Introduction
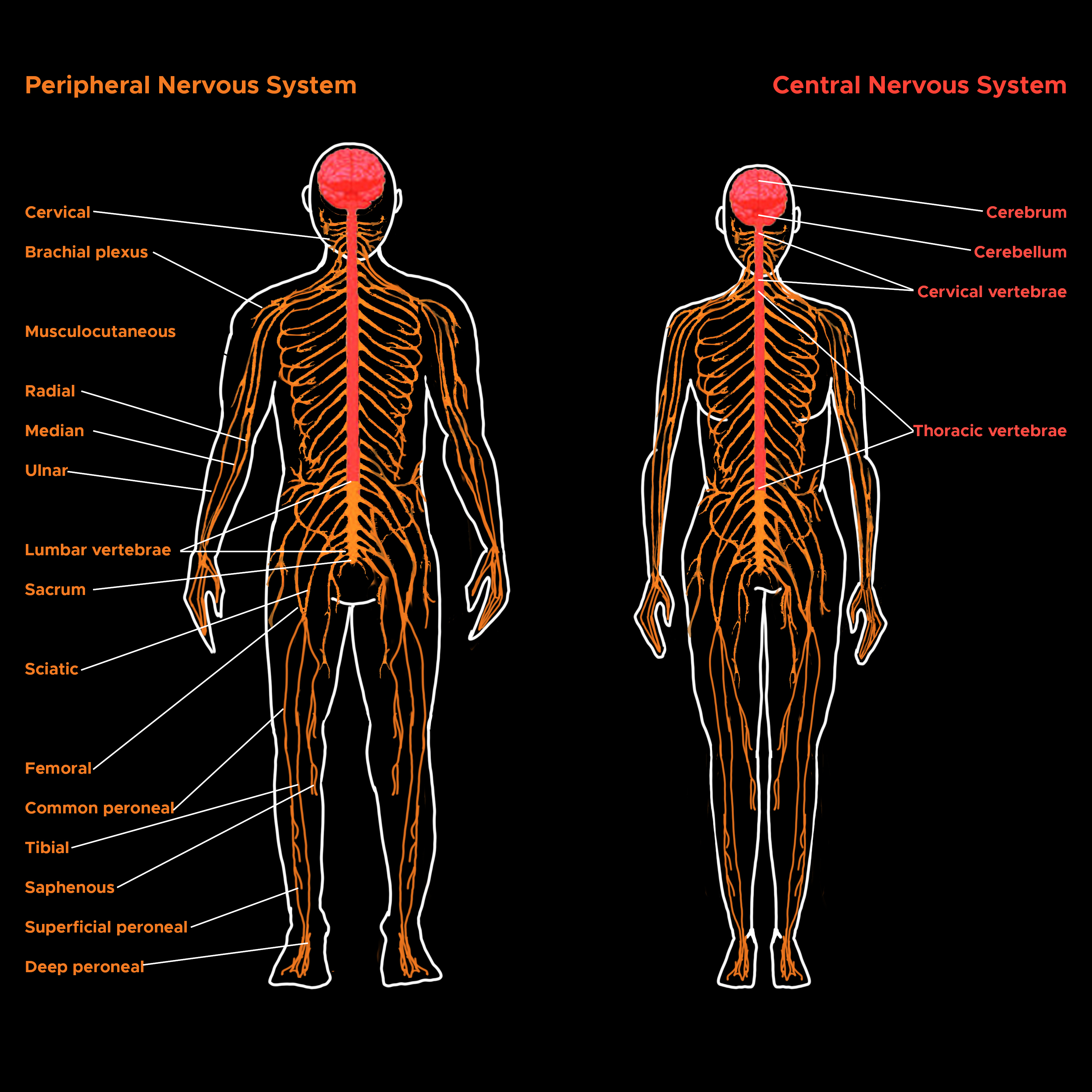
The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system. The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system consists of everything else. The CNS's responsibilities include receiving, processing, and responding to sensory information (see Image. Peripheral and Central Nervous Systems).
The brain is an organ of nervous tissue responsible for responses, sensation, movement, emotions, communication, thought processing, and memory. The skull, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluids protect the human brain. The nervous tissue is extremely delicate and can be damaged by the smallest amount of force. In addition, the brain has a blood-brain barrier that prevents the brain from any harmful substance floating in the blood.
The spinal cord is a vital aspect of the CNS found within the vertebral column. Its purpose is to send motor commands from the brain to the peripheral body and relay sensory information from the sensory organs to the brain. Bone, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluids provide spinal cord protection.
Structure and Function
The brain is divided into 2 hemispheres, the left and the right. While in constant communication, the left and right hemispheres are responsible for different behaviors, known as brain lateralization. The left hemisphere is more dominant in language, logic, and math abilities. The right hemisphere is more creative and dominant in artistic and musical situations and intuition.
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex is the outermost layer that surrounds the brain. It is composed of gray matter and filled with billions of neurons to conduct high-level executive functions. The cortex divides into 4 lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal, by different sulci.[1]
Frontal lobe
The frontal lobe, located anteriorly to the central sulcus, is responsible for voluntary motor function, problem-solving, attention, memory, and language. It also contains the motor cortex and the Broca area. The motor cortex allows for the precise voluntary movements of our skeletal muscles, while the Broca area controls motor functions responsible for producing language.
Parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is separated from the occipital lobe by the parieto-occipital sulcus and is behind the central sulcus. It is responsible for processing sensory information and contains the somatosensory cortex. Neurons in the parietal lobe receive information from sensory and proprioceptors throughout the body, process the can, and form an understanding of what is being touched based on previous knowledge.
Occipital lobe
The occipital lobe, the visual processing center, contains the visual cortex. Like the parietal lobe, it receives information from the retina and then uses past visual experiences to interpret and recognize stimuli.
Temporal lobe
The temporal lobe processes auditory stimuli through the auditory cortex. Sound energy activates mechanoreceptors located in the hair cells lining the cochlea, sending impulses to the auditory cortex. The impulse is processed and stored based on previous experiences. The Wernicke area is in the temporal lobe and functions in speech comprehension.
Basal Nuclei
The basal nuclei, also known as basal ganglia, are located deep within the cerebral white matter and comprise the caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus. These structures form the pallidum and striatum. The basal ganglia are responsible for muscle movements and coordination.[2]
Thalamus
The thalamus is the brain's relay center. It receives afferent impulses from sensory receptors throughout the body and processes the information for distribution to the appropriate cortical area. It is also responsible for regulating consciousness and sleep.
Hypothalamus
While the hypothalamus is one of the smallest parts of the brain, it is vital to maintaining homeostasis. The hypothalamus connects the CNS to the endocrine system. It is responsible for heart rate, blood pressure, appetite, thirst, temperature, and the release of various hormones. The hypothalamus also communicates with the pituitary gland to release or inhibit antidiuretic hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, growth hormone-releasing hormone, prolactin-inhibiting hormone, thyroid-releasing hormone, oxytocin.[3]
Pons
The pons are Found in the brainstem and connect the medulla oblongata and the thalamus. It comprises tracts responsible for relaying impulses from the motor cortex to the cerebellum, medulla, and thalamus.
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata is at the bottom of the brain stem, where the spinal cord meets the foramen magnum of the skull. It is responsible for autonomic functions, some of which are crucial for survival. The medulla oblongata monitors the body's respiratory system using chemoreceptors. These receptors can detect changes in blood chemistry. For example, if the blood is too acidic, the medulla oblongata increases the respiratory rate, allowing more oxygen to reach the blood.[4] It is also a cardiovascular and vasomotor center. The medulla oblongata can regulate the body's blood pressure, pulse, and cardiac contractions based on the body’s needs. Lastly, it controls reflexes like vomiting, swallowing, coughing, and sneezing.
Cerebellum
The cerebellum, known as the little brain, is responsible for smooth, coordinated voluntary movements. It is subdivided into the anterior, posterior, and flocculonodular lobes. The cerebellum contains a cerebellar circuit, using Purkinje cells and cerebellar peduncles to communicate with other brain parts. The superior cerebellar peduncle is composed of white matter that connects the cerebellum to the midbrain and allows arm and leg coordination. The inferior cerebellar peduncle connects the medulla and cerebellum using proprioceptors to maintain balance and posture. Lastly, the middle cerebellar peduncle is a one-way communication method from the pons to the cerebellum. It mostly comprises afferent fibers that alert the cerebellum about voluntary motor actions. The cerebellum communicates constantly with the cerebral cortex, taking higher-level instructions about the brain’s intentions, processing them through the cerebellar cortex, and then sending messages to the cerebral motor cortex to make voluntary muscle contractions. These contractions are calculated to determine the force, direction, and momentum necessary to ensure each contraction is smooth and coordinated.
Limbic System
The limbic system comprises the piriform cortex, hippocampus, septal nuclei, amygdala, nucleus accumbens, hypothalamus, and anterior nuclei of the thalamus.[5] The fornix and fiber tracts connect the limbic system parts, allowing them to control emotion, memory, and motivation. The piriform cortex is part of the olfactory system and is in the cortical area of the limbic system. The hypothalamus receives most of the limbic output, which explains psychosomatic illnesses, where emotional stressors cause somatic symptoms. For example, a patient who is currently having financial struggles might present to his primary care physician with hypertension and tachycardia. The septal nuclei, amygdala, and nucleus accumbens are found in the subcortical areas and are responsible for pleasure, emotional processing, and addiction, respectively.
Reticular Formation
The reticular formation is an extensive network of pathways containing neurons that begins in the brainstem and travels from the top of the midbrain to the medulla oblongata. These pathways have projecting reticular neurons that affect the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, thalamus, hypothalamus, and spinal cord. The reticular formation controls the body's level of consciousness through the reticular activation system (RAS). Sensory axons in visual, auditory, and sensory impulses activate RAS neurons in the brain stem. These neurons then relay information to the thalamus and cerebrum. Continuous stimulation of the RAS neurons causes the cerebrum to stay aroused; this gives the feeling of alertness. However, RAS can filter out repetitive, weak stimuli; this prevents the brain from responding to unimportant information and being sensory overloaded.
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord proper extends from the foramen magnum of the skull to the first or second lumbar vertebrae. It creates a 2-way pathway between the brain and the body and divides into 4 regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral. These regions are divided into 31 segments with 31 pairs of spinal nerves. There are 8 cervical nerves, 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves, 5 sacral nerves, and 1 coccygeal nerve. Each nerve exits the vertebral column, passing through the intervertebral foramina to its designated location in the body.
Due to cervical and lumbar enlargements, the spinal cord differs in width throughout its structure. The cervical enlargement occurs at C3 to T1, and the lumbar enlargement is at L1 to S2. The white matter is present outside the spinal cord, with gray matter in its core and cerebrospinal fluid in the central canal. The gray commissure and the dorsal, lateral, and ventral horns are all composed of gray matter. The gray commissure surrounds the central canal. The dorsal horns are made of interneurons, while the ventral horns are somatic motor neurons. Afferent neurons in the dorsal roots carry impulses from the body’s sensory receptors to the spinal cord, where the information begins to be processed. The ventral horns contain efferent motor neurons, which control the body's periphery. The axons of motor neurons are found in the body's skeletal and smooth muscles to regulate involuntary and voluntary reflexes.
The spinal cord ends in a cone-shaped structure called the conus medullaris, which is supported to the end of the coccyx by the filum terminale. Ligaments are found throughout the spinal column, securing the cord from top to bottom.
Ascending Pathway to the Brain
Sensory information travels from the body to the spinal cord before reaching the brain. This information ascends upwards using first, second, and third-order neurons. First-order neurons receive impulses from skin and proprioceptors and send them to the spinal cord. They then synapse with second-order neurons. Second-order neurons live in the dorsal horn and send impulses to the thalamus and cerebellum. Lastly, third-order neurons pick up these impulses in the thalamus and relay them to the somatosensory portion of the cerebrum. Somatosensory sensations are pressure, pain, temperature, and the body's senses.
Descending Pathway to the Brain
Descending tracts send motor signals from the brain to lower motor neurons. These efferent neurons then produce muscle movement.[6]
Embryology
The adult brain and spinal cord form during week 3 of embryological development. The ectoderm begins to thicken, forming the neural plate. The neutral place then folds inwards, creating the neural groove. Neural folds that migrate laterally flank the neural groove. The neural groove then develops into the neural tube, which forms the CNS structures.
The neural tube gets separated into an anterior and posterior end. The anterior end forms the primary brain vesicles, prosencephalon (forebrain), mesencephalon (midbrain), and rhombencephalon (hindbrain), while the posterior end becomes the spinal cord. The primary brain vesicles continue to differentiate, creating secondary brain vesicles. The forebrain separates to form the telencephalon and diencephalon, and the hindbrain splits to form the metencephalon and the myelencephalon (spinal brain).[7] The midbrain does not divide and stays in the mesencephalon. The development of the secondary brain vesicles produces the adult brain structures
- Telencephalon to cerebrum
- Diencephalon to hypothalamus, thalamus, retina
- Mesencephalon to the brain stem (midbrain)
- Metencephalon to the brain stem (pons), cerebellum
- Myelencephalon to the brain stem (medulla oblongata)
The central part of the neural tube forms continuous, hollow cavities known as ventricles. During month 6 of gestation, the cerebral cortex changes from a smooth to a wrinkled, convoluted appearance due to the cerebral hemispheres' continued growth. The elevated parts of the ridges are gyri, while the grooves have the name sulci. The convolutions allow for the increased brain surface area to fit within the skull. Throughout the brain, there are areas of white and gray matter. The gray matter contains neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, glia, and unmyelinated neurons. Contrary, white matter is composed of myelinated axons.[7]
The spinal cord, formed from the caudal portion of the neural tube, is composed of gray and white matter. At 6 weeks of gestation, the gray matter aggregates, forming the dorsal alar and ventral basal plates. Interneurons form from the alar plate, while motor neurons form from the basal plate. Dorsal root ganglia, which brings information from the periphery to the spinal cord, arise for the neural crest cells.
Blood Supply and Lymphatics
Due to the importance and delicate nature of the CNS, the body closely monitors the blood traveling to and from it. The cardiovascular system ensures continuous, oxygenated blood, as a drop in oxygenation level can be detrimental. The common carotid arteries branch off the aorta, which carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart for distribution. The common carotid further branches into the right and left internal and external arteries, supplying the cranium with blood. Vertebral arteries begin in the neck and branch as they enter the skull through the foramen magnum. They supply the anterior portion of the spinal cord. The vertebral arteries then merge into the basilar artery. The basilar artery is responsible for delivering blood to the brainstem and cerebellum. The circle of Willis ensures that blood continues to circulate even if one of the arteries is not working appropriately. The internal carotid and vertebral arteries compose the circle of Willis.[8] After being used in the CNS, blood travels back to the lungs for oxygenation. Multiple dural venous sinuses do this:
- Superior sagittal sinus
- The confluence of sinuses
- Transverse sinuses
- Sigmoid sinuses
- Jugular veins
- Carotid arteries
- Superior vena cava
- Lungs
Surgical Considerations
Anesthesia is a controlled state of temporary loss of sensation that allows the performance of painful medical procedures that would otherwise be unfeasible. There are many types of anesthesia, such as general, sedation, and local. However, they are all used to disrupt the cellular and intracellular communication in the CNS and peripheral nervous system.
General anesthesia involves the use of an analgesic, paralytic, and amnesia, which all work together to render the patient unconscious. Under general anesthesia, the activity of the CNS undergoes complete suppression, and there is a total loss of sensation. Neuromuscular blockers are used, requiring intubation and subsequent mechanical ventilation. Depolarizing neuromuscular blockers, such as succinylcholine, bind to the postsynaptic cholinergic receptors, causing depolarization. However, the removal of succinylcholine from the receptors is much slower, which inhibits the binding of acetylcholine and, therefore, prevents future depolarizations. Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers, like vecuronium, act as acetylcholine inhibitors, blocking the postsynaptic cholinergic receptors. However, when these neuromuscular blockers bind, they do not change the permeability of the ion channels.[9]
During regional anesthesia, the anesthesiologist numbs only the portion of the body that is the target of the operation. Spinal and epidurals are used as local anesthetic medication and get injected into the vertebral canal. Spinal anesthesia targets the spinal fluid, while the epidural injection is into the epidural space.
As with any surgical procedure, there is always a risk when going under anesthesia. Conditions that increase the risk of complications are obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and any disease process of the respiratory and cardiovascular system.[10]
Neurosurgeons have received training in diagnosing and treating patients with injuries or diseases affecting the CNS. They provide operative management of neurological disorders, such as tumors, stroke, head and spinal injuries, chronic pain, etc. Any surgical procedures have risks, especially when dealing with delicate nervous tissue in the brain and spinal cord. Complications of brain surgery include bleeding in the brain, speech, memory, coordination issues, stroke, brain swelling, and possible coma.
Clinical Significance
Wernicke Aphasia
Wernicke aphasia occurs most commonly after a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke. Strokes in the left middle cerebral artery prevent oxygenated blood from reaching the Wernicke area. In Wernicke's aphasia, a person can speak clearly and produce speech. However, their speech has no meaning, and they have difficulty understanding language.
Broca Aphasia
Broca aphasia, also known as expressive aphasia, is caused by a stroke, brain tumor, or brain trauma. When a stroke occurs in the Broca area, oxygen is cut off to that part of the brain. Hypoxia causes irreversible damage. During Broca aphasia, the person has difficulty producing speech. They can comprehend and know what they want to say but cannot form words to communicate the message.[11]
Traumatic Brain Injuries
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) occur when there is a disruption to normal brain activity, which can occur during a sports injury, a car accident, a penetrating object, or even a blunt object. TBI symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the injury. For example, a concussion can cause temporary dizziness or loss of consciousness, while a contusion causes lasting neurological damage. Contusions to the brain stem result in a coma. TBI can cause subdural or subarachnoid hemorrhage and cerebral edema. When the brain sustains a trauma, the blood vessels in the brain break. The blood begins to pool, increasing the intracranial pressure and compressing the brain tissue. Autonomic nervous system functions are lost as the brain pushes through the skull onto the spinal cord.
Cerebrovascular Accidents
Cerebrovascular accidents, also known as strokes, occur when the brain is not able to get oxygenated blood. The lack of oxygen causes hypoxia, and tissues in the brain start to die. Commonly, strokes are caused by a blood clot that has traveled from one location in the body to the cerebral artery in the brain. Depending on where the clot lands, the stroke symptoms are determined. For example, some people may experience left-sided paralysis, while others might have slurred speech. Transient ischemic attacks are considered small strokes as their symptoms are more temporary. In any cerebrovascular accident, time is crucial. Doctors can administer tissue plasminogen activator that breaks down the clot or surgically removes it if necessary. The severity of symptoms directly correlates to how long the brain’s oxygen supply has been cut off.
Alzheimer Disease
Alzheimer disease is a common type of dementia in which one’s brain cells and neural connections begin to degenerate and die. This condition presents with loss of memory and cognitive decline. Alzheimer's is progressive, with symptoms worsening over time.[12] Scientists have found aggregations of beta-amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles made of tau within the neurons in Alzheimer disease patients. These plaques and tangles result in the death of brain cells and form because of the misfolding of proteins within them. Alzheimer disease patients have decreased neural activity in the parietal cortex, hippocampus, and basal forebrain.
Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is a nervous system disorder that results in the deterioration of dopamine-releasing neurons in the substantia nigra.[13] The drop in dopamine levels creates tremors, unsteady movements, and loss of balance. Parkinson's disease is progressive as it usually starts as a tremor in one hand. Many patients exhibit a pill-rolling movement in their hand, bradykinesia, stiffness, and a mask life face as symptoms progress. A Parkinson's disease diagnosis results from looking at the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and a neurological and physical exam. While no cure exists for the disease, the severity of the symptoms can be controlled. Levodopa can pass through the blood-brain and undergo conversion into dopamine for CNS use. Deep brain stimulation is a surgical option that can stop abnormal brain activity and thus control the tremors. However, deep brain stimulation does not keep the disease from progressing.
Huntington Disease
Huntington disease is a hereditary, progressive brain disorder that is caused by a mutation in the huntingtin gene, HTT. The CAG segment in the HTT gene normally repeats up to 35 times. However, in someone with Huntington disease, the CAG segment is repeated up to 120 times. This large CAG segment causes the huntingtin protein to accumulate in the brain cells, eventually leading to cell death. Initially, Huntington disease causes chorea, involuntary jerking, and hand-flapping movements. As the disease progresses, cognitive decline occurs. Fatally follows within 15 years of diagnosis.
Spinal Cord Traumas
Symptoms of spinal cord injuries are dependent on where the injury occurs. If damage to the sensory tracts occurs, the sensation can be affected. However, if the ventral roots or ventral horns are damaged, paralysis occurs. Flaccid paralysis is when nerve impulses do not reach the intended muscles. Without stimulation, the muscles are unable to contract. Spastic paralysis is when the motor neurons undergo irregular stimulation, causing involuntary contraction. Paraplegia, paralysis of the lower limbs, occurs when the spinal cord gets cut between T1 and L1. Quadriplegia, paralysis of all limbs, is a result of an injury in the cervical region.
Poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis is a spinal cord inflammation caused by the virus Polio. Poliovirus spreads from human to human or through infected food and water. It demolishes the neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord, leading to paralysis. The infection of the poliovirus is preventable through the administration of the vaccine.[14]
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, also known as ALS and Lou Gehrig disease, destroys motor neurons that control voluntary and involuntary movements like breathing, speaking, and swallowing. ALS's cause is unknown, and unfortunately, there is no cure. Scientists believe that cell death is related to the excess amount of extracellular glutamate in ALS patients. Riluzole, which can disrupt the formation of glutamate, is used to slow down the progression and reduce the painful symptoms of ALS.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease in which the body attacks the myelin proteins of the CNS, disrupting the communication between the brain and the body. Multiple sclerosis is highly prevalent in young adults and presents as pain, weakness, vision loss, and loss of coordination. The severity of symptoms varies from patient to patient. Medication suppresses the body’s immune system and can help control the adverse effects of this disease.