Continuing Education Activity
Tonometry involves diagnostic testing to measure the pressure inside the eye or intraocular pressure (IOP). Glaucoma is a silent disease that causes irreversible functional peripheral visual field loss that can ultimately lead to blindness in the very late stages of the disease if not treated. Tonometry should be performed during routine ophthalmic examinations to screen for glaucoma and other ocular diseases. This activity reviews the main instruments based on the applanation principle and highlights the importance of obtaining precise, accurate, and reproducible measurements of IOP by clinicians. This activity shows the various methods, instruments, advantages, and limitations in applanation tonometry.
Objectives:
- Describe the principles of applanation tonometry based on the Imbert-Fick law.
- Summarize the different types of applanation tonometers used to take IOP readings.
- Describe each applanation tonometer's correct methodologies, techniques, indications, contraindications, limitations, and advantages.
- Review the importance of applanation tonometry in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up assessments in managing patients in a routine clinical setting.
Introduction
Tonometry involves diagnostic testing to measure the pressure inside the eye or intraocular pressure (IOP). Glaucoma is a silent disease that causes irreversible functional peripheral visual field loss that can ultimately lead to blindness in the very late stages of the disease if not treated. Tonometry should be performed during routine ophthalmic examinations to screen for glaucoma and other ocular diseases. IOP must be monitored periodically during the management of patients with glaucoma, ocular hypertension (OHT), and subjects at risk of developing glaucoma.
Normal IOP measures in the range of 10 to 21 (mmHg), which is based on average IOP levels in populations surveys in normal subjects, and less than 2 % of normal subjects show IOP greater than 21 mmHg.[1]
Possible causes for an IOP under normal rages (hypotonus) include uveitis, ocular traumas, retinal detachment, and post-surgery complications, especially after filtering surgery. Elevated IOP is normally caused by glaucoma. The definition of glaucoma in the past years has evolved from a disease solely defined by IOP>21 mmHg to include the assessments of functional and morphological defects.
The concept of determining and re-evaluating a personalized target IOP is currently an important issue in managing patients. These ranges in mmHg are associated with levels of IOP that are thought to cause a minimal likelihood of optic nerve damage or visual field loss, or progression of an existing lesion due to OHT.[2]
Treatment of OHT and glaucoma involves lowering IOP using local drop therapy, laser, and/or surgery. It is thus of utmost importance that instruments used to measure IOP are properly calibrated, accurate and precise, considering that the treatment options are based on IOP levels, together with visual field results, clinical evaluations, and morphological assessments of the optic nerve and retinal nerve fiber layer.
The true IOP inside the eyeball can be measured by inserting a probe in the anterior chamber to measure the manometric pressure. However, this invasive technique tends to be strictly used in animal models and can surely not be considered in a routine clinical setting.[3]
Numerous instruments and tonometers have been created since the 1800s to measure IOP, which have been designed to provide accurate, reliable, precise, and reproducible measurements of IOP. Each method has advantages, disadvantages, and limits and is more or less influenced by ocular factors, rendering some methods clinically acceptable and practical while others are obsolete.
Tonometers are based on different concepts and principles of physics that define how IOP levels are measured and what factors can theoretically influence these readings. The force needed to applanate, indent, and/or rebound the surface of the eye is used to estimate and calculate the IOP provided by the numerous tonometers used to date. It is important to note that IOP readings can be influenced by numerous factors based on each tonometer used.[4]
These factors can influence accuracy, precision, repeatability, measurement variability, and specificity. The factors that need to be considered include the amount of fluorescein, excessive tear production, corneal astigmatism, scarring, scleral rigidity, corneal edema, central corneal thickness, and arterial perfusion, central venous pressures, eye position, etc.[4]
Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT) is currently the most widely accepted method used to measure IOP and is considered the gold standard tonometer in clinics.[5] GAT indirectly measures the IOP by assessing the force needed to flatten a predetermined surface area of the cornea. Taken simplistically, if the eyeball is hard, it takes more force to flatten the surface of the cornea, which is directly influenced by the IOP. GAT is based on the principles of applanation tonometry. Other instruments that have been built using the principles of applanation include the Perkins applanation tonometer, non-contact tonometers, and the Ocular Response tonometer (ORA).[6]
Indications
Tonometry is routinely used in a clinical setting to measure IOP. Indications for applanation tonometry include:
- Periodic screening for glaucoma.[7]
- Diagnosis of OHT and all forms of glaucoma.[8]
- Management and follow-up assessments of IOP in patients with OHT and glaucoma.[9]
- Diagnosis, management, and differential diagnosis of numerous ophthalmologic conditions that cause elevated IOP (i.e., Posner-Schlossman syndrome, uveitis, a long-term steroid medication, pigment dispersion syndrome, etc.).[10][11]
- IOP assessment before and after surgery.[12]
- Diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with infection, trauma without globe rupture, inflammation, etc.[13]
Contraindications
There are several cases in which applanation should be avoided or limited due to the nature of the testing method, which includes:
- The various methods used in applanation tonometry involve contact of the cornea with the instrument tip or with a column of air. Thus open globe wounds and traumas are contraindications.
- Goldmann and Perkins's applanation tonometry involves administering fluorescein and local topical anesthesia. Patients who do not tolerate these substances should preferably be assessed for IOP with alternative tonometers that are either non-touch or do not require drops or fluorescein.[14][15]
- When performing tonometry, keratoconjunctivitis can be transmitted to the contralateral eye or other patients; thus, contact and air-puff tonometry need to be thoroughly disinfected or preferably avoided.[16]
- GAT and Perkins require assessing the rings formed from the prism in the tip after direct contact with the cornea; thus, patients with central corneal scarring, elevated irregular astigmatism, unhealed corneal abrasions, and/or corneal ulcers should avoid IOP measurements with these tonometers.[17]
- Most applanation tonometers (except for Perkins, which can be used in a supine position and is portable) require cooperative patients in an upright position. Children tend to have limited collaboration.[18] Bedridden and/or non-collaborative patients cannot undergo these types of tonometry.
Equipment
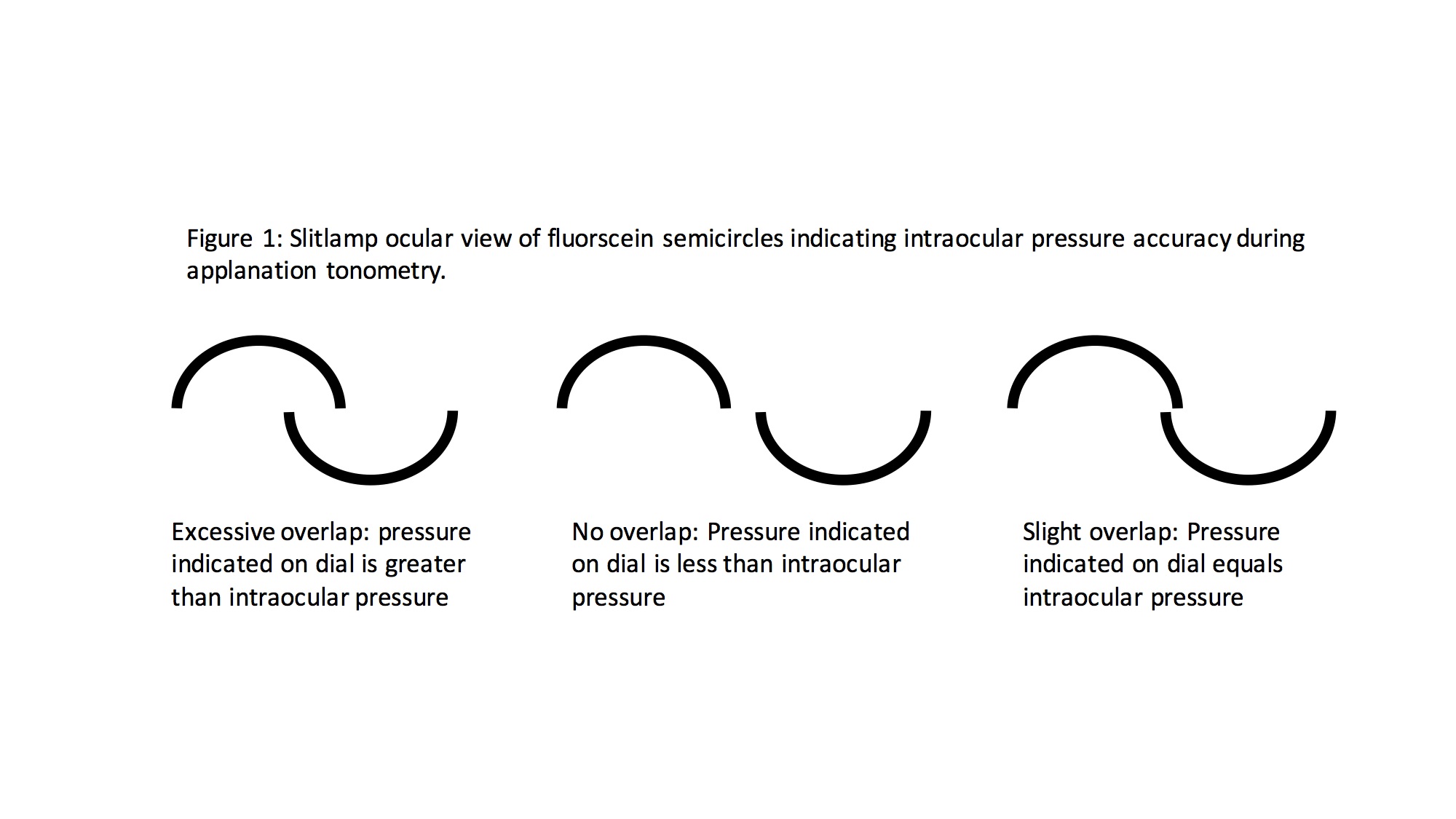
Applanation tonometry is based on the applanation principle described by Imbert and Fick in the late 1800s.[19][20] With regards to applanation tonometry, the law states that pressure (P) within a closed sphere, expressed in mmHg, can be approximated by the force (F) necessary to flatten the cornea in a fixed area, measured in grams, divided by the surface (S) of the flattened area, given in square millimeters. The Imbert-Fick law is defined as P=F/S.[21]
The first applanation tonometer was built by Adolph Weber in 1867, which was later improved and used in clinics in 1885 by Alexei Maklaloff.[22] A more modern version of this applanation tonometer was then later proposed by Posner-Inglima in 1967.[23]
Most of these early instruments did not gain widespread use because of several limitations, which included measurements subject to various errors, difficulties in using the instrument, non-practicability in a clinical setting, etc.
Hans Goldmann invented GAT in 1948, and to this date, it remains the gold standard technique for measuring IOP. Although the Imbert-Fick principle assumes that the sphere is thin-walled without rigidity and elasticity, Goldmann was convinced that corneal elastic properties and thickness were not significantly variable amongst individuals.[20]
Much later, numerous clinical studies showed that corneal properties, including thickness, elasticity, rigidity, and hysteresis, can influence IOP measurements with GAT.[24][25][26] A more complete version of the Imbert-Fick law includes the effect of the surface tension from the tear film (s) and the corneal resistance (b), giving rise to the formula P=F+s-b/S.[27][28]
Eyes with thick corneas tend to show overestimated GAT readings, while those with thin corneas give rise to underestimated IOP readings with GAT, in addition to being a risk for developing glaucoma.[29][30][31]
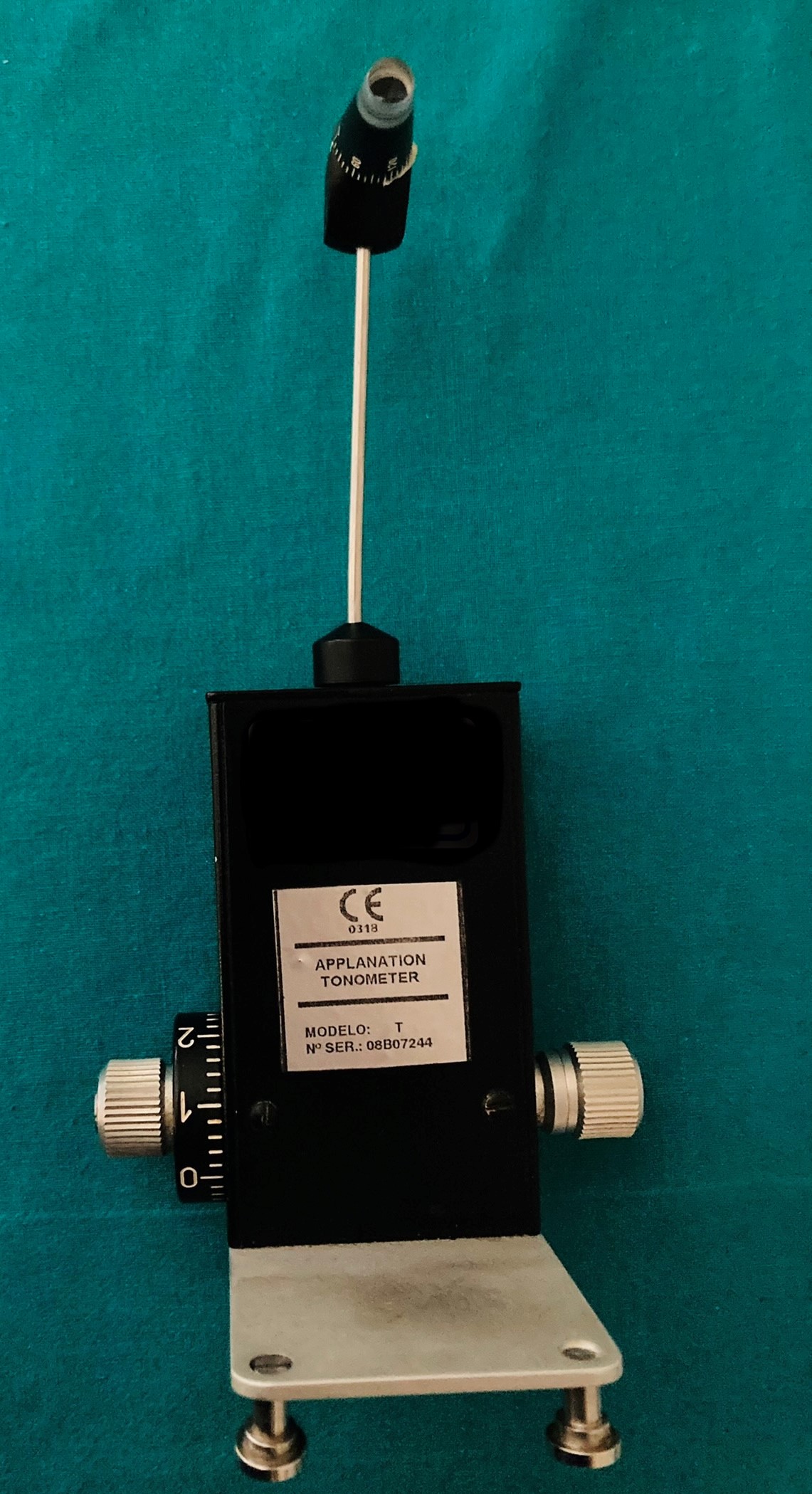
The Goldmann tonometer (See tonometer image) needs to be mounted on a slit lamp, and measurements are taken in an upright position (See slit-lamp image).
Applanation tonometry can be classified as either contact or non-contact. GAT and Perkins are considered as contact applanation tonometers. Air-puff tonometry and ocular response analyzer are defined as non-contact tonometry (NCT). These NCT instruments generate force by air as opposed to direct contact with the cornea and do not require fluorescein and local topical anesthesia.
Goldmann Applanation Tonometer (GAT)
The GAT instrument is composed of a small metal device weighing less than a kilogram, with a height of about 18 cm, a width of 10 cm, and a depth of 4 cm (See tonometer image). The tonometer is made up of a prism holder, a thin metal sensor arm, and a metal weight housing that has a measuring drum equipped with a rotating dial with a range of measurements from 0 to 80 mmHg (See tonometer with dial image).
The tonometer needs to be positioned on a slit-lamp (See slit-lamp image), which can either be permanently fastened and pivoted in front of the eye with a rotating swiveling arm or placed on a metal guided base-plate and used in the retractable version. The tonometer should be calibrated periodically with a control weight bar to ensure accurate measurements.
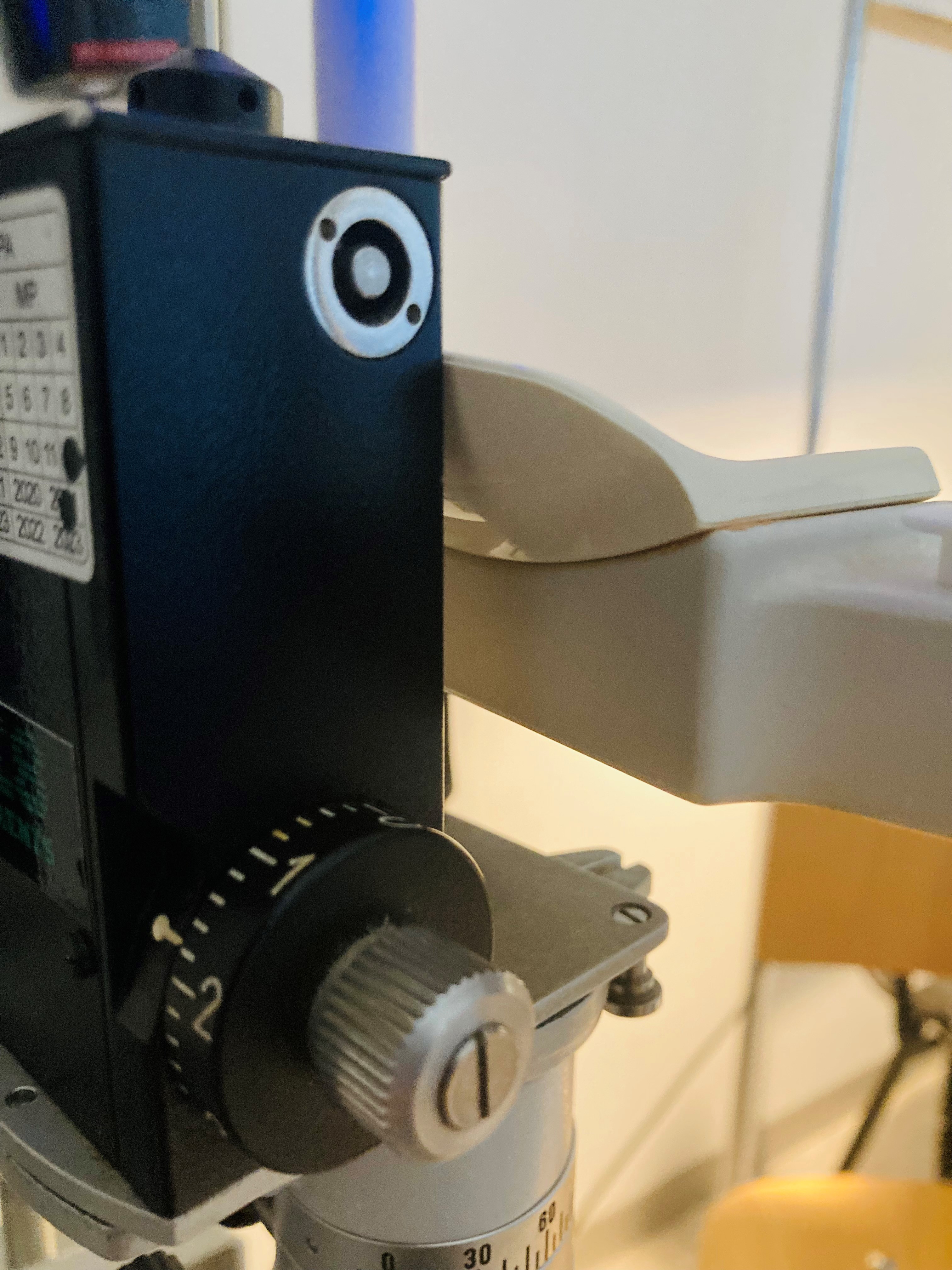
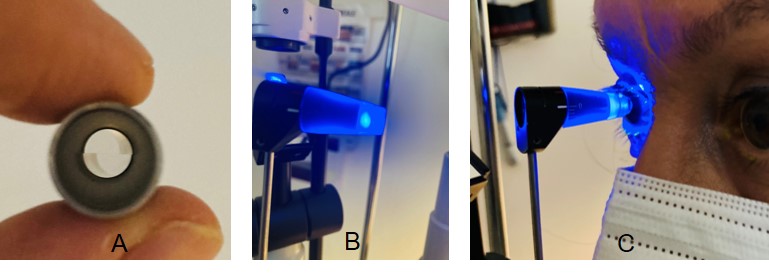
A truncated plastic cone with an embedded doubling measuring prism (See tip images) having a diameter of 7 mm is mounted on the tip of the rod and used to take the IOP measurements; thus, proper cleaning and disinfection are essential when using GAT. Tonosafe disposable prisms are currently available to limit cross-infection risks in patients.
Perkins Applanation Tonometer
The Perkins tonometer, first described by ES Perkins in 1965, uses the same principles as GAT with the advantage of being portable, thus can be used in patients that cannot be positioned in front of a slit-lamp or in a supine potion (i.e., bedridden subjects or patients under general anesthesia).[32]
The device is equipped with an adjustable forehead rest, prism holder for the same type of cone used in GAT, illumination source, viewing lens, milled thumb-wheel with a scale for IOP measurement, and a battery charging port for wireless use. The instrument, however, is rather difficult to use, has limited positioning stability during use, and has a high learning curve to obtain accurate and precise IOP measurements.
Air-Puff Tonometer (non-contact)
NCT was first proposed in the 1970s.[33] Non-contact air-puff tonometry uses a column of air emitted with increasing intensity to applanate the cornea to measure IOP. Sensors and light beams in the instrument are used to regulate the production of air, which is then halted when the cornea is flattened. The IOP measurements, which are based on the force needed to applanate the cornea, are taken by the waveforms of the reflected lights that are analyzed by the sensor detectors and converted by the internal algorithm of the instrument.[34]
There is no direct contact with the eye, and measuring prisms are not used; thus, anesthesia drops and fluorescein are not required. Several desktop tonometers exist, like the Pulsair model, while others are built-in together with refractometers and pachymeters. The Pulsair and Keeler Air-Puff instruments are also available in portable handheld models. The advantages of NCT include the ease of use and the fact that anesthesia, fluorescein, and slit-lamp are not required, making this type of instrument potentially useful in screening settings, in children and patients with limited collaboration, and administered by paramedical staff.[35][36][37]
The disadvantages, however, are that IOP measurements tend to be less accurate than those taken with GAT, giving rise to underestimated and overestimated IOP measurements in higher and lower levels of IOP, respectively.[38] Moreover, studies have shown that NCT measurements are instrument-dependent, greatly influenced by CCT, and offer limited sensitivity and accuracy compared to GAT.[39][40]
Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA, non-contact)
The ORA is a newer version of NCT proposed by Luce in 2005.[41][42] The dimensions of this countertop instrument are approximately 50 cm x 27 cm x 36 cm, and the weight is about 10 kilograms. The instrument is equipped with an interactive operating display on one side and a testing patient mode on the other side with a forehead rest, illuminating nosepiece, an objective for patient fixation and measurement, and an air tube that generates the air impulses.
The instrument uses air impulses to assess IOP and corneal biomechanics based on corneal deformation. The force of the column of air used in this NCT keeps increasing until the cornea is indented in an inward motion, then decreases slowly until the cornea is again flattened as it moves outwardly.[43]
Corneal elasticity or hysteresis is assessed based on the differences between the forces at the initial and rebound applanation points using internal mathematical calculations. The ORA provides two corneal parameters known as corneal hysteresis and corneal resistance factor, which theoretically provide information regarding the viscoelastic mechanical properties of the cornea.[41]
The ORA provides corneal compensated IOP measurements based on individual biomechanics results that have been reported to be less influenced by corneal properties and thickness measurements when compared to GAT; however, several studies have shown that ORA tends to overestimate IOP at elevated levels, and measurements are affected by corneal thickness and other properties.[44]
Future studies are needed to determine whether or not these new parameters provided by ORA will prove to be of clinical interest in the management of glaucoma, which remains debatable and of little use in current routine practice.
Technique or Treatment
Contact tonometry with GAT and Perkins tonometers involves direct contact with the cornea (Figure 4). The process of measuring IOP according to the Imbert-Fick principle involves the applanation of the anterior central portion of the cornea. GAT and Perkins utilize the same system to measure IOP, differing only in that GAT requires a slit-lamp (See slit-lamp image), while Perkins is portable and can also be taken in a supine position.
In performing contact applanation tonometry, local anesthesia drops and fluorescein dye must be applied to the eyes. The tonometer tip with the split-image prism (See tip images) is gently applied to the surface of the central portion of the cornea. The tonometer measures the force needed the flatten the cornea in a central diameter of 3.06 mm.[20]
Measurements are taken using a filtered cobalt blue light, which highlights the borders of the semicircles formed by the tip prism (See tip images). The clinician calibrates the force needed on the eye using the rotating dial of the tonometer (See tonometer with dial image) until the superior and inferior arcs align so that the inner margins just touch (See images with arcs). The IOP is measured in mmHg.
Although contact applanation tonometry is considered the gold standard, the disadvantages of GAT include the need for a slit-lamp, upright position of the patient, installation of anesthesia and fluorescein, skilled ability of the clinician, and decreased accuracy in scarred or irregular corneas. Perkins tonometry shows the same disadvantages as GAT, except that it is portable and can be used in a supine position.
Various factors can affect the precision and accuracy of applanation tonometers, which include central corneal thickness, corneal hysteresis, choroidal rigidity, tear film thickness, amount of fluorescein used, high-grade astigmatism, previous refractive surgery, corneal edema, etc.
With regards to NCT, the technique for measuring IOP is rather simple. It involves correctly positioning the patient in front of the instrument and activating the air puff to measure IOP. The force needed to flatten the cornea by the impulse of air is then converted into IOP measurements by the internal software of the tonometers.
The advantages of NCT, when compared to GAT and Perkins, include the fact that it is rapid, simple to perform, and does not require the use of local anesthesia drops and/or fluorescein. NCT can be an interesting tool in select patients and screening; however, it is not recommended in the routine clinical setting, especially in managing patients with elevated IOP and glaucoma.
Complications
Applanation tonometry, especially contact tonometers like GAT and Perkins that involve direct applanation with the cornea, should be avoided or limited to select cases in the presence of eyes with abrasion, severe trauma and/or globe rupture, signs of infection, and intolerance to fluorescein and/or local anesthesia drops.
Clinical Significance
IOP measurements are of utmost importance in diagnosing, screening, and managing patients with glaucoma. Treatment with local drops, laser, and/or surgery to avoid the onset and worsening of glaucomatous optic neuropathy and visual field defect progression involves lowering IOP, which is the only risk factor that can be modified in glaucoma cases.
GAT is considered the gold standard in the routine clinical management of patients. Alternative methods of tonometry can be considered in select cases; however, routine clinical management to date remains IOP with GAT.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT), which is the gold standard method in measuring IOP, is usually performed by the ophthalmologist and optometrist. Other applanation methods that do not require local anesthesia and fluorescein can also be carried out by nurses, ophthalmic technicians, or emergency medicine.
Proper training and communication are needed in tonometry when managing patients, especially considering that accurate IOP measurements at diagnosis and follow-up examinations are of utmost importance in determining therapeutic strategies.
GAT needs to be mounted on a slit lamp and tonometry performed on patients in an upright position. Topical anesthesia and fluorescein are used to obtain accurate measurements. Alternative methods can be considered when GAT may prove to be less suitable, which include: open globe wounds; patients that do not tolerate anesthesia drops or fluorescein; eyes with keratoconjunctivitis or central corneal scarring, elevated irregular astigmatism, unhealed corneal abrasions, and/or corneal ulcers. Alternative tonometers may be used in bedridden and non-collaborative.
Tonometry readings should be accurate and precise, so choosing the correct instrument to measure IOP when managing patients is crucial. Glaucoma and other ophthalmic conditions can give rise to irreversible vision loss and reduced peripheral vision, which is why IOP needs to be properly assessed at periodic examinations to provide thorough management of patients.[45] [Level 1]
Nursing, Allied Health, and Interprofessional Team Interventions
The nursing, allied health, and interprofessional staff help maintain tonometers. The nursing staff is also aware of the calibration and correct method of storage of the tonometers. They also help in the disposal and replacement of the prism of the tonometer.
Nursing, Allied Health, and Interprofessional Team Monitoring
The nursing, allied health, and interprofessional staff assist in monitoring the proper functioning of the tonometers. In case of any error, the maintenance department helps rectify the fault.