Continuing Education Activity
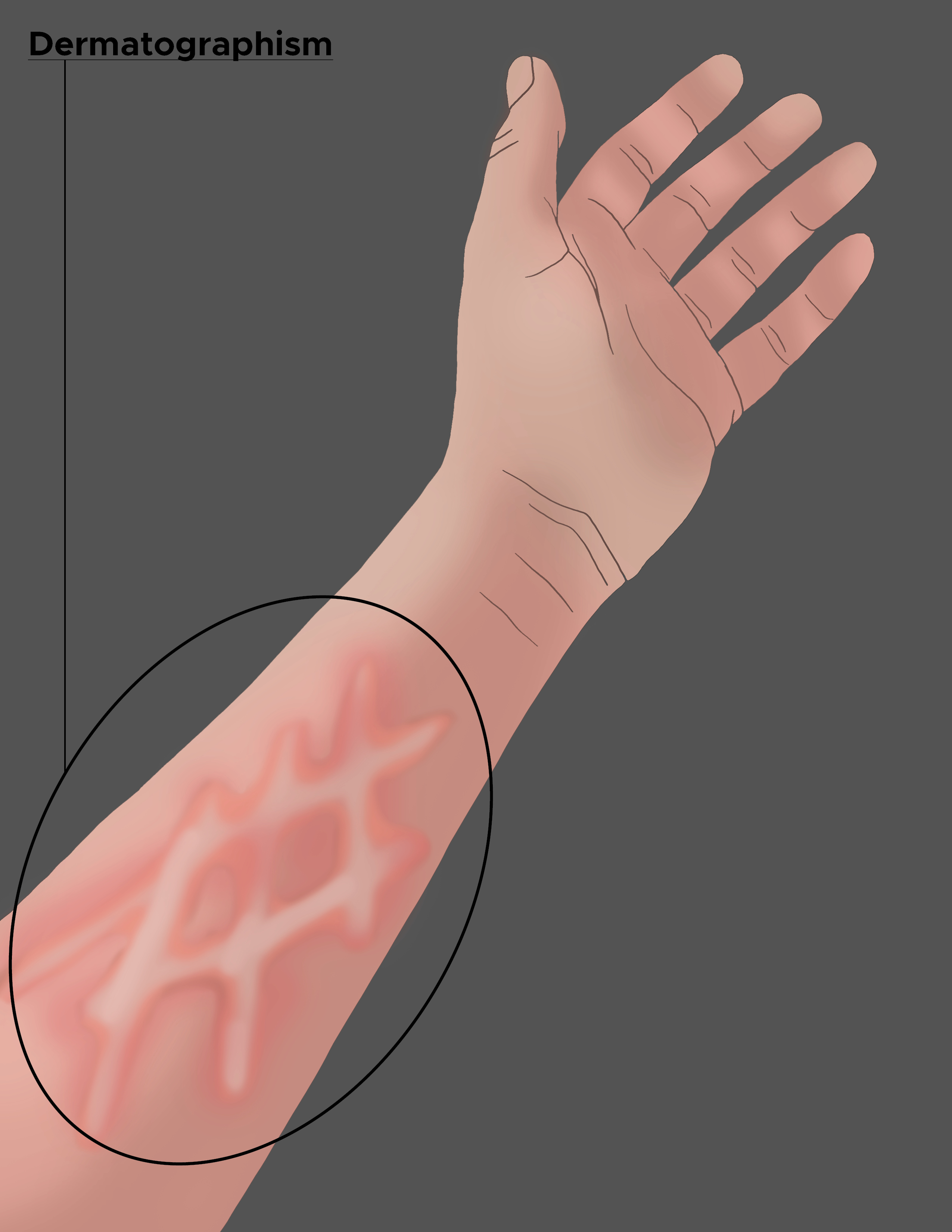
Dermatographism, also known as dermographism urticaria, or urticaria factitia, is an urticarial eruption upon pressure or trauma to the skin. The literal meaning is "to write on the skin." Downward pressure on the skin produces a linear wheal in the shape of the applied external force. Dermatographism is the most common type of inducible/physical urticaria, occurring in approximately 2% to 5% of the population. A small subset of those with dermatographism becomes symptomatic with pruritus along with the erythematous wheals. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of dermatographism and the role of interprofessional team members in collaborating to provide well-coordinated care and enhance patient outcomes.
Objectives:
- Review the differential diagnosis for dermatographism.
- Describe the presentation of dermatographism.
- Summarize the treatment options for dermatographism.
- Outline the evaluation and management of dermatographism and interprofessional team members' role in collaborating to provide well-coordinated care and enhance patient outcomes.
Introduction
Dermatographism, also known as Dermographism urticaria, or urticaria factitia, is an urticarial eruption upon pressure or trauma to the skin. Urticarial skin reactions present as erythematous wheals in the dermis and can have innumerable causes. Dermatographism is the most common type of inducible/physical urticaria, occurring in approximately 2% to 5% of the population. Downward pressure on the skin produces linear erythematous wheals in the dermis in the shape of the external force applied, earning the name dermatographism, which literally means "writing on the skin." A small subset of people with dermatographism becomes symptomatic with pruritus, stinging, prickling sensations that can be bothersome for the patient.[1]
Etiology
The exact cause of dermatographism is unknown. However, the release of histamine from mast cells is thought to play a role.[2] Dermatographism has been seen in people with diabetes, hyperthyroid, hypothyroid, menopause, pregnancy, or medication-related.
Epidemiology
Dermatographism is the most common type of urticaria, frequently presenting in young adults with the peak incidence in the second and third decades. There has not been shown a relationship between race and dermatographism. One study of pediatric patients showed a female predominance.[3] One report cited a case of familial dermatographism.[4]
Hypereosinophilic syndrome is associated with atopic children and increases dermatographism; these are associated with atopic children and an increased number of eosinophils in the blood. One-third of patients that experience traumatic life events, along with psychological co-morbidities, experience dermatographism.[5] Furthermore, stressful events like pregnancy (commonly in the second trimester) and the onset of menopause have seen a higher incidence of the condition. Behcet disease, a condition marked by oral and genital ulcers, is another disease where dermatographism is a common integumentary finding.
Symptomatic dermatographism is thought to be generally idiopathic, but various explanations have been considered. The higher consensus revolves around Helicobacter pylori, antibiotics such as penicillin, bites, or scabies as the more common presentations to suggest this correlation. Lastly, congenital symptomatic dermatographism is the presenting sign in systemic mastocytosis.[6]
Pathophysiology
No concluding mechanism explains why dermatographism occurs. Mechanical trauma activates vasoactive mediators released from mast cells secondary to antigen interaction to the bound IgE. This is thought to cause an exaggerated biological response known as the "triple response of Lewis." Initially, the capillaries become dilated, producing a superficial erythematous phase. Next, an axon-reflex flare and communication to sensory nerve fibers cause an expansion of erythema, secondary to arteriolar dilation. Lastly, the linear wheal is formed through fluid transudation. This entire response takes, on average, up to 5 minutes after an external stimulus stroking of the skin. The wheal can persist anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes, unlike the normal triple response of Lewis that subsides in under 10 minutes. Mediators such as histamine, leukotrienes, bradykinin, heparin, kallikrein, and peptides such as substance P are all considered to play a role in this process.
Histopathology
The histopathology of dermatographism demonstrates dermal edema with few perivascular mononuclear cells similar to acute urticaria histology.
History and Physical
Dermatographism lesions appear following mechanical trauma to the skin, most consistently stroking of the skin. A wheal forms and develops in approximately 5 to 10 minutes. The wheal will persist for about 15 to 30 minutes. The deeper the edema into the dermis, the larger the wheal will appear. In symptomatic dermatographism, pruritus accompanies the wheal. The pruritus worsens at night (thought to be related to the pressure of the bedding and sheets contacting the skin) and friction to the area from external stimuli, heat, stress, emotion, and exercise.
Dermatographism most commonly involves the trunk and extremities, and other body surfaces. The least common areas reported are the scalp and genital area; however, symptomatic dermatographism has been correlated in the literature with dyspareunia and vulvodynia.[7]
There are several rare subtypes of dermatographism:
- Red dermatographism (small punctate wheals, predominantly on the trunk)
- Follicular dermatographism (isolated urticarial papules)
- Cholinergic dermatographism (similar to cholinergic urticaria – large erythematous line marked by punctate wheals)
- Delayed dermatographism (tender urticarial lesion reappears 3 to 8 hours after the initial injury that persist up to 48 hours)
- Cold-precipitated
- Exercise-induced
- Familial
Treatment / Management
Prevention and avoidance of precipitating factors such as physical stimuli and decreasing stressors are important factors in controlling dermatographism. Most patients are asymptomatic, and therapy should be restricted to symptomatic patients. Choice therapy includes treatment with H1 antihistamines such as cetirizine or loratadine. H2 antihistamines can be combined for more complete therapy if H1 blockers are insufficient to control the pruritus. Hydroxyzine, a sedating antihistamine, is a valid option and can be taken before sleep.
Omalizumab is under consideration in research trials focusing on treating dermatographism with 72% efficacy on 150 mg and 58% efficacy on 300 mg. Notably, patients' Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) scale improved by at least 4 points, showing a statistically significant clinical difference.[8]
Light therapy has shown some efficacy in treating dermatographism, yet most patients relapse within 2 to 3 months of completing therapy.
Adjunctive treatment with over-the-counter vitamin C 1000 mg daily is thought to help degrade histamine and increase removal, diminishing the triple response of Lewis.[9]
Differential Diagnosis
If dermatographism is the leading differential, false dermatographism must be ruled out, a condition that presents clinically similar to dermatographism but has a different underlying mechanism. False dermographism has several different forms, including white, black, and yellow. White dermatographism is secondary to allergic contact dermatitis and is prevalent in atopic individuals. Black dermatographism occurs after contact with metallic objects. Yellow dermatographism is due to bile deposits in the skin.
Another condition that presents similarly to symptomatic dermatographism is latex allergy. This commonly is seen on the hands and genital region and will often be related to a history of physically contacting latex in gloves, rubber bands, balloons, toys, or contraceptive use. [10] Mastocytosis, a disorder caused by an increase in the number of mast cells, can also present with pruritic red-brown pigmented lesions. Mastocytosis can be cutaneous or systemic, depending on what area is infiltrated with mast cells. One sign of mastocytosis is called the "Darier sign," which is swelling, pruritus, and erythema in response to pressure applied to the skin. Systemic mastocytosis is more common in adults, and symptoms are based primarily on the organ affected, such as the liver, spleen, bone marrow, or small intestine. Urticaria pigmentosa is the most common cutaneous mastocytosis in children, is rare and benign.[11]
Prognosis
Dermatographism is a benign condition. In a minority of cases, pruritus can accompany the condition. Compared to the other chronic urticarias, symptomatic dermatographism displays the most expedited clearance of the condition after 5 years (36%) and 10 years (51%).[12]
Complications
Dermatographism has no direct complications. However, if the patient uses sedating antihistamines for treatment, they may need to exercise caution before engaging in certain activities such as driving or operating machinery.
Deterrence and Patient Education
Dermatographism can be unsettling in its laborious course without resolve. However, the condition is benign, and patients must be aware of this. The treatment involved, antihistamines, can result in drowsiness; therefore, it is best to advise the patient not to take the medication before operating a vehicle.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Dermatographism is a benign yet startling lesion to most patients and their parents. Thus, it is imperative to educate the patient and their parents properly on the risk factors associated with the onset of dermatographism to avoid such stressors. To properly educate, it is ideal to target the audience in a team-based approach.
- Evaluation by the primary care physician
- Consult the dermatologist when the diagnosis is in question
- Encourage reduction of external stimuli, effective management, and treatment options.