental extraction of the lead by the patient. The use of a temporary pacer should be kept to the shortest duration possible to avoid patients' risk of immobility, infection, thromboembolism, and risk of cardiac perforation. The potential complications must be kept in mind as sometimes the risk-benefit ratio may significantly outweigh justifying its potential use. European Task force guidelines and other expert consensus usually strongly lean towards the fact that temporary transvenous pacing should be avoided as far as possible, and the treatment time should be kept as brief as possible.[6][1][7]
Based on the European guidelines and a wide expert consensus,
- Temporary transvenous pacer should not be used routinely as a knee-jerk reaction in AV block and preferably be used as a last resort when the response to positive chronotropic drugs such as isoproterenol, epinephrine, or low-dose dopamine is insufficient.
- Temporary transvenous pacing should be ideally limited to cases of (i) high-degree AV block without a stable escape rhythm, (ii) life-threatening bradyarrhythmias that may occur during interventional procedures such as percutaneous coronary intervention, or, rarely, in acute settings such as acute myocardial infarction, drug toxicity or in a condition with a concomitant systemic infection where permanent pacing device should ideally be delayed until clearance of infection. For example, patients with stable blood pressure, a persistent junctional escape rhythm, a persistent ventricular escape rhythm, or those with a subacute onset can be monitored carefully on telemetry.
- If the indication for permanent pacing is definitely established, every effort should be made to implant a permanent pacer as soon as possible. The general expert notion is that routine implantation of a temporary pacer before a permanent pacer may increase the risk of complications such as device infection of a permanent implant, other risks of possible complications related to two invasive procedures instead of one, and also potentially increase the risk of cardiac perforation, especially in cases with an extended delay between the temporary pacer and permanent pacer lead implantation.
In patients with heart block secondary to an acute myocardial infarction, temporary pacing can be considered in the cath lab. In patients with acute inferior infarct secondary to an occluded right coronary artery, timely restoration of arterial perfusion may often lead to improvement of the complete heart block. On the contrary, a complete heart block related to an anterior infarction is more likely to eventually require the placement of a permanent pacemaker than patients with inferior infarction. In a large recent study utilizing the National Inpatient Sample databases in patients with STEMI, the incidence of complete heart block was found to be approximately 2.2% in acute ST-elevation MI patients. It demonstrated that the in-hospital mortality was significantly higher in patients with complete heart block than those without it. Although temporary pacing was higher in inferior MI patients, the need for an eventual permanent pacemaker was significantly higher in anterior MI patients.[6][7]
Regardless, cardiac catheterization and attempt for successful restoration of perfusion should not be delayed in patients with acute MI and complete heart block. Timely perfusion increases the likelihood of native rhythm restoration.
Differential Diagnosis
Third-degree heart block is often a straightforward diagnosis on the 12-lead ECG. It is characterized by the presence of a complete AV-dissociation, with an atrial rate being faster than the ventricular rate. It is crucial to differentiate complete heart block from AV dissociation related to other causes, such as in idioventricular rhythms where the ventricular rate is faster than the atrial rate. Sometimes, second-degree heart blocks and high-degree AV blocks may masquerade as complete heart blocks. Repeating ECGs or longer rhythm strips are often helpful in making such a distinction.
Prognosis
The long-term prognosis of third-degree AV block is not well studied (as it often requires treatment in acute settings). The prognosis likely depends on the patient's underlying disease burden and the severity of the clinical presentation on arrival. Complete heart block is sometimes reversible in settings such as acute MI by restoring coronary perfusion and in conditions such as Lyme disease by antibiotic treatment. Historically, high-grade AV blocks have been considered a marker of poor prognosis in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, and more recent studies indicate that this continues to be true in the era of percutaneous coronary intervention.[8]
As previously mentioned, the presence of a complete heart block in acute MI is an independent predictor for increased mortality in these patients. Complete heart block occurs more frequently in patients with inferior MI than anterior MI. Although the use of temporary pacing was higher in inferior MI patients, the need for an eventual permanent pacemaker was significantly higher in anterior MI patients. Also, the mortality associated with complete heart block is higher in patients with anterior MI compared to inferior MI.[9]
The recommendation is that a pacemaker is placed in patients with a persistent third-degree AV block, although the term "persistent" is often a matter of clinician judgment.[10] An Italian survey of just over 24000 patients found that 21% received pacing for third-degree AV blocks.[11] Although a pacemaker is a definitive treatment for patients with third-degree AV block, it does carry some burden of heart failure itself. A 2017 study concluded that patients with AV blocks are more prone to develop heart failure than those without an AV block, both acutely (over six months) and chronically (6 months to 4 years), which may be related to the dependence on frequent RV pacing.[12]
Complications
Patients with third-degree heart blocks are vulnerable to decreased perfusion related to symptomatic bradycardia and decreased cardiac output. Patients may experience syncope-related falls and head injuries. Critically ill patients may be unable to protect their airways, develop nausea, possibly aspirate, and may have delirium. Treatment-related complications in the short term are malposition or dislodgement of a pacemaker lead and cardiac perforation in the short term, and pacemaker-associated heart failure in the long term. As is true for the prognosis of third-degree heart block, complications frequently depend on a patient's overall health and compensatory mechanisms.
Consultations
A cardiology consultation should be sought in all patients suffering from third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block. In patients with coexistent acute myocardial infarction, congestive cardiac failure, or symptoms of hypoperfusion, an emergent cardiologic consultation is indicated. An electrophysiologist should also be consulted whenever appropriate.
Deterrence and Patient Education
Patient education should focus on diminishing the overall disease burden. Although not directly causative, underlying cardiac risk factors like diabetes mellitus and hypertension, as discussed above, are associated with an increased prevalence of third-degree AV block. Generally speaking, a focus on overall cardiac health would be expected to improve the prognosis.
After implanting a permanent pacemaker, patients should have counseling about wound care and receive post-operative instructions. The patients should often refrain from driving for about 2 to 3 weeks and should use an arm sling during the night and intermittently during the day to prevent any arm movement above the shoulder level. They should receive education regarding devices known to cause significant electromagnetic interference with the pacemaker, although this is less of a concern with newer-generation pacing devices available in the market. Patients should also be educated about periodic pacemaker check-ups, including but not limited to the lead function, lead thresholds, and battery life evaluation.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
The management of patients with third-degree AV block requires interprofessional care coordination. The initial diagnosis often starts with the hospitalist, intensivist, or emergency department physician. The initial phase of stabilization of the critically ill patient with third-degree AV block requires close coordination and communication of the physician, nurses, and ancillary healthcare workers to carry out the principles of the bradycardia algorithm of advanced cardiac life support. If the patient is not currently in a critical care setting, the care teams must coordinate appropriate transportation to a critical care facility.
Nursing will assist with care irrespective of whether it is medical treatment or if the pacing is the choice of therapy. If medical, the nurses will coordinate with the pharmacist to verify all dosing, and the pharmacist will perform medication reconciliation and report any concerns. Nursing staff will administer drugs (e.g., epinephrine) and monitor for effectiveness or adverse events.
Critically ill patients with third-degree AV block should be treated in the emergency department, intensive care unit, or the cardiac catheterization laboratory. During and following the initial patient stabilization, coordination and communication among physicians, nurses, and ancillary staff are of utmost importance as the patient will require close monitoring and possibly rapid interventions if the clinical scenario changes. The primary care team needs to coordinate with consulting clinicians; usually the intensivist and the cardiologist or electrophysiologist, to place the patient in a monitored setting or place a temporary intravenous pacer until an evaluation of the underlying etiology is done and the decision can be made to implant a permanent pacemaker. No evidence was discovered outlying the specific goals or practices to improve healthcare team performance, but typical procedures and policies used to activate critical care teams are necessary as appropriate to the healthcare setting.
Ultimately, third-degree AV block cases require an interprofessional team approach, including physicians, specialists, specialty-trained nurses, and pharmacists, all collaborating across disciplines to achieve optimal patient results. [Level 5]