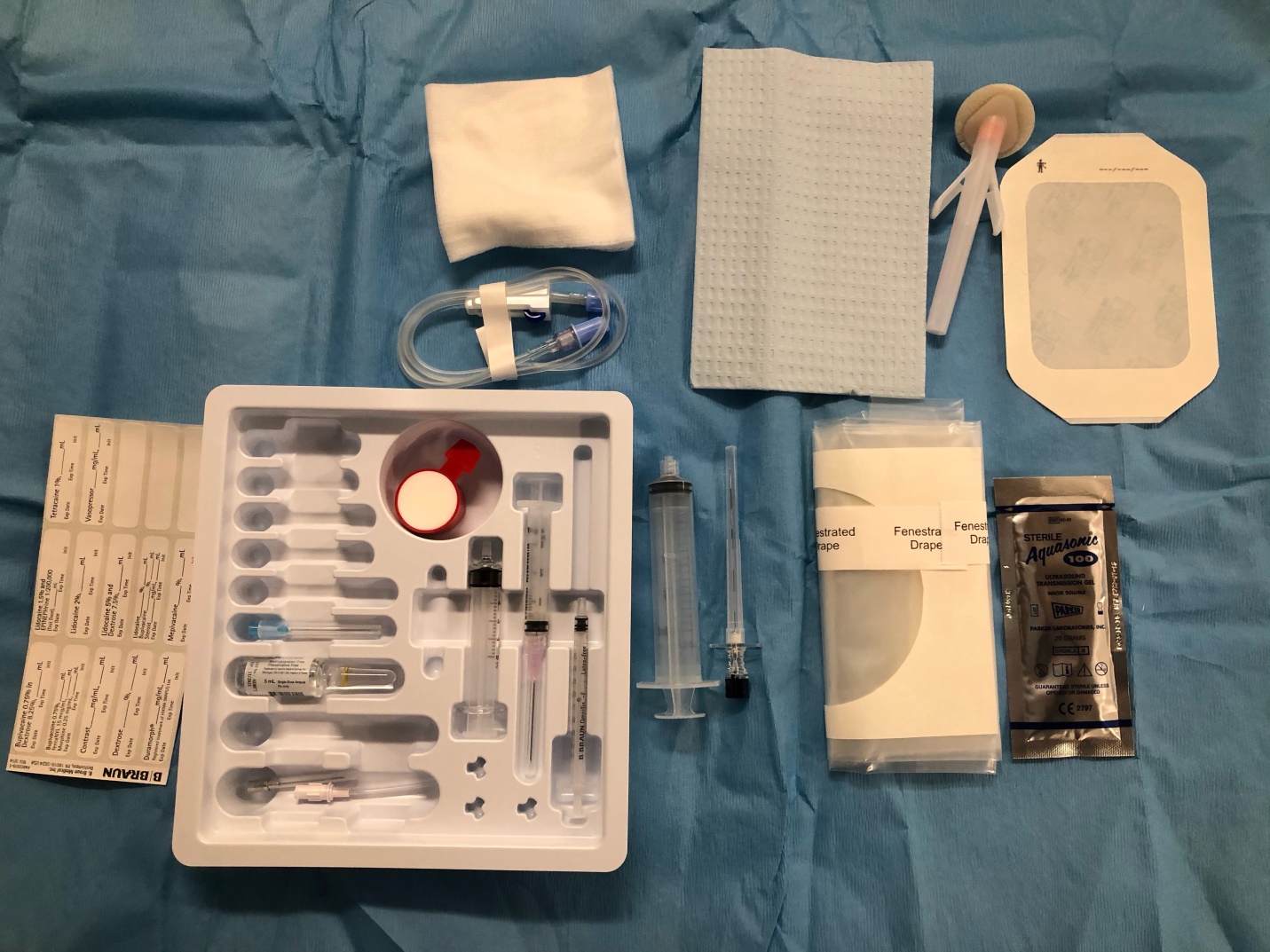
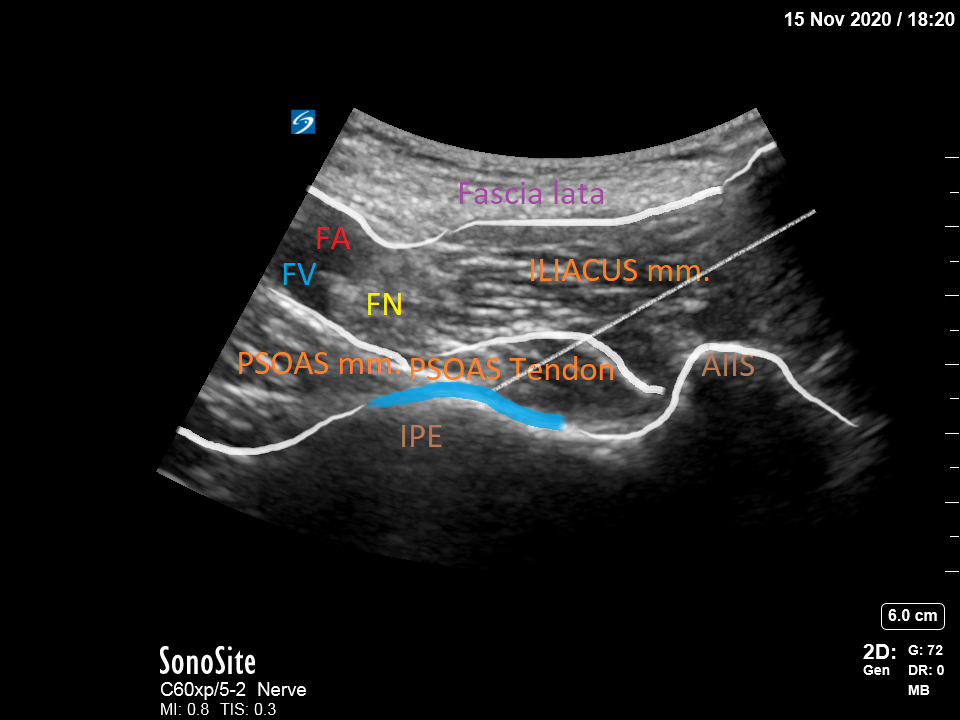
[1]
Girón-Arango L, Peng PWH, Chin KJ, Brull R, Perlas A. Pericapsular Nerve Group (PENG) Block for Hip Fracture. Regional anesthesia and pain medicine. 2018 Nov:43(8):859-863. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000847. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 30063657]
[2]
Lee DJ, Elfar JC. Timing of hip fracture surgery in the elderly. Geriatric orthopaedic surgery & rehabilitation. 2014 Sep:5(3):138-40. doi: 10.1177/2151458514537273. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 25360345]
[3]
Keene GS, Parker MJ, Pryor GA. Mortality and morbidity after hip fractures. BMJ (Clinical research ed.). 1993 Nov 13:307(6914):1248-50
[PubMed PMID: 8166806]
[4]
Scala VA,Lee LSK,Atkinson RE, Implementing Regional Nerve Blocks in Hip Fracture Programs: A Review of Regional Nerve Blocks, Protocols in the Literature, and the Current Protocol at The Queen's Medical Center in Honolulu, HI. Hawai'i journal of health
[PubMed PMID: 31773105]
[5]
Acharya U, Lamsal R. Pericapsular Nerve Group Block: An Excellent Option for Analgesia for Positional Pain in Hip Fractures. Case reports in anesthesiology. 2020:2020():1830136. doi: 10.1155/2020/1830136. Epub 2020 Mar 12
[PubMed PMID: 32231802]
Level 3 (low-level) evidence
[6]
Sakamoto J, Manabe Y, Oyamada J, Kataoka H, Nakano J, Saiki K, Okamoto K, Tsurumoto T, Okita M. Anatomical study of the articular branches innervated the hip and knee joint with reference to mechanism of referral pain in hip joint disease patients. Clinical anatomy (New York, N.Y.). 2018 Jul:31(5):705-709. doi: 10.1002/ca.23077. Epub 2018 Apr 16
[PubMed PMID: 29577432]
[7]
Kampa RJ, Prasthofer A, Lawrence-Watt DJ, Pattison RM. The internervous safe zone for incision of the capsule of the hip. A cadaver study. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British volume. 2007 Jul:89(7):971-6
[PubMed PMID: 17673597]
[8]
Short AJ,Barnett JJG,Gofeld M,Baig E,Lam K,Agur AMR,Peng PWH, Anatomic Study of Innervation of the Anterior Hip Capsule: Implication for Image-Guided Intervention. Regional anesthesia and pain medicine. 2018 Feb;
[PubMed PMID: 29140962]
[9]
Martin HD, Khoury AN, Schroder R, Gomez-Hoyos J, Yeramaneni S, Reddy M, James Palmer I. The effects of hip abduction on sciatic nerve biomechanics during terminal hip flexion. Journal of hip preservation surgery. 2017 Jul:4(2):178-186. doi: 10.1093/jhps/hnx008. Epub 2017 Apr 11
[PubMed PMID: 28630740]
[10]
Kukreja P, Avila A, Northern T, Dangle J, Kolli S, Kalagara H. A Retrospective Case Series of Pericapsular Nerve Group (PENG) Block for Primary Versus Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Analgesia. Cureus. 2020 May 19:12(5):e8200. doi: 10.7759/cureus.8200. Epub 2020 May 19
[PubMed PMID: 32572357]
Level 2 (mid-level) evidence
[11]
Horlocker TT, Vandermeuelen E, Kopp SL, Gogarten W, Leffert LR, Benzon HT. Regional Anesthesia in the Patient Receiving Antithrombotic or Thrombolytic Therapy: American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine Evidence-Based Guidelines (Fourth Edition). Regional anesthesia and pain medicine. 2018 Apr:43(3):263-309. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000763. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 29561531]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence
[12]
Kehlet H, Multimodal approach to control postoperative pathophysiology and rehabilitation. British journal of anaesthesia. 1997 May;
[PubMed PMID: 9175983]
[13]
Højer Karlsen AP, Geisler A, Petersen PL, Mathiesen O, Dahl JB. Postoperative pain treatment after total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review. Pain. 2015 Jan:156(1):8-30. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.0000000000000003. Epub
[PubMed PMID: 25599296]
Level 1 (high-level) evidence